Ralph Weischedel
BBN
Remember what you did so you know what to do next
Oct 30, 2023



Abstract:We explore using a moderately sized large language model (GPT-J 6B parameters) to create a plan for a simulated robot to achieve 30 classes of goals in ScienceWorld, a text game simulator for elementary science experiments. Previously published empirical work claimed that large language models (LLMs) are a poor fit (Wang et al., 2022) compared to reinforcement learning. Using the Markov assumption (a single previous step), the LLM outperforms the reinforcement learning-based approach by a factor of 1.4. When we fill the LLM's input buffer with as many prior steps as possible, improvement rises to 3.5x. Even when training on only 6.5% of the training data, we observe a 2.2x improvement over the reinforcement-learning-based approach. Our experiments show that performance varies widely across the 30 classes of actions, indicating that averaging over tasks can hide significant performance issues. In work contemporaneous with ours, Lin et al. (2023) demonstrated a two-part approach (SwiftSage) that uses a small LLM (T5-large) complemented by OpenAI's massive LLMs to achieve outstanding results in ScienceWorld. Our 6-B parameter, single-stage GPT-J matches the performance of SwiftSage's two-stage architecture when it incorporates GPT-3.5 turbo which has 29-times more parameters than GPT-J.
Understanding Procedural Knowledge by Sequencing Multimodal Instructional Manuals
Oct 16, 2021



Abstract:The ability to sequence unordered events is an essential skill to comprehend and reason about real world task procedures, which often requires thorough understanding of temporal common sense and multimodal information, as these procedures are often communicated through a combination of texts and images. Such capability is essential for applications such as sequential task planning and multi-source instruction summarization. While humans are capable of reasoning about and sequencing unordered multimodal procedural instructions, whether current machine learning models have such essential capability is still an open question. In this work, we benchmark models' capability of reasoning over and sequencing unordered multimodal instructions by curating datasets from popular online instructional manuals and collecting comprehensive human annotations. We find models not only perform significantly worse than humans but also seem incapable of efficiently utilizing the multimodal information. To improve machines' performance on multimodal event sequencing, we propose sequentiality-aware pretraining techniques that exploit the sequential alignment properties of both texts and images, resulting in > 5% significant improvements.
Perhaps PTLMs Should Go to School -- A Task to Assess Open Book and Closed Book QA
Oct 04, 2021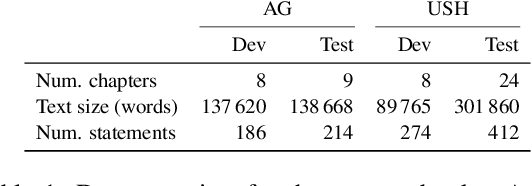
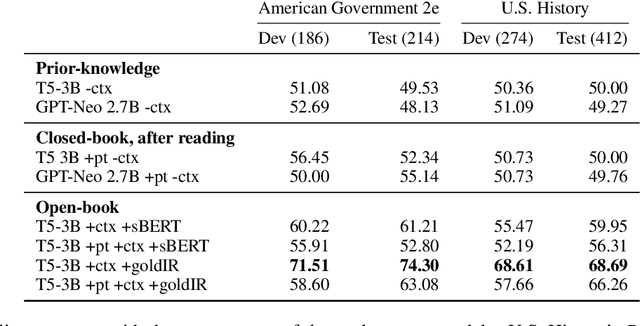
Abstract:Our goal is to deliver a new task and leaderboard to stimulate research on question answering and pre-trained language models (PTLMs) to understand a significant instructional document, e.g., an introductory college textbook or a manual. PTLMs have shown great success in many question-answering tasks, given significant supervised training, but much less so in zero-shot settings. We propose a new task that includes two college-level introductory texts in the social sciences (American Government 2e) and humanities (U.S. History), hundreds of true/false statements based on review questions written by the textbook authors, validation/development tests based on the first eight chapters of the textbooks, blind tests based on the remaining textbook chapters, and baseline results given state-of-the-art PTLMs. Since the questions are balanced, random performance should be ~50%. T5, fine-tuned with BoolQ achieves the same performance, suggesting that the textbook's content is not pre-represented in the PTLM. Taking the exam closed book, but having read the textbook (i.e., adding the textbook to T5's pre-training), yields at best minor improvement (56%), suggesting that the PTLM may not have "understood" the textbook (or perhaps misunderstood the questions). Performance is better (~60%) when the exam is taken open-book (i.e., allowing the machine to automatically retrieve a paragraph and use it to answer the question).
Plot-guided Adversarial Example Construction for Evaluating Open-domain Story Generation
Apr 12, 2021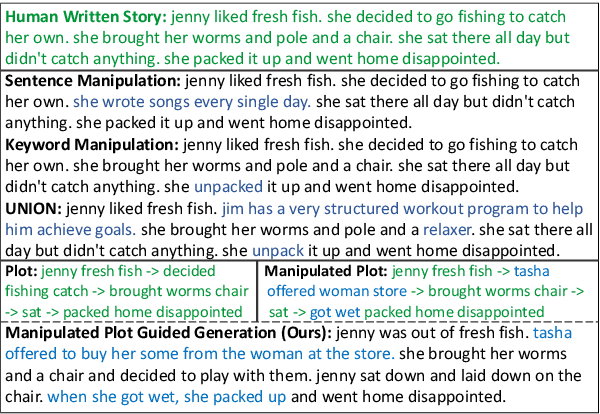
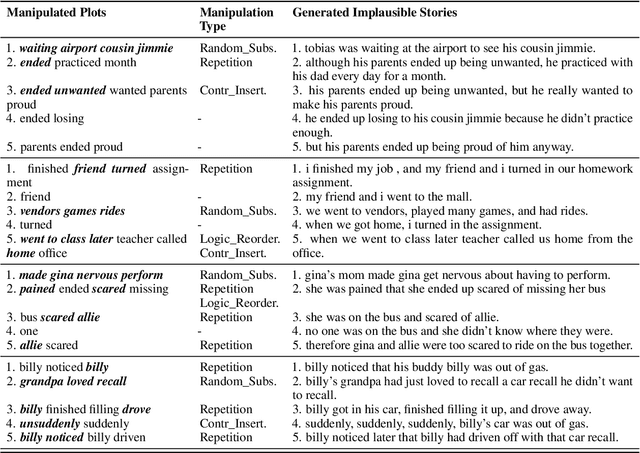
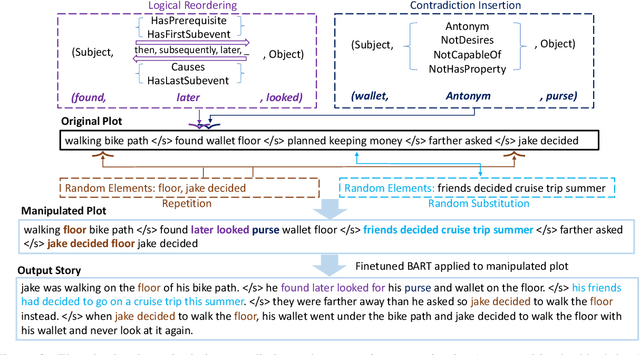
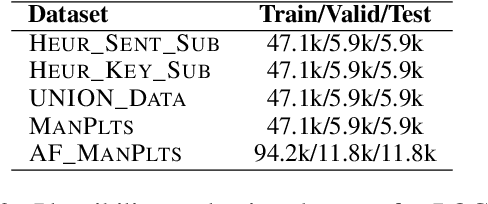
Abstract:With the recent advances of open-domain story generation, the lack of reliable automatic evaluation metrics becomes an increasingly imperative issue that hinders the fast development of story generation. According to conducted researches in this regard, learnable evaluation metrics have promised more accurate assessments by having higher correlations with human judgments. A critical bottleneck of obtaining a reliable learnable evaluation metric is the lack of high-quality training data for classifiers to efficiently distinguish plausible and implausible machine-generated stories. Previous works relied on \textit{heuristically manipulated} plausible examples to mimic possible system drawbacks such as repetition, contradiction, or irrelevant content in the text level, which can be \textit{unnatural} and \textit{oversimplify} the characteristics of implausible machine-generated stories. We propose to tackle these issues by generating a more comprehensive set of implausible stories using {\em plots}, which are structured representations of controllable factors used to generate stories. Since these plots are compact and structured, it is easier to manipulate them to generate text with targeted undesirable properties, while at the same time maintain the grammatical correctness and naturalness of the generated sentences. To improve the quality of generated implausible stories, we further apply the adversarial filtering procedure presented by \citet{zellers2018swag} to select a more nuanced set of implausible texts. Experiments show that the evaluation metrics trained on our generated data result in more reliable automatic assessments that correlate remarkably better with human judgments compared to the baselines.
Machine-Assisted Script Curation
Jan 14, 2021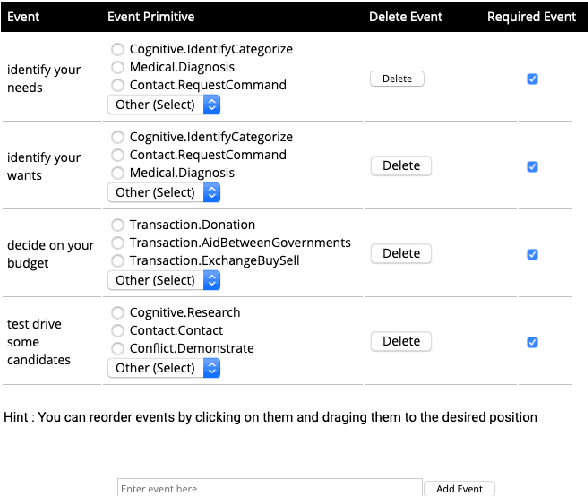
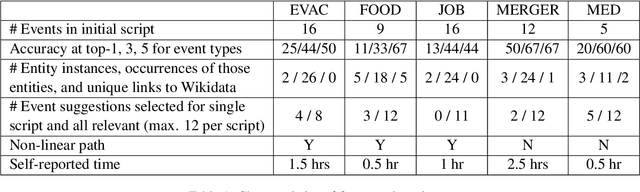
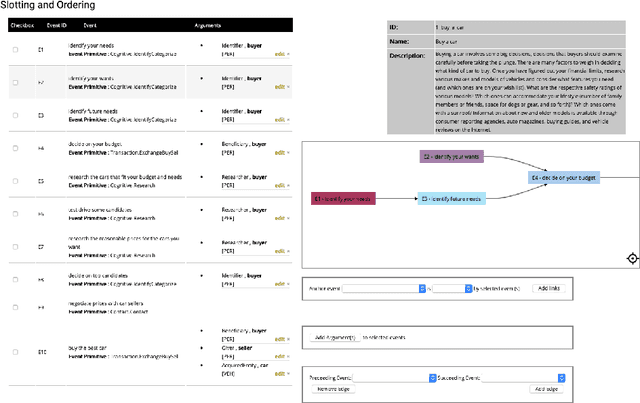
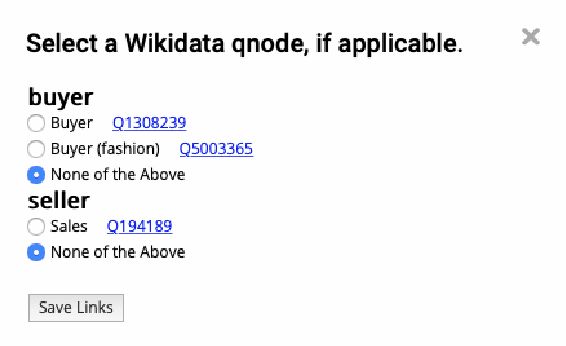
Abstract:We describe Machine-Aided Script Curator (MASC), a system for human-machine collaborative script authoring. Scripts produced with MASC include (1) English descriptions of sub-events that comprise a larger, complex event; (2) event types for each of those events; (3) a record of entities expected to participate in multiple sub-events; and (4) temporal sequencing between the sub-events. MASC automates portions of the script creation process with suggestions for event types, links to Wikidata, and sub-events that may have been forgotten. We illustrate how these automations are useful to the script writer with a few case-study scripts.
Content Planning for Neural Story Generation with Aristotelian Rescoring
Oct 09, 2020



Abstract:Long-form narrative text generated from large language models manages a fluent impersonation of human writing, but only at the local sentence level, and lacks structure or global cohesion. We posit that many of the problems of story generation can be addressed via high-quality content planning, and present a system that focuses on how to learn good plot structures to guide story generation. We utilize a plot-generation language model along with an ensemble of rescoring models that each implement an aspect of good story-writing as detailed in Aristotle's Poetics. We find that stories written with our more principled plot-structure are both more relevant to a given prompt and higher quality than baselines that do not content plan, or that plan in an unprincipled way.
Learning to Generalize for Sequential Decision Making
Oct 05, 2020
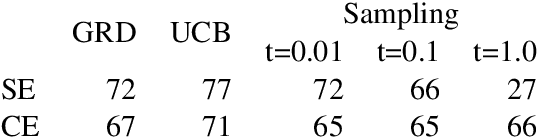


Abstract:We consider problems of making sequences of decisions to accomplish tasks, interacting via the medium of language. These problems are often tackled with reinforcement learning approaches. We find that these models do not generalize well when applied to novel task domains. However, the large amount of computation necessary to adequately train and explore the search space of sequential decision making, under a reinforcement learning paradigm, precludes the inclusion of large contextualized language models, which might otherwise enable the desired generalization ability. We introduce a teacher-student imitation learning methodology and a means of converting a reinforcement learning model into a natural language understanding model. Together, these methodologies enable the introduction of contextualized language models into the sequential decision making problem space. We show that models can learn faster and generalize more, leveraging both the imitation learning and the reformulation. Our models exceed teacher performance on various held-out decision problems, by up to 7% on in-domain problems and 24% on out-of-domain problems.
Predictive Engagement: An Efficient Metric For Automatic Evaluation of Open-Domain Dialogue Systems
Nov 04, 2019



Abstract:User engagement is a critical metric for evaluating the quality of open-domain dialogue systems. Prior work has focused on conversation-level engagement by using heuristically constructed features such as the number of turns and the total time of the conversation. In this paper, we investigate the possibility and efficacy of estimating utterance-level engagement and define a novel metric, {\em predictive engagement}, for automatic evaluation of open-domain dialogue systems. Our experiments demonstrate that (1) human annotators have high agreement on assessing utterance-level engagement scores; (2) conversation-level engagement scores can be predicted from properly aggregated utterance-level engagement scores. Furthermore, we show that the utterance-level engagement scores can be learned from data. These scores can improve automatic evaluation metrics for open-domain dialogue systems, as shown by correlation with human judgements. This suggests that predictive engagement can be used as a real-time feedback for training better dialogue models.
Deep Structured Neural Network for Event Temporal Relation Extraction
Sep 24, 2019



Abstract:We propose a novel deep structured learning framework for event temporal relation extraction. The model consists of 1) a recurrent neural network (RNN) to learn scoring functions for pair-wise relations, and 2) a structured support vector machine (SSVM) to make joint predictions. The neural network automatically learns representations that account for long-term contexts to provide robust features for the structured model, while the SSVM incorporates domain knowledge such as transitive closure of temporal relations as constraints to make better globally consistent decisions. By jointly training the two components, our model combines the benefits of both data-driven learning and knowledge exploitation. Experimental results on three high-quality event temporal relation datasets (TCR, MATRES, and TB-Dense) demonstrate that incorporated with pre-trained contextualized embeddings, the proposed model achieves significantly better performances than the state-of-the-art methods on all three datasets. We also provide thorough ablation studies to investigate our model.
Plan-And-Write: Towards Better Automatic Storytelling
Nov 20, 2018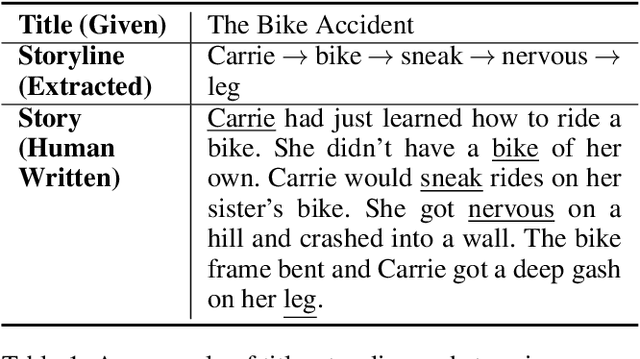
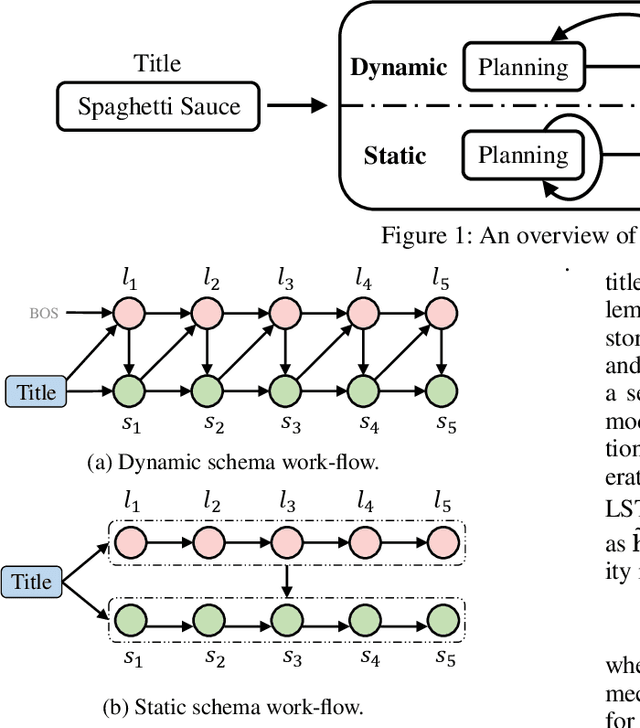

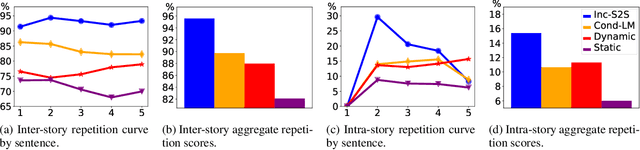
Abstract:Automatic storytelling is challenging since it requires generating long, coherent natural language to describes a sensible sequence of events. Despite considerable efforts on automatic story generation in the past, prior work either is restricted in plot planning, or can only generate stories in a narrow domain. In this paper, we explore open-domain story generation that writes stories given a title (topic) as input. We propose a plan-and-write hierarchical generation framework that first plans a storyline, and then generates a story based on the storyline. We compare two planning strategies. The dynamic schema interweaves story planning and its surface realization in text, while the static schema plans out the entire storyline before generating stories. Experiments show that with explicit storyline planning, the generated stories are more diverse, coherent, and on topic than those generated without creating a full plan, according to both automatic and human evaluations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge