Alex Hedges
Remember what you did so you know what to do next
Oct 30, 2023



Abstract:We explore using a moderately sized large language model (GPT-J 6B parameters) to create a plan for a simulated robot to achieve 30 classes of goals in ScienceWorld, a text game simulator for elementary science experiments. Previously published empirical work claimed that large language models (LLMs) are a poor fit (Wang et al., 2022) compared to reinforcement learning. Using the Markov assumption (a single previous step), the LLM outperforms the reinforcement learning-based approach by a factor of 1.4. When we fill the LLM's input buffer with as many prior steps as possible, improvement rises to 3.5x. Even when training on only 6.5% of the training data, we observe a 2.2x improvement over the reinforcement-learning-based approach. Our experiments show that performance varies widely across the 30 classes of actions, indicating that averaging over tasks can hide significant performance issues. In work contemporaneous with ours, Lin et al. (2023) demonstrated a two-part approach (SwiftSage) that uses a small LLM (T5-large) complemented by OpenAI's massive LLMs to achieve outstanding results in ScienceWorld. Our 6-B parameter, single-stage GPT-J matches the performance of SwiftSage's two-stage architecture when it incorporates GPT-3.5 turbo which has 29-times more parameters than GPT-J.
Perhaps PTLMs Should Go to School -- A Task to Assess Open Book and Closed Book QA
Oct 04, 2021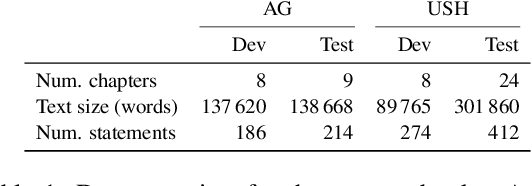
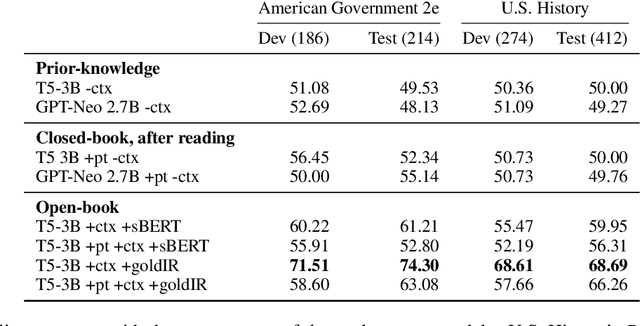
Abstract:Our goal is to deliver a new task and leaderboard to stimulate research on question answering and pre-trained language models (PTLMs) to understand a significant instructional document, e.g., an introductory college textbook or a manual. PTLMs have shown great success in many question-answering tasks, given significant supervised training, but much less so in zero-shot settings. We propose a new task that includes two college-level introductory texts in the social sciences (American Government 2e) and humanities (U.S. History), hundreds of true/false statements based on review questions written by the textbook authors, validation/development tests based on the first eight chapters of the textbooks, blind tests based on the remaining textbook chapters, and baseline results given state-of-the-art PTLMs. Since the questions are balanced, random performance should be ~50%. T5, fine-tuned with BoolQ achieves the same performance, suggesting that the textbook's content is not pre-represented in the PTLM. Taking the exam closed book, but having read the textbook (i.e., adding the textbook to T5's pre-training), yields at best minor improvement (56%), suggesting that the PTLM may not have "understood" the textbook (or perhaps misunderstood the questions). Performance is better (~60%) when the exam is taken open-book (i.e., allowing the machine to automatically retrieve a paragraph and use it to answer the question).
Machine-Assisted Script Curation
Jan 14, 2021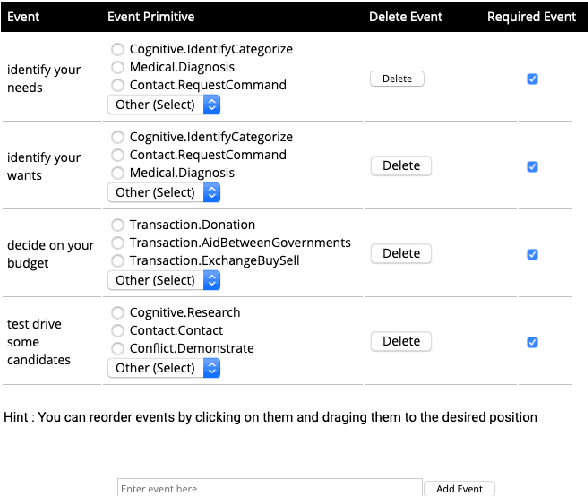
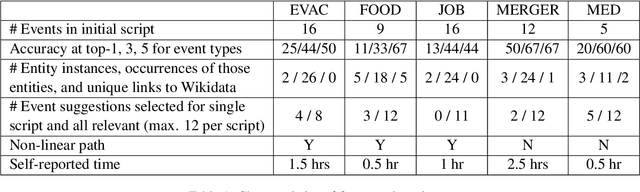
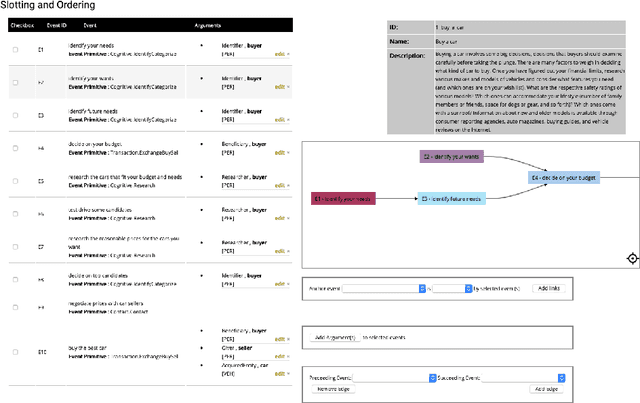
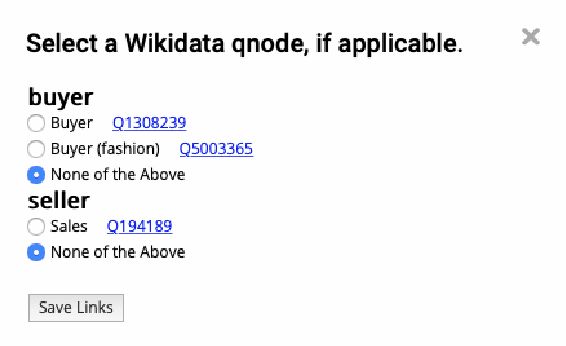
Abstract:We describe Machine-Aided Script Curator (MASC), a system for human-machine collaborative script authoring. Scripts produced with MASC include (1) English descriptions of sub-events that comprise a larger, complex event; (2) event types for each of those events; (3) a record of entities expected to participate in multiple sub-events; and (4) temporal sequencing between the sub-events. MASC automates portions of the script creation process with suggestions for event types, links to Wikidata, and sub-events that may have been forgotten. We illustrate how these automations are useful to the script writer with a few case-study scripts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge