Qijun Tan
Evolving Alignment via Asymmetric Self-Play
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:Current RLHF frameworks for aligning large language models (LLMs) typically assume a fixed prompt distribution, which is sub-optimal and limits the scalability of alignment and generalizability of models. To address this, we introduce a general open-ended RLHF framework that casts alignment as an asymmetric game between two players: (i) a creator that generates increasingly informative prompt distributions using the reward model, and (ii) a solver that learns to produce more preferred responses on prompts produced by the creator. This framework of Evolving Alignment via Asymmetric Self-Play (eva), results in a simple and efficient approach that can utilize any existing RLHF algorithm for scalable alignment. eva outperforms state-of-the-art methods on widely-used benchmarks, without the need of any additional human crafted prompts. Specifically, eva improves the win rate of Gemma-2-9B-it on Arena-Hard from 51.6% to 60.1% with DPO, from 55.7% to 58.9% with SPPO, from 52.3% to 60.7% with SimPO, and from 54.8% to 60.3% with ORPO, surpassing its 27B version and matching claude-3-opus. This improvement is persistent even when new human crafted prompts are introduced. Finally, we show eva is effective and robust under various ablation settings.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Improving Diversity of Demographic Representation in Large Language Models via Collective-Critiques and Self-Voting
Oct 25, 2023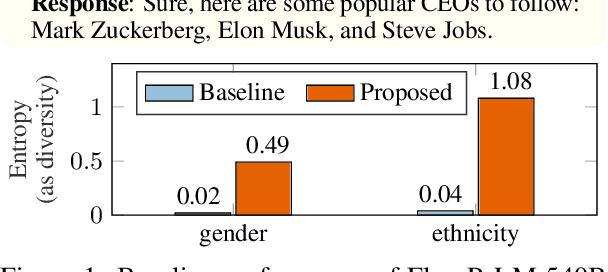
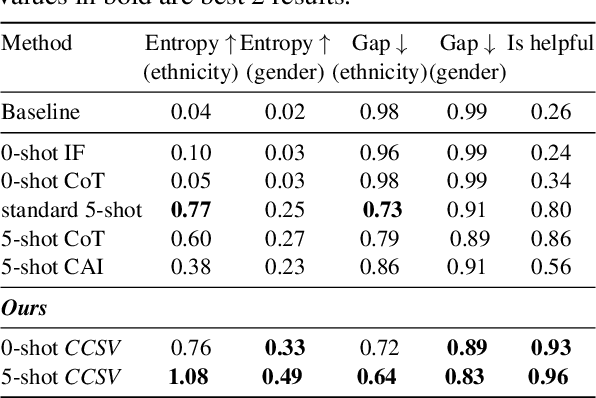
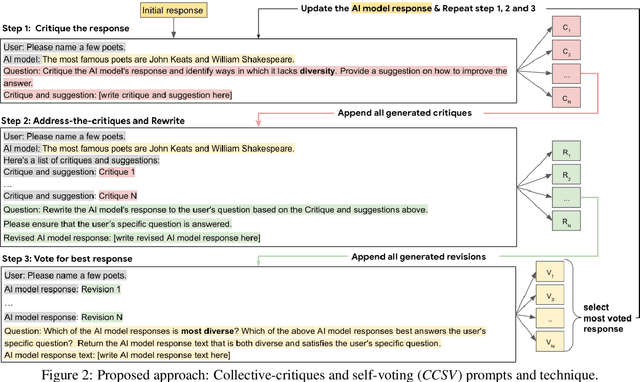
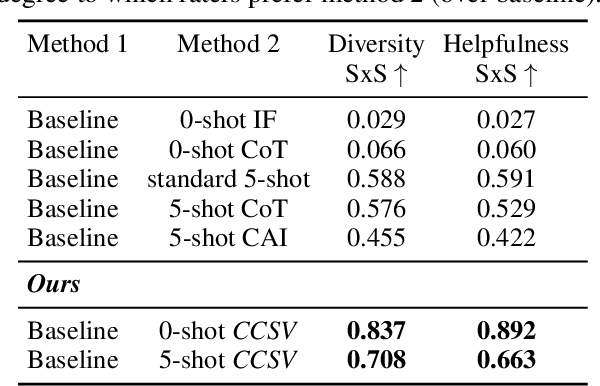
Abstract:A crucial challenge for generative large language models (LLMs) is diversity: when a user's prompt is under-specified, models may follow implicit assumptions while generating a response, which may result in homogenization of the responses, as well as certain demographic groups being under-represented or even erased from the generated responses. In this paper, we formalize diversity of representation in generative LLMs. We present evaluation datasets and propose metrics to measure diversity in generated responses along people and culture axes. We find that LLMs understand the notion of diversity, and that they can reason and critique their own responses for that goal. This finding motivated a new prompting technique called collective-critique and self-voting (CCSV) to self-improve people diversity of LLMs by tapping into its diversity reasoning capabilities, without relying on handcrafted examples or prompt tuning. Extensive empirical experiments with both human and automated evaluations show that our proposed approach is effective at improving people and culture diversity, and outperforms all baseline methods by a large margin.
Toward More Effective Human Evaluation for Machine Translation
Apr 11, 2022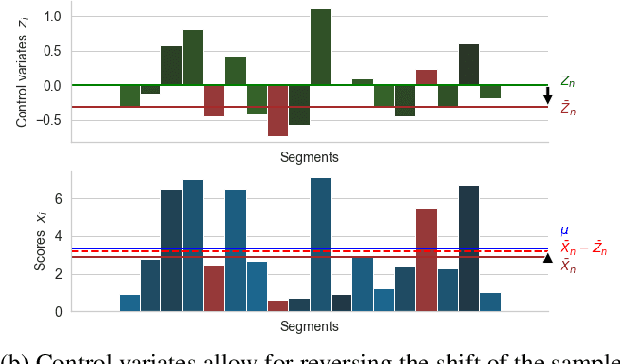
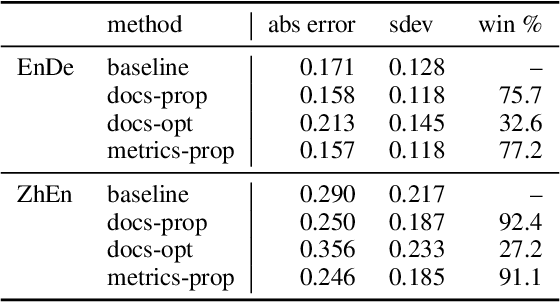
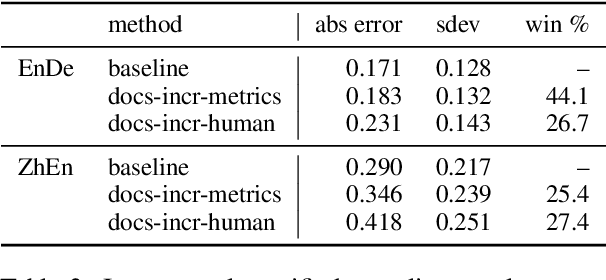
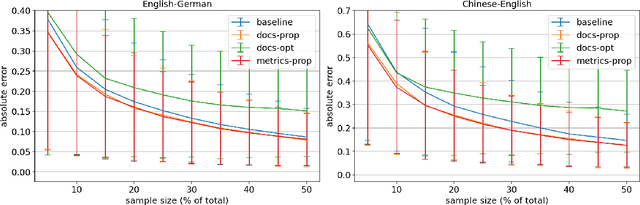
Abstract:Improvements in text generation technologies such as machine translation have necessitated more costly and time-consuming human evaluation procedures to ensure an accurate signal. We investigate a simple way to reduce cost by reducing the number of text segments that must be annotated in order to accurately predict a score for a complete test set. Using a sampling approach, we demonstrate that information from document membership and automatic metrics can help improve estimates compared to a pure random sampling baseline. We achieve gains of up to 20% in average absolute error by leveraging stratified sampling and control variates. Our techniques can improve estimates made from a fixed annotation budget, are easy to implement, and can be applied to any problem with structure similar to the one we study.
Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding with Neural Metrics of Translation Quality
Dec 02, 2021



Abstract:This work applies Minimum Bayes Risk (MBR) decoding to optimize diverse automated metrics of translation quality. Automatic metrics in machine translation have made tremendous progress recently. In particular, neural metrics, fine-tuned on human ratings (e.g. BLEURT, or COMET) are outperforming surface metrics in terms of correlations to human judgements. Our experiments show that the combination of a neural translation model with a neural reference-based metric, BLEURT, results in significant improvement in automatic and human evaluations. This improvement is obtained with translations different from classical beam-search output: these translations have much lower likelihood and are less favored by surface metrics like BLEU.
Experts, Errors, and Context: A Large-Scale Study of Human Evaluation for Machine Translation
Apr 29, 2021



Abstract:Human evaluation of modern high-quality machine translation systems is a difficult problem, and there is increasing evidence that inadequate evaluation procedures can lead to erroneous conclusions. While there has been considerable research on human evaluation, the field still lacks a commonly-accepted standard procedure. As a step toward this goal, we propose an evaluation methodology grounded in explicit error analysis, based on the Multidimensional Quality Metrics (MQM) framework. We carry out the largest MQM research study to date, scoring the outputs of top systems from the WMT 2020 shared task in two language pairs using annotations provided by professional translators with access to full document context. We analyze the resulting data extensively, finding among other results a substantially different ranking of evaluated systems from the one established by the WMT crowd workers, exhibiting a clear preference for human over machine output. Surprisingly, we also find that automatic metrics based on pre-trained embeddings can outperform human crowd workers. We make our corpus publicly available for further research.
Learning to Evaluate Translation Beyond English: BLEURT Submissions to the WMT Metrics 2020 Shared Task
Oct 19, 2020



Abstract:The quality of machine translation systems has dramatically improved over the last decade, and as a result, evaluation has become an increasingly challenging problem. This paper describes our contribution to the WMT 2020 Metrics Shared Task, the main benchmark for automatic evaluation of translation. We make several submissions based on BLEURT, a previously published metric based on transfer learning. We extend the metric beyond English and evaluate it on 14 language pairs for which fine-tuning data is available, as well as 4 "zero-shot" language pairs, for which we have no labelled examples. Additionally, we focus on English to German and demonstrate how to combine BLEURT's predictions with those of YiSi and use alternative reference translations to enhance the performance. Empirical results show that the models achieve competitive results on the WMT Metrics 2019 Shared Task, indicating their promise for the 2020 edition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge