Pu Jin
Anomaly Detection in Aerial Videos with Transformers
Sep 25, 2022



Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are widely applied for purposes of inspection, search, and rescue operations by the virtue of low-cost, large-coverage, real-time, and high-resolution data acquisition capacities. Massive volumes of aerial videos are produced in these processes, in which normal events often account for an overwhelming proportion. It is extremely difficult to localize and extract abnormal events containing potentially valuable information from long video streams manually. Therefore, we are dedicated to developing anomaly detection methods to solve this issue. In this paper, we create a new dataset, named DroneAnomaly, for anomaly detection in aerial videos. This dataset provides 37 training video sequences and 22 testing video sequences from 7 different realistic scenes with various anomalous events. There are 87,488 color video frames (51,635 for training and 35,853 for testing) with the size of $640 \times 640$ at 30 frames per second. Based on this dataset, we evaluate existing methods and offer a benchmark for this task. Furthermore, we present a new baseline model, ANomaly Detection with Transformers (ANDT), which treats consecutive video frames as a sequence of tubelets, utilizes a Transformer encoder to learn feature representations from the sequence, and leverages a decoder to predict the next frame. Our network models normality in the training phase and identifies an event with unpredictable temporal dynamics as an anomaly in the test phase. Moreover, To comprehensively evaluate the performance of our proposed method, we use not only our Drone-Anomaly dataset but also another dataset. We will make our dataset and code publicly available. A demo video is available at https://youtu.be/ancczYryOBY. We make our dataset and code publicly available .
FuTH-Net: Fusing Temporal Relations and Holistic Features for Aerial Video Classification
Sep 22, 2022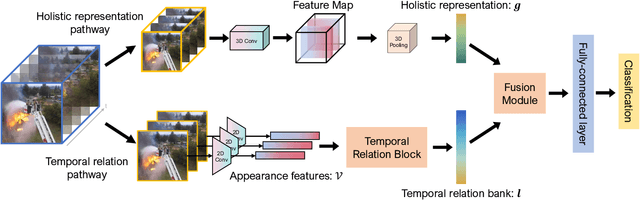

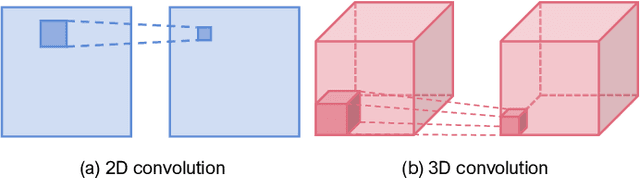
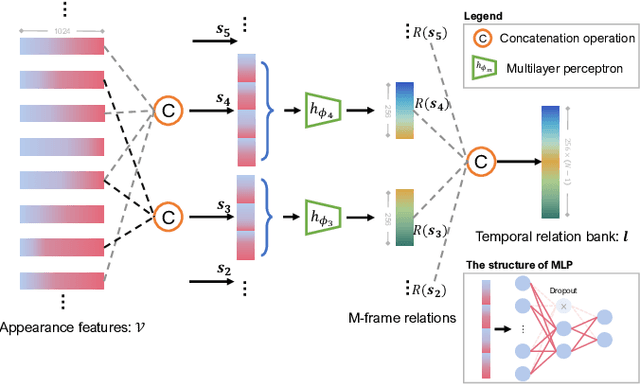
Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are now widely applied to data acquisition due to its low cost and fast mobility. With the increasing volume of aerial videos, the demand for automatically parsing these videos is surging. To achieve this, current researches mainly focus on extracting a holistic feature with convolutions along both spatial and temporal dimensions. However, these methods are limited by small temporal receptive fields and cannot adequately capture long-term temporal dependencies which are important for describing complicated dynamics. In this paper, we propose a novel deep neural network, termed FuTH-Net, to model not only holistic features, but also temporal relations for aerial video classification. Furthermore, the holistic features are refined by the multi-scale temporal relations in a novel fusion module for yielding more discriminative video representations. More specially, FuTH-Net employs a two-pathway architecture: (1) a holistic representation pathway to learn a general feature of both frame appearances and shortterm temporal variations and (2) a temporal relation pathway to capture multi-scale temporal relations across arbitrary frames, providing long-term temporal dependencies. Afterwards, a novel fusion module is proposed to spatiotemporal integrate the two features learned from the two pathways. Our model is evaluated on two aerial video classification datasets, ERA and Drone-Action, and achieves the state-of-the-art results. This demonstrates its effectiveness and good generalization capacity across different recognition tasks (event classification and human action recognition). To facilitate further research, we release the code at https://gitlab.lrz.de/ai4eo/reasoning/futh-net.
Self-supervised Audiovisual Representation Learning for Remote Sensing Data
Aug 02, 2021



Abstract:Many current deep learning approaches make extensive use of backbone networks pre-trained on large datasets like ImageNet, which are then fine-tuned to perform a certain task. In remote sensing, the lack of comparable large annotated datasets and the wide diversity of sensing platforms impedes similar developments. In order to contribute towards the availability of pre-trained backbone networks in remote sensing, we devise a self-supervised approach for pre-training deep neural networks. By exploiting the correspondence between geo-tagged audio recordings and remote sensing imagery, this is done in a completely label-free manner, eliminating the need for laborious manual annotation. For this purpose, we introduce the SoundingEarth dataset, which consists of co-located aerial imagery and audio samples all around the world. Using this dataset, we then pre-train ResNet models to map samples from both modalities into a common embedding space, which encourages the models to understand key properties of a scene that influence both visual and auditory appearance. To validate the usefulness of the proposed approach, we evaluate the transfer learning performance of pre-trained weights obtained against weights obtained through other means. By fine-tuning the models on a number of commonly used remote sensing datasets, we show that our approach outperforms existing pre-training strategies for remote sensing imagery. The dataset, code and pre-trained model weights will be available at https://github.com/khdlr/SoundingEarth.
MultiScene: A Large-scale Dataset and Benchmark for Multi-scene Recognition in Single Aerial Images
Apr 07, 2021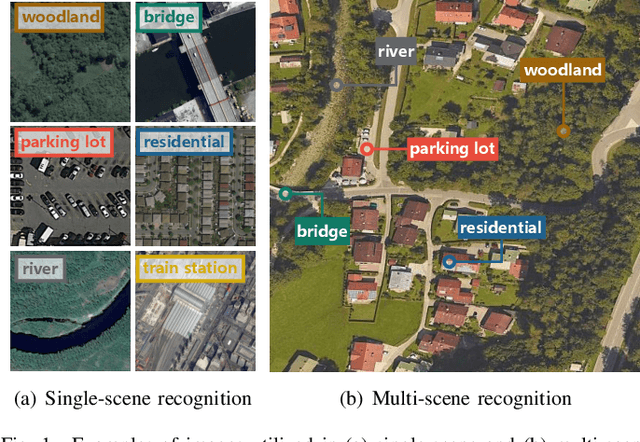
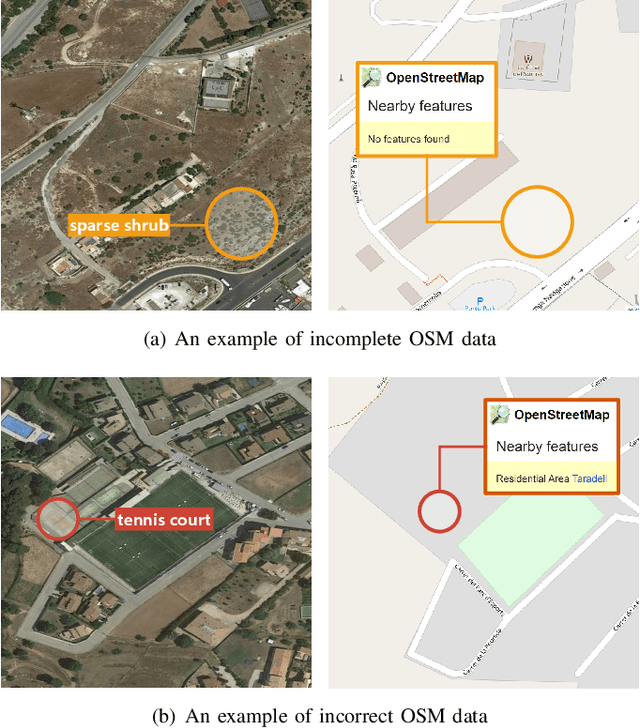
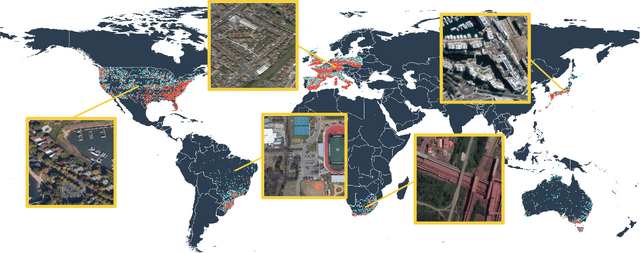
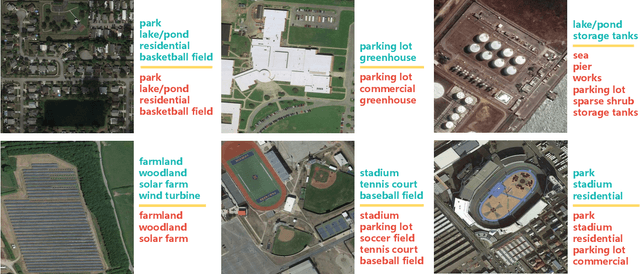
Abstract:Aerial scene recognition is a fundamental research problem in interpreting high-resolution aerial imagery. Over the past few years, most studies focus on classifying an image into one scene category, while in real-world scenarios, it is more often that a single image contains multiple scenes. Therefore, in this paper, we investigate a more practical yet underexplored task -- multi-scene recognition in single images. To this end, we create a large-scale dataset, called MultiScene, composed of 100,000 unconstrained high-resolution aerial images. Considering that manually labeling such images is extremely arduous, we resort to low-cost annotations from crowdsourcing platforms, e.g., OpenStreetMap (OSM). However, OSM data might suffer from incompleteness and incorrectness, which introduce noise into image labels. To address this issue, we visually inspect 14,000 images and correct their scene labels, yielding a subset of cleanly-annotated images, named MultiScene-Clean. With it, we can develop and evaluate deep networks for multi-scene recognition using clean data. Moreover, we provide crowdsourced annotations of all images for the purpose of studying network learning with noisy labels. We conduct experiments with extensive baseline models on both MultiScene-Clean and MultiScene to offer benchmarks for multi-scene recognition in single images and learning from noisy labels for this task, respectively. To facilitate progress, we will make our dataset and pre-trained models available.
Instance segmentation of buildings using keypoints
Jun 06, 2020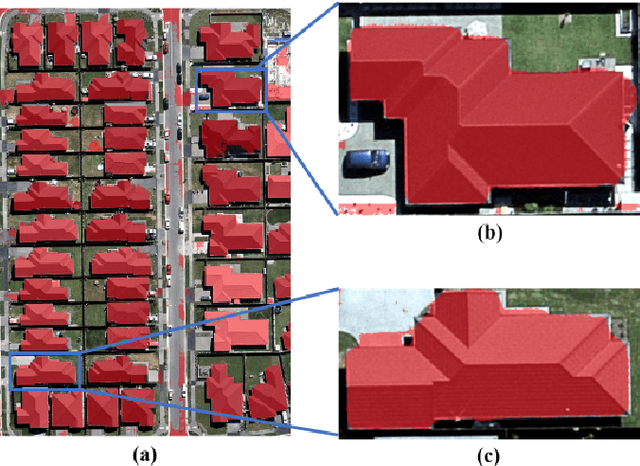
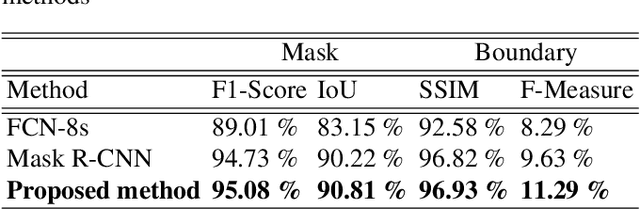
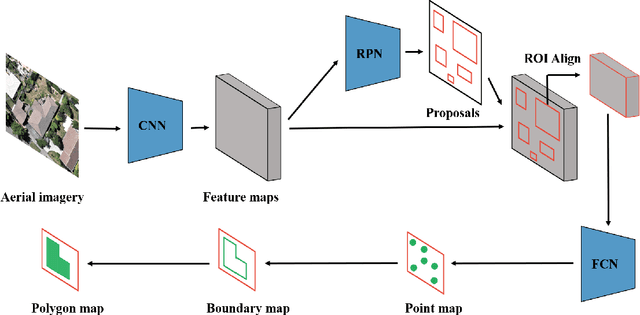
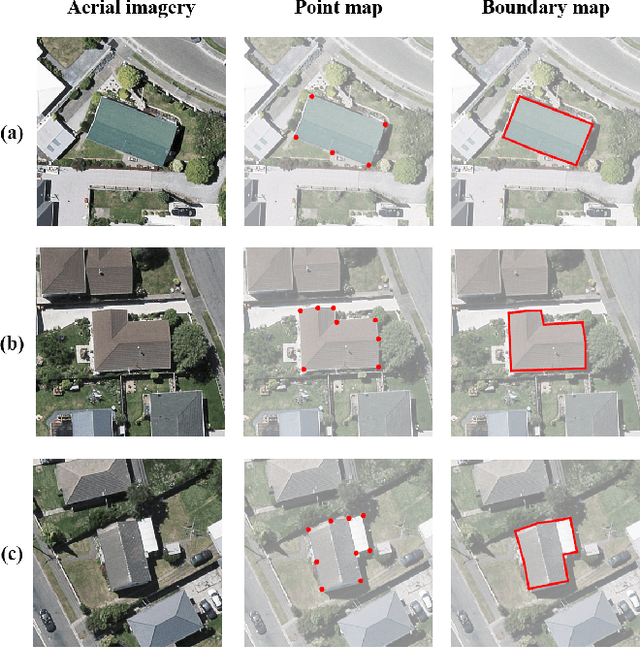
Abstract:Building segmentation is of great importance in the task of remote sensing imagery interpretation. However, the existing semantic segmentation and instance segmentation methods often lead to segmentation masks with blurred boundaries. In this paper, we propose a novel instance segmentation network for building segmentation in high-resolution remote sensing images. More specifically, we consider segmenting an individual building as detecting several keypoints. The detected keypoints are subsequently reformulated as a closed polygon, which is the semantic boundary of the building. By doing so, the sharp boundary of the building could be preserved. Experiments are conducted on selected Aerial Imagery for Roof Segmentation (AIRS) dataset, and our method achieves better performance in both quantitative and qualitative results with comparison to the state-of-the-art methods. Our network is a bottom-up instance segmentation method that could well preserve geometric details.
Cross-Task Transfer for Multimodal Aerial Scene Recognition
May 18, 2020



Abstract:Aerial scene recognition is a fundamental task in remote sensing and has recently received increased interest. While the visual information from overhead images with powerful models and efficient algorithms yields good performance on scene recognition, additional information is always a bonus, for example, the corresponding audio information. In this paper, for improving the performance on the aerial scene recognition, we explore a novel audiovisual aerial scene recognition task using both images and sounds as input. Based on an observation that some specific sound events are more likely to be heard at a given geographic location, we propose to exploit the knowledge from the sound events to improve the performance on the aerial scene recognition. For this purpose, we have constructed a new dataset named AuDio Visual Aerial sceNe reCognition datasEt (ADVANCE). With the help of this dataset, we evaluate three proposed approaches for transferring the sound event knowledge to the aerial scene recognition task in a multimodal learning framework, and show the benefit of exploiting the audio information for the aerial scene recognition. The source code is publicly available for reproducibility purposes.https://github.com/DTaoo/Multimodal-Aerial-Scene-Recognition.
ERA: A Dataset and Deep Learning Benchmark for Event Recognition in Aerial Videos
Mar 05, 2020



Abstract:Along with the increasing use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), large volumes of aerial videos have been produced. It is unrealistic for humans to screen such big data and understand their contents. Hence methodological research on the automatic understanding of UAV videos is of paramount importance. In this paper, we introduce a novel problem of event recognition in unconstrained aerial videos in the remote sensing community and present a large-scale, human-annotated dataset, named ERA (Event Recognition in Aerial videos), consisting of 2,864 videos each with a label from 25 different classes corresponding to an event unfolding 5 seconds. The ERA dataset is designed to have a significant intra-class variation and inter-class similarity and captures dynamic events in various circumstances and at dramatically various scales. Moreover, to offer a benchmark for this task, we extensively validate existing deep networks. We expect that the ERA dataset will facilitate further progress in automatic aerial video comprehension. The website is https://lcmou.github.io/ERA_Dataset/
AID++: An Updated Version of AID on Scene Classification
Jun 03, 2018



Abstract:Aerial image scene classification is a fundamental problem for understanding high-resolution remote sensing images and has become an active research task in the field of remote sensing due to its important role in a wide range of applications. However, the limitations of existing datasets for scene classification, such as the small scale and low-diversity, severely hamper the potential usage of the new generation deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Although huge efforts have been made in building large-scale datasets very recently, e.g., the Aerial Image Dataset (AID) which contains 10,000 image samples, they are still far from sufficient to fully train a high-capacity deep CNN model. To this end, we present a larger-scale dataset in this paper, named as AID++, for aerial scene classification based on the AID dataset. The proposed AID++ consists of more than 400,000 image samples that are semi-automatically annotated by using the existing the geographical data. We evaluate several prevalent CNN models on the proposed dataset, and the results show that our dataset can be used as a promising benchmark for scene classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge