Praveen Paritosh
Google LLC
DMLR: Data-centric Machine Learning Research -- Past, Present and Future
Nov 21, 2023


Abstract:Drawing from discussions at the inaugural DMLR workshop at ICML 2023 and meetings prior, in this report we outline the relevance of community engagement and infrastructure development for the creation of next-generation public datasets that will advance machine learning science. We chart a path forward as a collective effort to sustain the creation and maintenance of these datasets and methods towards positive scientific, societal and business impact.
Modeling subjectivity (by Mimicking Annotator Annotation) in toxic comment identification across diverse communities
Nov 01, 2023Abstract:The prevalence and impact of toxic discussions online have made content moderation crucial.Automated systems can play a vital role in identifying toxicity, and reducing the reliance on human moderation.Nevertheless, identifying toxic comments for diverse communities continues to present challenges that are addressed in this paper.The two-part goal of this study is to(1)identify intuitive variances from annotator disagreement using quantitative analysis and (2)model the subjectivity of these viewpoints.To achieve our goal, we published a new dataset\footnote{\url{https://github.com/XXX}} with expert annotators' annotations and used two other public datasets to identify the subjectivity of toxicity.Then leveraging the Large Language Model(LLM),we evaluate the model's ability to mimic diverse viewpoints on toxicity by varying size of the training data and utilizing same set of annotators as the test set used during model training and a separate set of annotators as the test set.We conclude that subjectivity is evident across all annotator groups, demonstrating the shortcomings of majority-rule voting. Moving forward, subjective annotations should serve as ground truth labels for training models for domains like toxicity in diverse communities.
DataPerf: Benchmarks for Data-Centric AI Development
Jul 20, 2022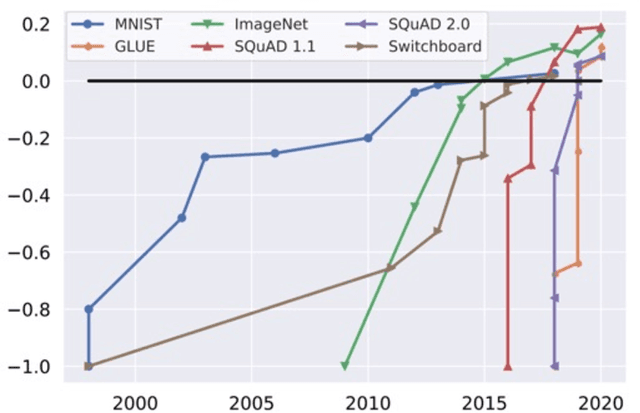
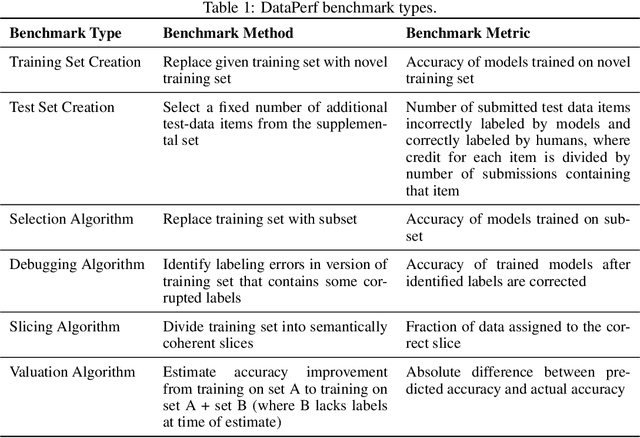
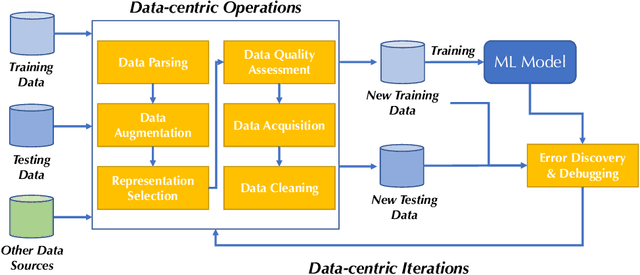
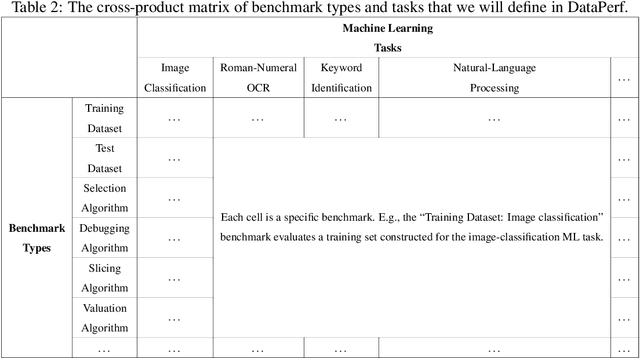
Abstract:Machine learning (ML) research has generally focused on models, while the most prominent datasets have been employed for everyday ML tasks without regard for the breadth, difficulty, and faithfulness of these datasets to the underlying problem. Neglecting the fundamental importance of datasets has caused major problems involving data cascades in real-world applications and saturation of dataset-driven criteria for model quality, hindering research growth. To solve this problem, we present DataPerf, a benchmark package for evaluating ML datasets and dataset-working algorithms. We intend it to enable the "data ratchet," in which training sets will aid in evaluating test sets on the same problems, and vice versa. Such a feedback-driven strategy will generate a virtuous loop that will accelerate development of data-centric AI. The MLCommons Association will maintain DataPerf.
k-Rater Reliability: The Correct Unit of Reliability for Aggregated Human Annotations
Mar 24, 2022


Abstract:Since the inception of crowdsourcing, aggregation has been a common strategy for dealing with unreliable data. Aggregate ratings are more reliable than individual ones. However, many natural language processing (NLP) applications that rely on aggregate ratings only report the reliability of individual ratings, which is the incorrect unit of analysis. In these instances, the data reliability is under-reported, and a proposed k-rater reliability (kRR) should be used as the correct data reliability for aggregated datasets. It is a multi-rater generalization of inter-rater reliability (IRR). We conducted two replications of the WordSim-353 benchmark, and present empirical, analytical, and bootstrap-based methods for computing kRR on WordSim-353. These methods produce very similar results. We hope this discussion will nudge researchers to report kRR in addition to IRR.
Data Excellence for AI: Why Should You Care
Nov 19, 2021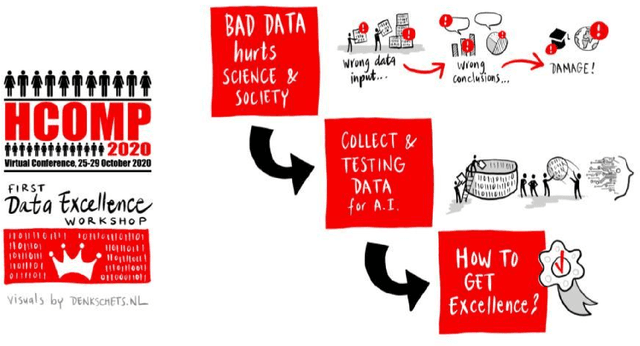

Abstract:The efficacy of machine learning (ML) models depends on both algorithms and data. Training data defines what we want our models to learn, and testing data provides the means by which their empirical progress is measured. Benchmark datasets define the entire world within which models exist and operate, yet research continues to focus on critiquing and improving the algorithmic aspect of the models rather than critiquing and improving the data with which our models operate. If "data is the new oil," we are still missing work on the refineries by which the data itself could be optimized for more effective use.
* To appear in ACM Interactions, 29(2) March-April, 2022. 4 pages
Cross-replication Reliability -- An Empirical Approach to Interpreting Inter-rater Reliability
Jun 11, 2021
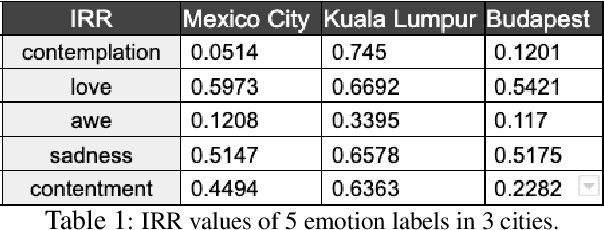
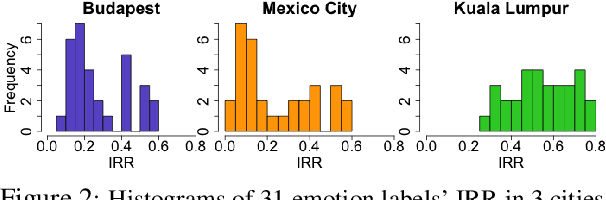
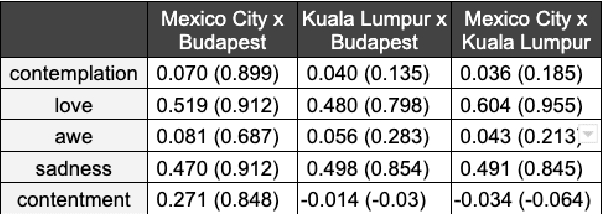
Abstract:We present a new approach to interpreting IRR that is empirical and contextualized. It is based upon benchmarking IRR against baseline measures in a replication, one of which is a novel cross-replication reliability (xRR) measure based on Cohen's kappa. We call this approach the xRR framework. We opensource a replication dataset of 4 million human judgements of facial expressions and analyze it with the proposed framework. We argue this framework can be used to measure the quality of crowdsourced datasets.
Metrology for AI: From Benchmarks to Instruments
Nov 05, 2019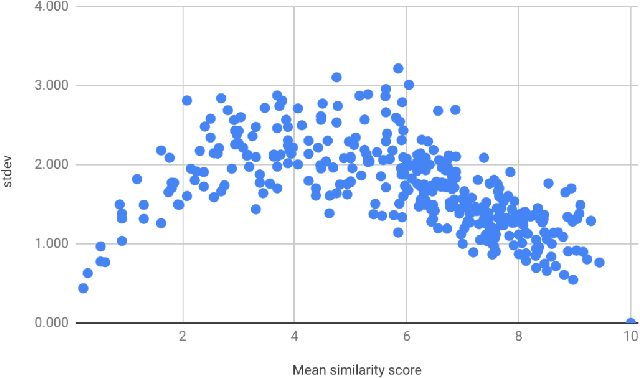
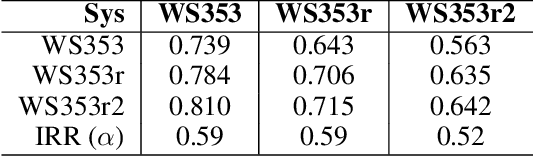

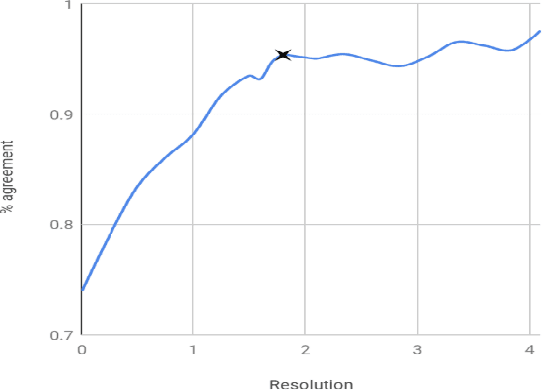
Abstract:In this paper we present the first steps towards hardening the science of measuring AI systems, by adopting metrology, the science of measurement and its application, and applying it to human (crowd) powered evaluations. We begin with the intuitive observation that evaluating the performance of an AI system is a form of measurement. In all other science and engineering disciplines, the devices used to measure are called instruments, and all measurements are recorded with respect to the characteristics of the instruments used. One does not report mass, speed, or length, for example, of a studied object without disclosing the precision (measurement variance) and resolution (smallest detectable change) of the instrument used. It is extremely common in the AI literature to compare the performance of two systems by using a crowd-sourced dataset as an instrument, but failing to report if the performance difference lies within the capability of that instrument to measure. To illustrate the adoption of metrology to benchmark datasets we use the word similarity benchmark WS353 and several previously published experiments that use it for evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge