Ka Wong
k-Rater Reliability: The Correct Unit of Reliability for Aggregated Human Annotations
Mar 24, 2022


Abstract:Since the inception of crowdsourcing, aggregation has been a common strategy for dealing with unreliable data. Aggregate ratings are more reliable than individual ones. However, many natural language processing (NLP) applications that rely on aggregate ratings only report the reliability of individual ratings, which is the incorrect unit of analysis. In these instances, the data reliability is under-reported, and a proposed k-rater reliability (kRR) should be used as the correct data reliability for aggregated datasets. It is a multi-rater generalization of inter-rater reliability (IRR). We conducted two replications of the WordSim-353 benchmark, and present empirical, analytical, and bootstrap-based methods for computing kRR on WordSim-353. These methods produce very similar results. We hope this discussion will nudge researchers to report kRR in addition to IRR.
Cross-replication Reliability -- An Empirical Approach to Interpreting Inter-rater Reliability
Jun 11, 2021
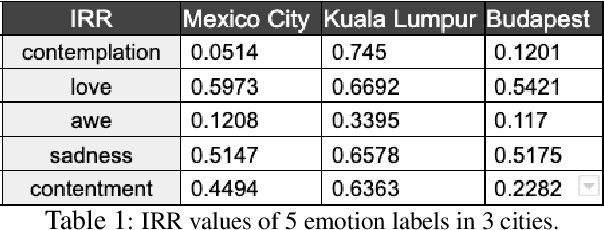
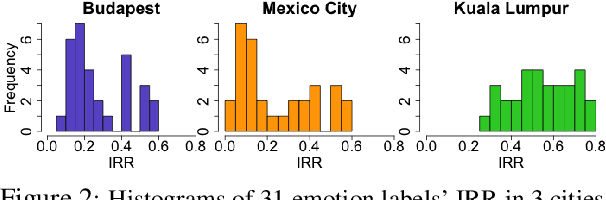
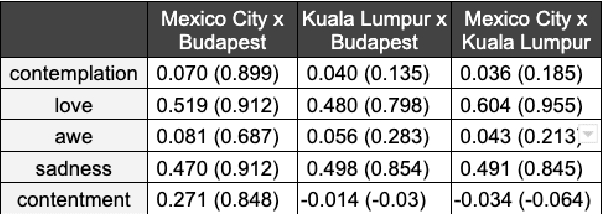
Abstract:We present a new approach to interpreting IRR that is empirical and contextualized. It is based upon benchmarking IRR against baseline measures in a replication, one of which is a novel cross-replication reliability (xRR) measure based on Cohen's kappa. We call this approach the xRR framework. We opensource a replication dataset of 4 million human judgements of facial expressions and analyze it with the proposed framework. We argue this framework can be used to measure the quality of crowdsourced datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge