Pinkesh Badjatiya
Unsupervised Hierarchical Concept Learning
Oct 06, 2020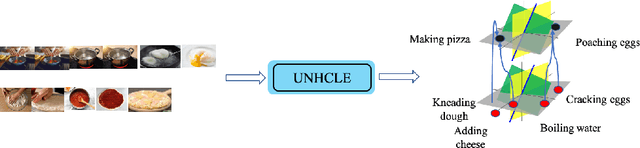
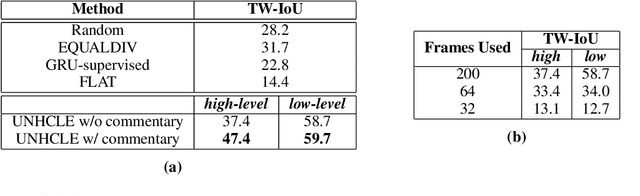
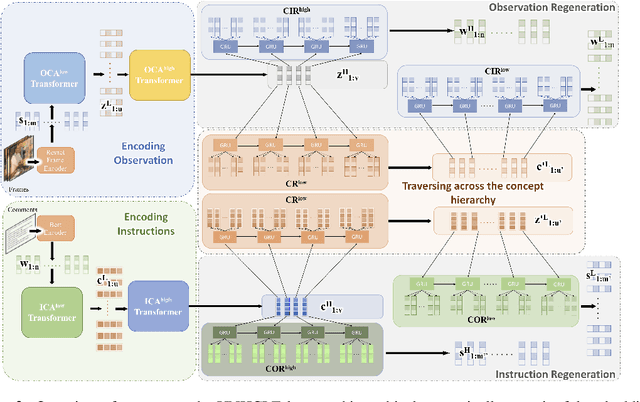
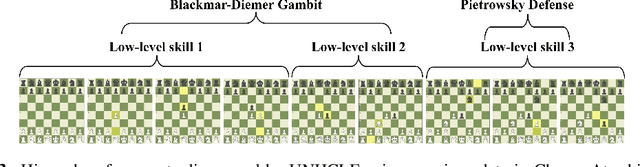
Abstract:Discovering concepts (or temporal abstractions) in an unsupervised manner from demonstration data in the absence of an environment is an important problem. Organizing these discovered concepts hierarchically at different levels of abstraction is useful in discovering patterns, building ontologies, and generating tutorials from demonstration data. However, recent work to discover such concepts without access to any environment does not discover relationships (or a hierarchy) between these discovered concepts. In this paper, we present a Transformer-based concept abstraction architecture UNHCLE (pronounced uncle) that extracts a hierarchy of concepts in an unsupervised way from demonstration data. We empirically demonstrate how UNHCLE discovers meaningful hierarchies using datasets from Chess and Cooking domains. Finally, we show how UNHCLE learns meaningful language labels for concepts by using demonstration data augmented with natural language for cooking and chess. All of our code is available at https://github.com/UNHCLE/UNHCLE
MixBoost: Synthetic Oversampling with Boosted Mixup for Handling Extreme Imbalance
Sep 03, 2020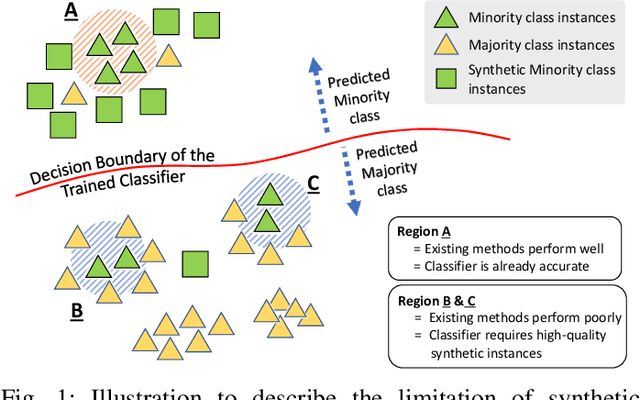
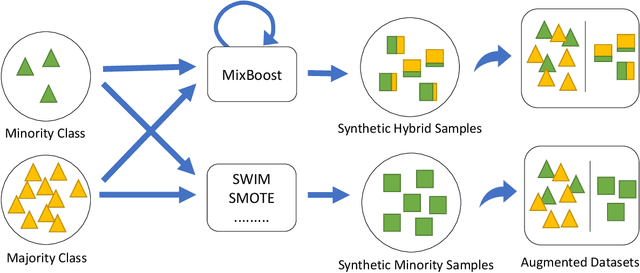
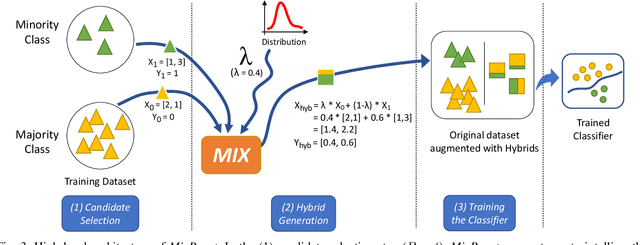
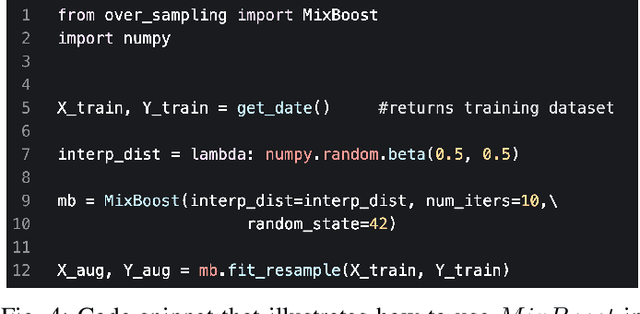
Abstract:Training a classification model on a dataset where the instances of one class outnumber those of the other class is a challenging problem. Such imbalanced datasets are standard in real-world situations such as fraud detection, medical diagnosis, and computational advertising. We propose an iterative data augmentation method, MixBoost, which intelligently selects (Boost) and then combines (Mix) instances from the majority and minority classes to generate synthetic hybrid instances that have characteristics of both classes. We evaluate MixBoost on 20 benchmark datasets, show that it outperforms existing approaches, and test its efficacy through significance testing. We also present ablation studies to analyze the impact of the different components of MixBoost.
TRACE: Transform Aggregate and Compose Visiolinguistic Representations for Image Search with Text Feedback
Sep 03, 2020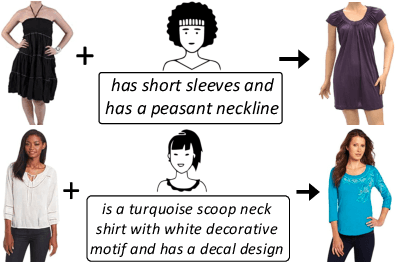
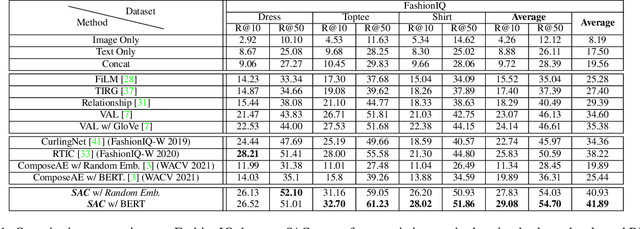
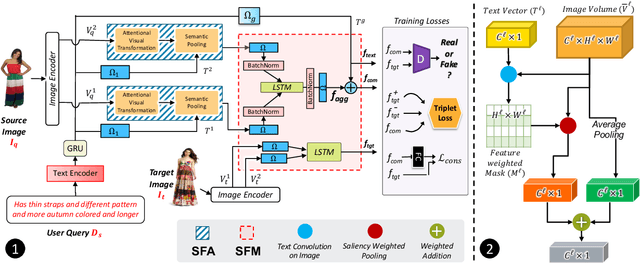
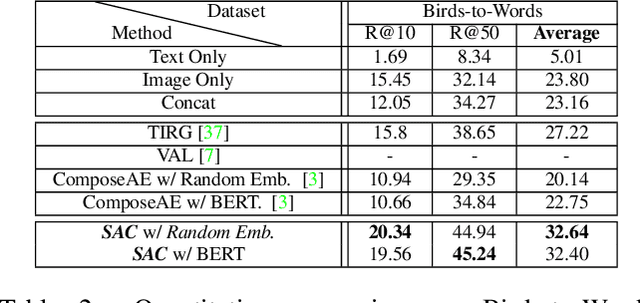
Abstract:The ability to efficiently search for images over an indexed database is the cornerstone for several user experiences. Incorporating user feedback, through multi-modal inputs provide flexible and interaction to serve fine-grained specificity in requirements. We specifically focus on text feedback, through descriptive natural language queries. Given a reference image and textual user feedback, our goal is to retrieve images that satisfy constraints specified by both of these input modalities. The task is challenging as it requires understanding the textual semantics from the text feedback and then applying these changes to the visual representation. To address these challenges, we propose a novel architecture TRACE which contains a hierarchical feature aggregation module to learn the composite visio-linguistic representations. TRACE achieves the SOTA performance on 3 benchmark datasets: FashionIQ, Shoes, and Birds-to-Words, with an average improvement of at least ~5.7%, ~3%, and ~5% respectively in R@K metric. Our extensive experiments and ablation studies show that TRACE consistently outperforms the existing techniques by significant margins both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Inducing Cooperative behaviour in Sequential-Social dilemmas through Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning using Status-Quo Loss
Feb 13, 2020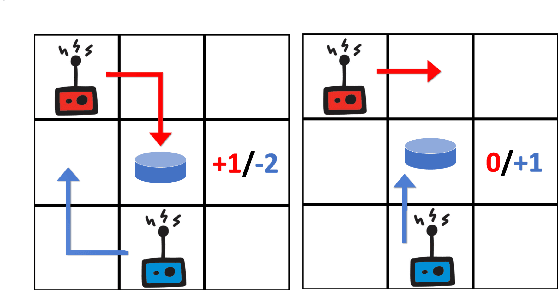


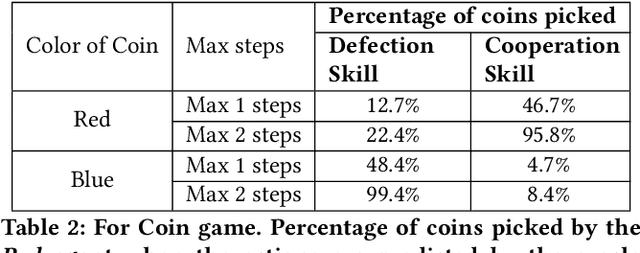
Abstract:In social dilemma situations, individual rationality leads to sub-optimal group outcomes. Several human engagements can be modeled as a sequential (multi-step) social dilemmas. However, in contrast to humans, Deep Reinforcement Learning agents trained to optimize individual rewards in sequential social dilemmas converge to selfish, mutually harmful behavior. We introduce a status-quo loss (SQLoss) that encourages an agent to stick to the status quo, rather than repeatedly changing its policy. We show how agents trained with SQLoss evolve cooperative behavior in several social dilemma matrix games. To work with social dilemma games that have visual input, we propose GameDistill. GameDistill uses self-supervision and clustering to automatically extract cooperative and selfish policies from a social dilemma game. We combine GameDistill and SQLoss to show how agents evolve socially desirable cooperative behavior in the Coin Game.
Stereotypical Bias Removal for Hate Speech Detection Task using Knowledge-based Generalizations
Jan 15, 2020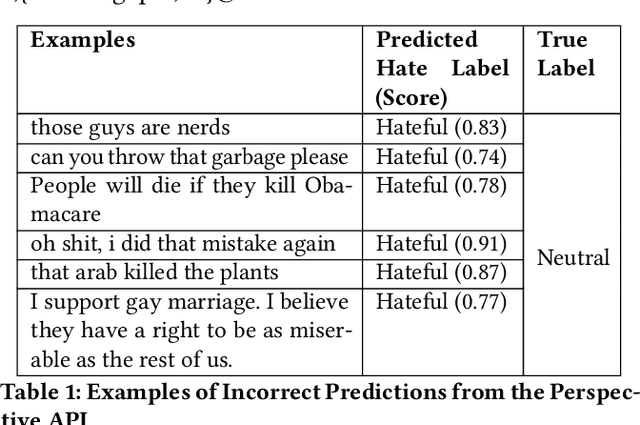
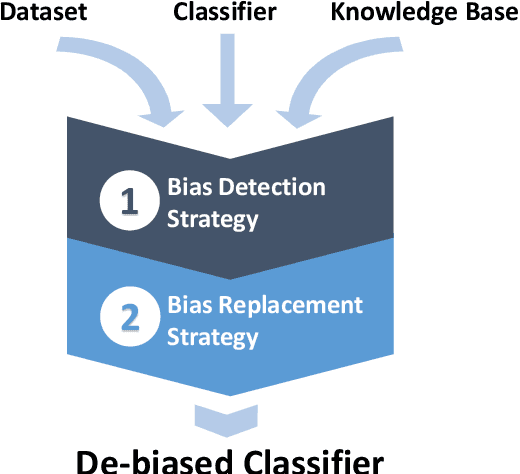
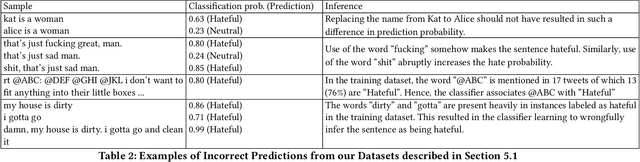
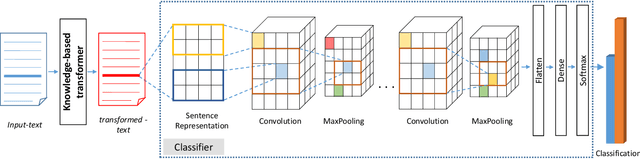
Abstract:With the ever-increasing cases of hate spread on social media platforms, it is critical to design abuse detection mechanisms to proactively avoid and control such incidents. While there exist methods for hate speech detection, they stereotype words and hence suffer from inherently biased training. Bias removal has been traditionally studied for structured datasets, but we aim at bias mitigation from unstructured text data. In this paper, we make two important contributions. First, we systematically design methods to quantify the bias for any model and propose algorithms for identifying the set of words which the model stereotypes. Second, we propose novel methods leveraging knowledge-based generalizations for bias-free learning. Knowledge-based generalization provides an effective way to encode knowledge because the abstraction they provide not only generalizes content but also facilitates retraction of information from the hate speech detection classifier, thereby reducing the imbalance. We experiment with multiple knowledge generalization policies and analyze their effect on general performance and in mitigating bias. Our experiments with two real-world datasets, a Wikipedia Talk Pages dataset (WikiDetox) of size ~96k and a Twitter dataset of size ~24k, show that the use of knowledge-based generalizations results in better performance by forcing the classifier to learn from generalized content. Our methods utilize existing knowledge-bases and can easily be extended to other tasks
Multi-label Categorization of Accounts of Sexism using a Neural Framework
Nov 18, 2019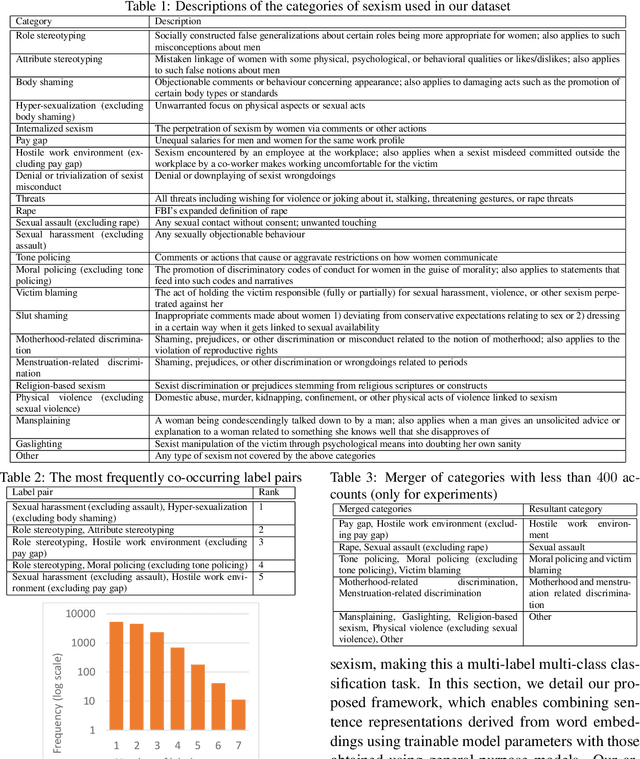
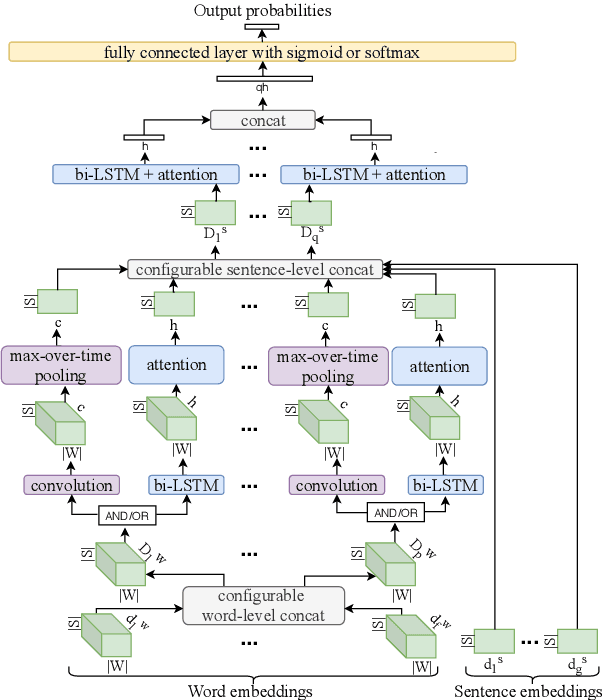


Abstract:Sexism, an injustice that subjects women and girls to enormous suffering, manifests in blatant as well as subtle ways. In the wake of growing documentation of experiences of sexism on the web, the automatic categorization of accounts of sexism has the potential to assist social scientists and policy makers in studying and countering sexism better. The existing work on sexism classification, which is different from sexism detection, has certain limitations in terms of the categories of sexism used and/or whether they can co-occur. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work on the multi-label classification of sexism of any kind(s), and we contribute the largest dataset for sexism categorization. We develop a neural solution for this multi-label classification that can combine sentence representations obtained using models such as BERT with distributional and linguistic word embeddings using a flexible, hierarchical architecture involving recurrent components and optional convolutional ones. Further, we leverage unlabeled accounts of sexism to infuse domain-specific elements into our framework. The best proposed method outperforms several deep learning as well as traditional machine learning baselines by an appreciable margin.
Attention-based Neural Text Segmentation
Aug 29, 2018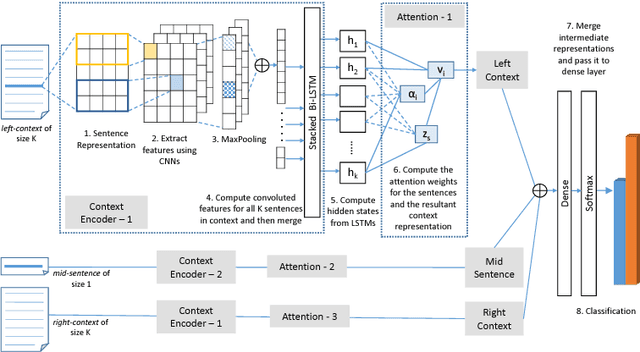
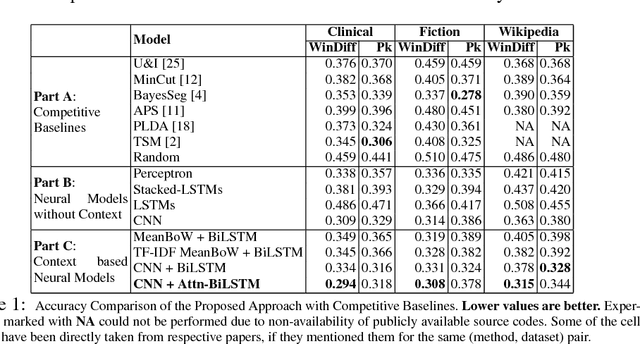
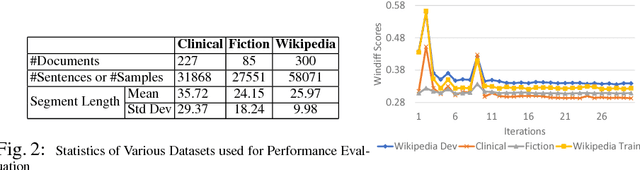
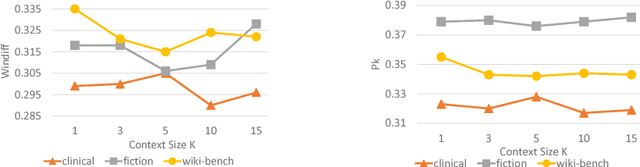
Abstract:Text segmentation plays an important role in various Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks like summarization, context understanding, document indexing and document noise removal. Previous methods for this task require manual feature engineering, huge memory requirements and large execution times. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first one to present a novel supervised neural approach for text segmentation. Specifically, we propose an attention-based bidirectional LSTM model where sentence embeddings are learned using CNNs and the segments are predicted based on contextual information. This model can automatically handle variable sized context information. Compared to the existing competitive baselines, the proposed model shows a performance improvement of ~7% in WinDiff score on three benchmark datasets.
Deep Learning for Hate Speech Detection in Tweets
Jun 01, 2017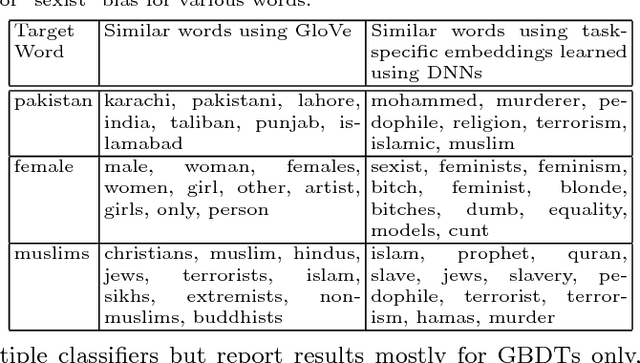
Abstract:Hate speech detection on Twitter is critical for applications like controversial event extraction, building AI chatterbots, content recommendation, and sentiment analysis. We define this task as being able to classify a tweet as racist, sexist or neither. The complexity of the natural language constructs makes this task very challenging. We perform extensive experiments with multiple deep learning architectures to learn semantic word embeddings to handle this complexity. Our experiments on a benchmark dataset of 16K annotated tweets show that such deep learning methods outperform state-of-the-art char/word n-gram methods by ~18 F1 points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge