Patrick Riley
Evolving symbolic density functionals
Mar 25, 2022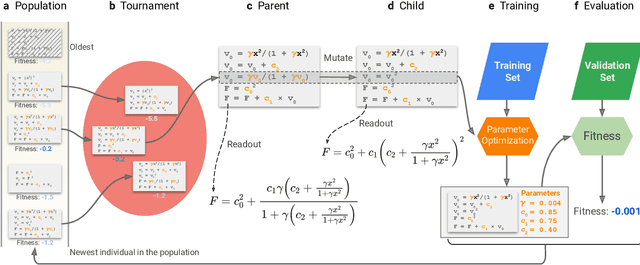
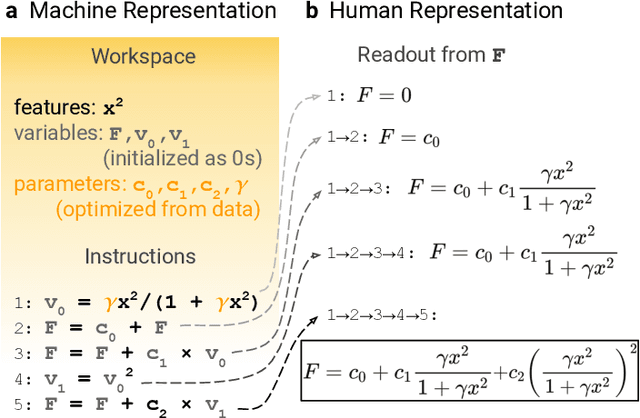
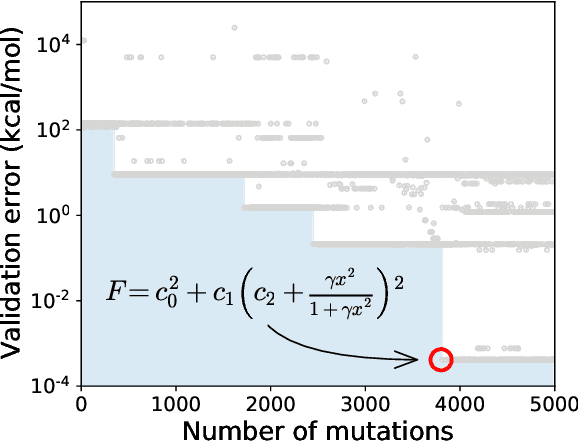
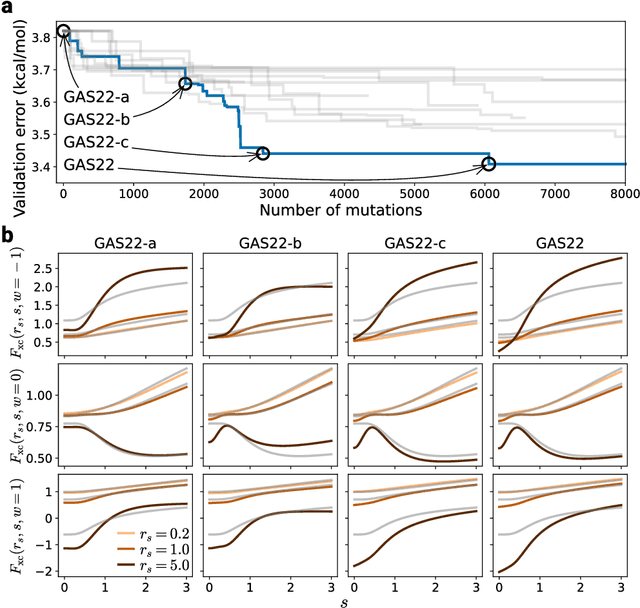
Abstract:Systematic development of accurate density functionals has been a decades-long challenge for scientists. Despite the emerging application of machine learning (ML) in approximating functionals, the resulting ML functionals usually contain more than tens of thousands parameters, which makes a huge gap in the formulation with the conventional human-designed symbolic functionals. We propose a new framework, Symbolic Functional Evolutionary Search (SyFES), that automatically constructs accurate functionals in the symbolic form, which is more explainable to humans, cheaper to evaluate, and easier to integrate to existing density functional theory codes than other ML functionals. We first show that without prior knowledge, SyFES reconstructed a known functional from scratch. We then demonstrate that evolving from an existing functional $\omega$B97M-V, SyFES found a new functional, GAS22 (Google Accelerated Science 22), that performs better on main-group chemistry. Our framework opens a new direction in leveraging computing power for the systematic development of symbolic density functionals.
Kohn-Sham equations as regularizer: building prior knowledge into machine-learned physics
Sep 17, 2020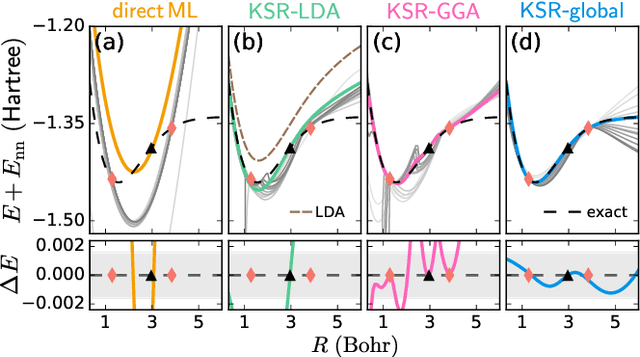
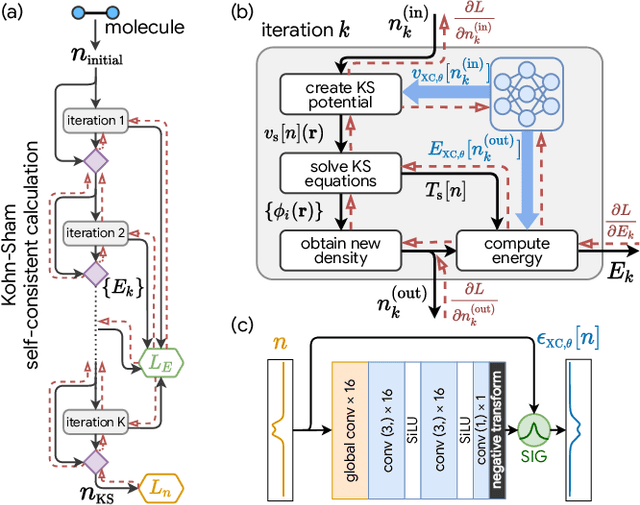
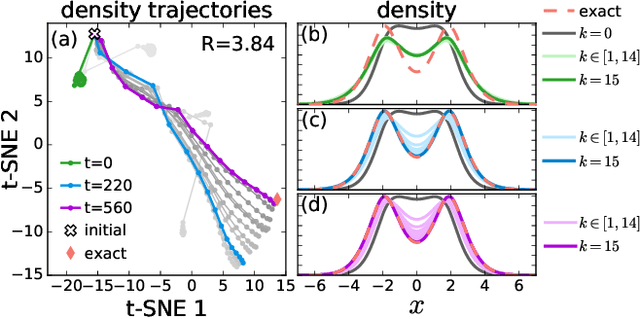
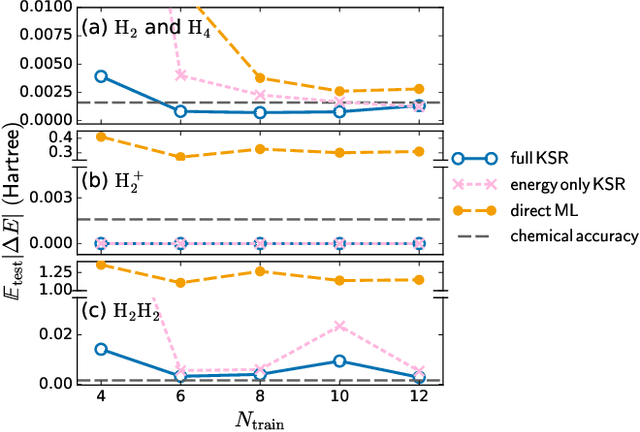
Abstract:Including prior knowledge is important for effective machine learning models in physics, and is usually achieved by explicitly adding loss terms or constraints on model architectures. Prior knowledge embedded in the physics computation itself rarely draws attention. We show that solving the Kohn-Sham equations when training neural networks for the exchange-correlation functional provides an implicit regularization that greatly improves generalization. Two separations suffice for learning the entire one-dimensional H$_2$ dissociation curve within chemical accuracy, including the strongly correlated region. Our models also generalize to unseen types of molecules and overcome self-interaction error.
Scaling Symbolic Methods using Gradients for Neural Model Explanation
Jun 29, 2020
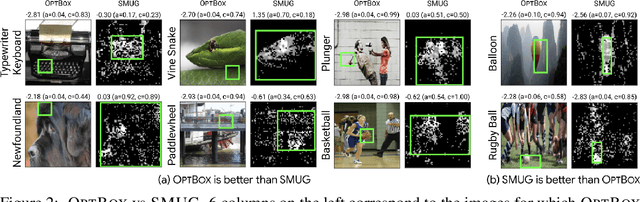
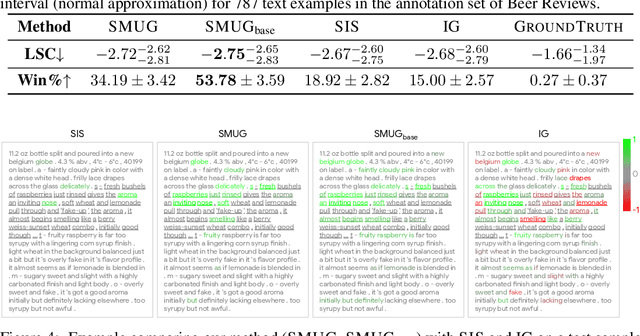

Abstract:Symbolic techniques based on Satisfiability Modulo Theory (SMT) solvers have been proposed for analyzing and verifying neural network properties, but their usage has been fairly limited owing to their poor scalability with larger networks. In this work, we propose a technique for combining gradient-based methods with symbolic techniques to scale such analyses and demonstrate its application for model explanation. In particular, we apply this technique to identify minimal regions in an input that are most relevant for a neural network's prediction. Our approach uses gradient information (based on Integrated Gradients) to focus on a subset of neurons in the first layer, which allows our technique to scale to large networks. The corresponding SMT constraints encode the minimal input mask discovery problem such that after masking the input, the activations of the selected neurons are still above a threshold. After solving for the minimal masks, our approach scores the mask regions to generate a relative ordering of the features within the mask. This produces a saliency map which explains "where a model is looking" when making a prediction. We evaluate our technique on three datasets - MNIST, ImageNet, and Beer Reviews, and demonstrate both quantitatively and qualitatively that the regions generated by our approach are sparser and achieve higher saliency scores compared to the gradient-based methods alone.
Machine learning on DNA-encoded libraries: A new paradigm for hit-finding
Jan 31, 2020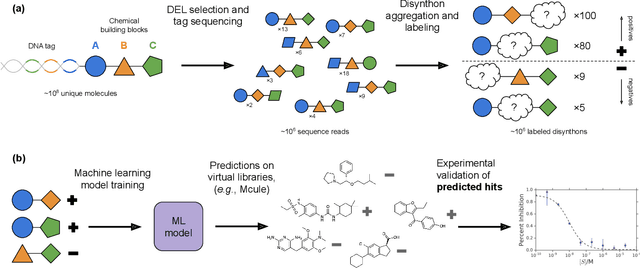
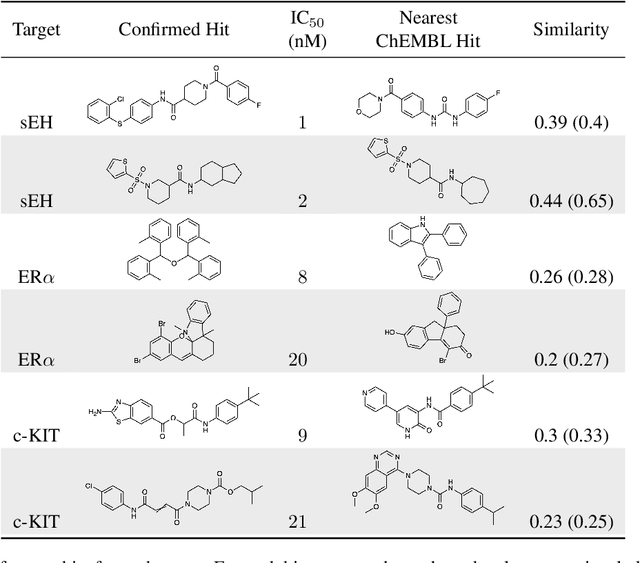
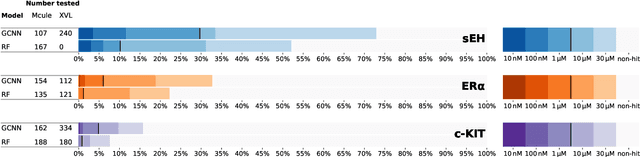
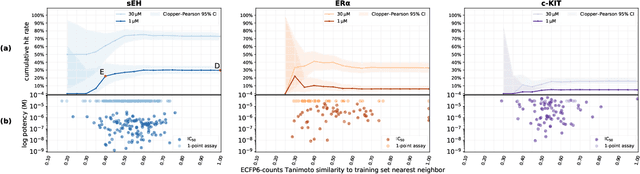
Abstract:DNA-encoded small molecule libraries (DELs) have enabled discovery of novel inhibitors for many distinct protein targets of therapeutic value through screening of libraries with up to billions of unique small molecules. We demonstrate a new approach applying machine learning to DEL selection data by identifying active molecules from a large commercial collection and a virtual library of easily synthesizable compounds. We train models using only DEL selection data and apply automated or automatable filters with chemist review restricted to the removal of molecules with potential for instability or reactivity. We validate this approach with a large prospective study (nearly 2000 compounds tested) across three diverse protein targets: sEH (a hydrolase), ER{\alpha} (a nuclear receptor), and c-KIT (a kinase). The approach is effective, with an overall hit rate of {\sim}30% at 30 {\textmu}M and discovery of potent compounds (IC50 <10 nM) for every target. The model makes useful predictions even for molecules dissimilar to the original DEL and the compounds identified are diverse, predominantly drug-like, and different from known ligands. Collectively, the quality and quantity of DEL selection data; the power of modern machine learning methods; and access to large, inexpensive, commercially-available libraries creates a powerful new approach for hit finding.
Decoding Molecular Graph Embeddings with Reinforcement Learning
Apr 18, 2019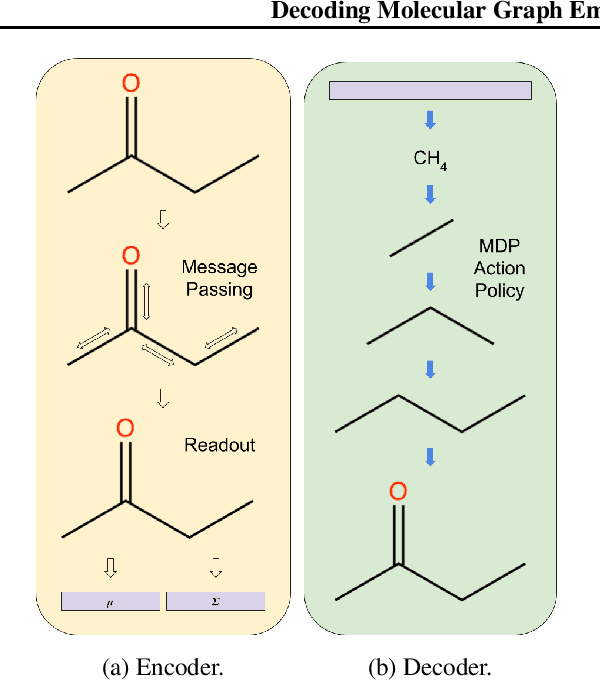
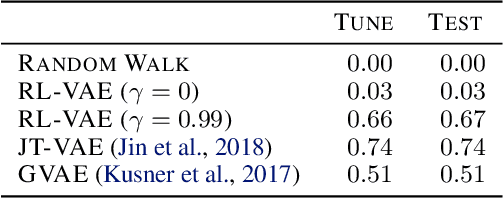
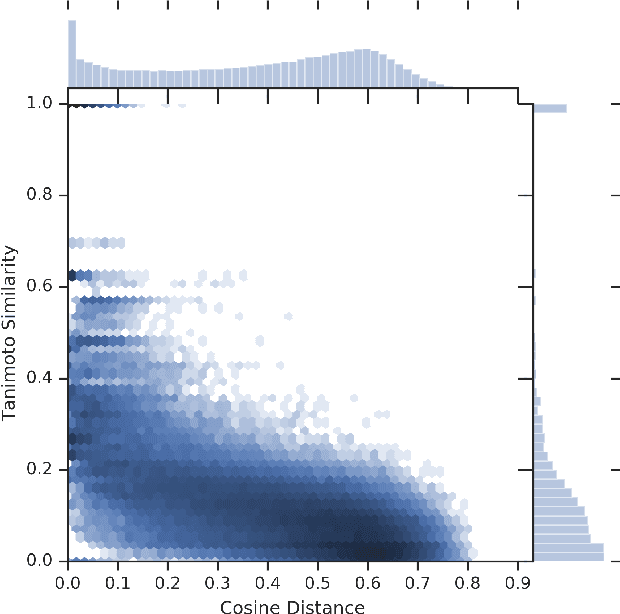
Abstract:We present RL-VAE, a graph-to-graph variational autoencoder that uses reinforcement learning to decode molecular graphs from latent embeddings. Methods have been described previously for graph-to-graph autoencoding, but these approaches require sophisticated decoders that increase the complexity of training and evaluation (such as requiring parallel encoders and decoders or non-trivial graph matching). Here, we repurpose a simple graph generator to enable efficient decoding and generation of molecular graphs.
Neural-Guided Symbolic Regression with Semantic Prior
Jan 23, 2019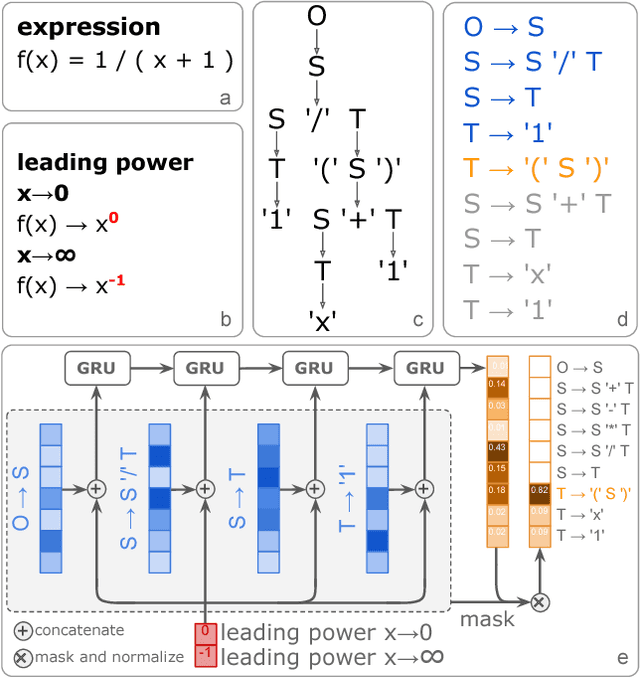
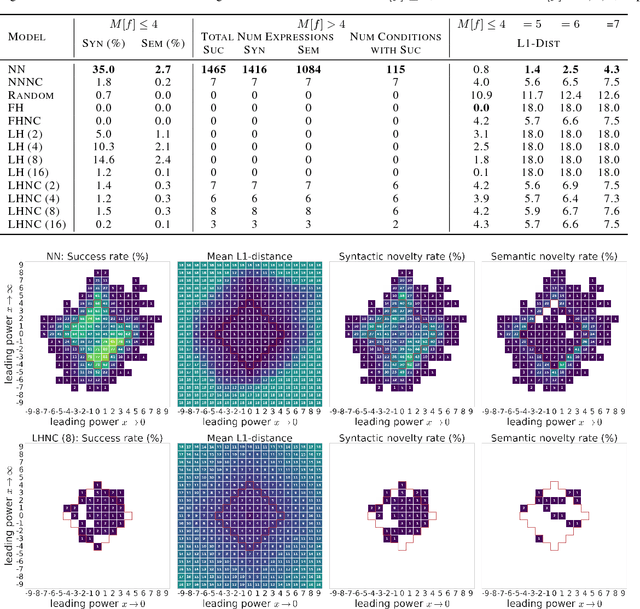
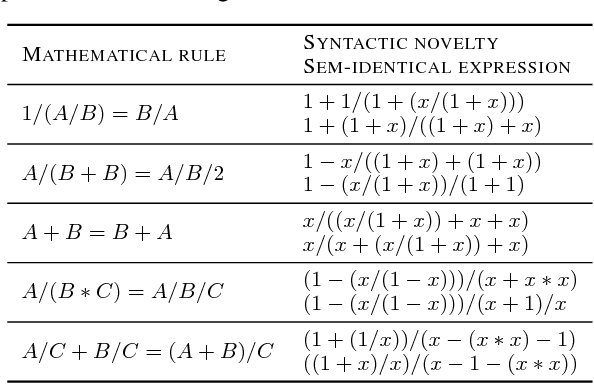
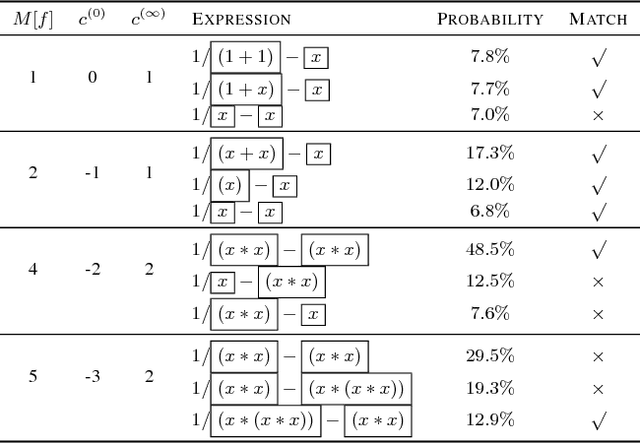
Abstract:Symbolic regression has been shown to be quite useful in many domains from discovering scientific laws to industrial empirical modeling. Existing methods focus on numerically fitting the given data. However, in many domains, symbolically derivable properties of the desired expressions are known. We illustrate these "semantic priors" with leading powers (the polynomial behavior as the input approaches 0 and $\infty$). We introduce an expression generating neural network that significantly favors the generation of expressions with desired leading powers, even generalizing to powers not in the training set. We then describe our Neural-Guided Monte Carlo Tree Search (NG-MCTS) algorithm for symbolic regression. We extensively evaluate our method on thousands of symbolic regression tasks and desired expressions to show that it significantly outperforms baseline algorithms and exhibits discovery of novel expressions outside of the training set.
Optimization of Molecules via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Oct 23, 2018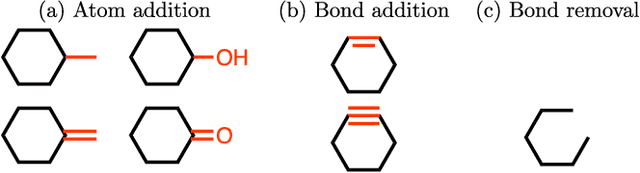
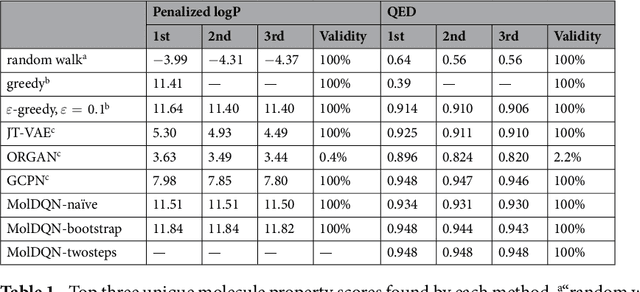
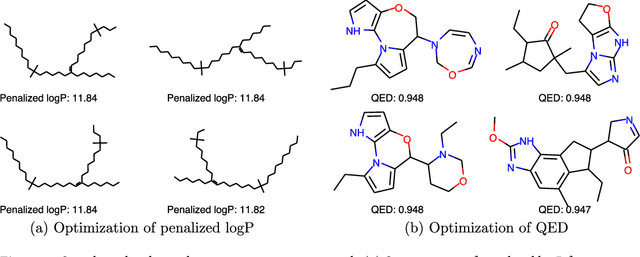
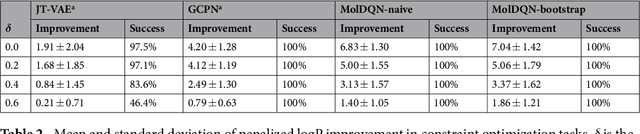
Abstract:We present a framework, which we call Molecule Deep $Q$-Networks (MolDQN), for molecule optimization by combining domain knowledge of chemistry and state-of-the-art reinforcement learning techniques (prioritized experience replay, double $Q$-learning, and randomized value functions). We directly define modifications on molecules, thereby ensuring 100% chemical validity. Further, we operate without pre-training on any dataset to avoid possible bias from the choice of that set. As a result, our model outperforms several other state-of-the-art algorithms by having a higher success rate of acquiring molecules with better properties. Inspired by problems faced during medicinal chemistry lead optimization, we extend our model with multi-objective reinforcement learning, which maximizes drug-likeness while maintaining similarity to the original molecule. We further show the path through chemical space to achieve optimization for a molecule to understand how the model works.
Tensor field networks: Rotation- and translation-equivariant neural networks for 3D point clouds
May 18, 2018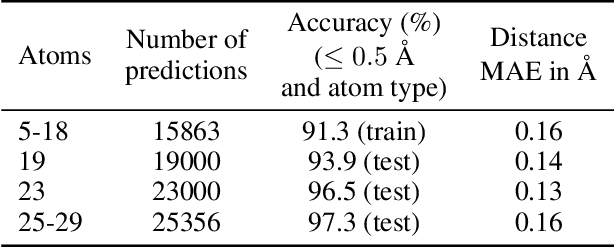
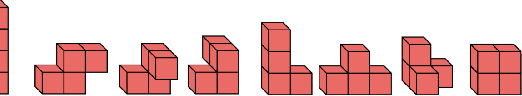
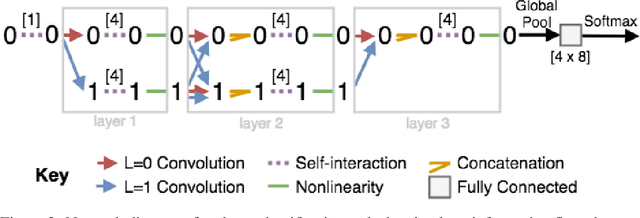
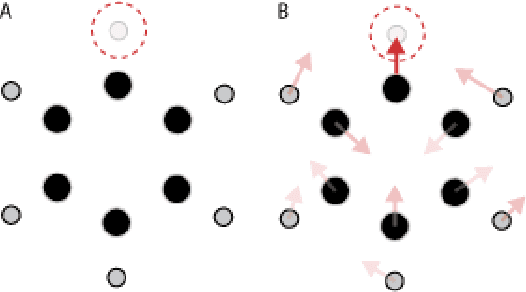
Abstract:We introduce tensor field neural networks, which are locally equivariant to 3D rotations, translations, and permutations of points at every layer. 3D rotation equivariance removes the need for data augmentation to identify features in arbitrary orientations. Our network uses filters built from spherical harmonics; due to the mathematical consequences of this filter choice, each layer accepts as input (and guarantees as output) scalars, vectors, and higher-order tensors, in the geometric sense of these terms. We demonstrate the capabilities of tensor field networks with tasks in geometry, physics, and chemistry.
Molecular Graph Convolutions: Moving Beyond Fingerprints
Aug 18, 2016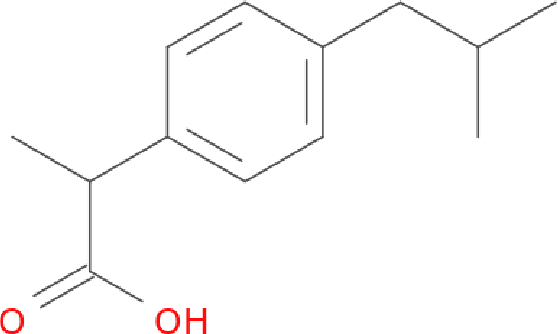
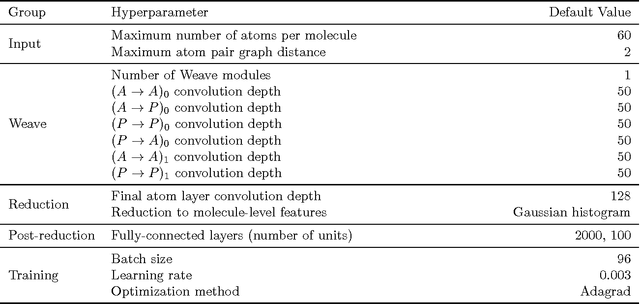
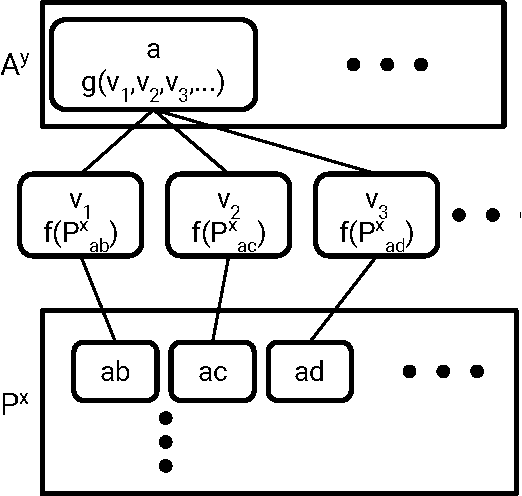
Abstract:Molecular "fingerprints" encoding structural information are the workhorse of cheminformatics and machine learning in drug discovery applications. However, fingerprint representations necessarily emphasize particular aspects of the molecular structure while ignoring others, rather than allowing the model to make data-driven decisions. We describe molecular "graph convolutions", a machine learning architecture for learning from undirected graphs, specifically small molecules. Graph convolutions use a simple encoding of the molecular graph---atoms, bonds, distances, etc.---which allows the model to take greater advantage of information in the graph structure. Although graph convolutions do not outperform all fingerprint-based methods, they (along with other graph-based methods) represent a new paradigm in ligand-based virtual screening with exciting opportunities for future improvement.
* See "Version information" section
Massively Multitask Networks for Drug Discovery
Feb 06, 2015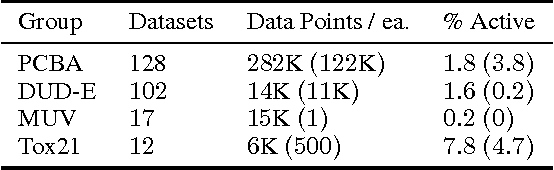
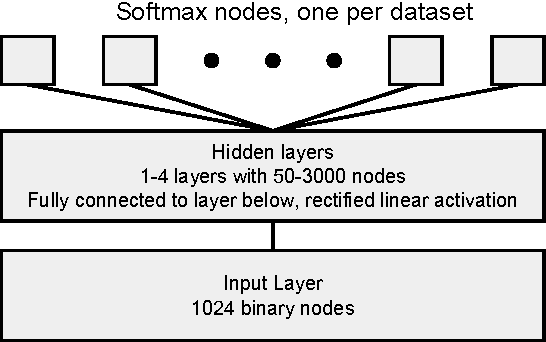
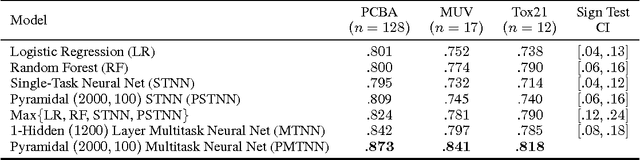
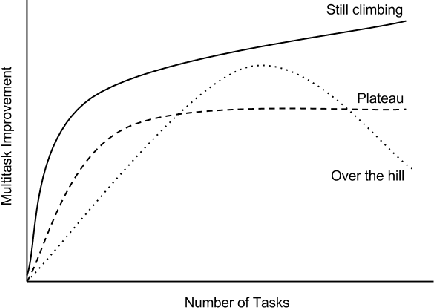
Abstract:Massively multitask neural architectures provide a learning framework for drug discovery that synthesizes information from many distinct biological sources. To train these architectures at scale, we gather large amounts of data from public sources to create a dataset of nearly 40 million measurements across more than 200 biological targets. We investigate several aspects of the multitask framework by performing a series of empirical studies and obtain some interesting results: (1) massively multitask networks obtain predictive accuracies significantly better than single-task methods, (2) the predictive power of multitask networks improves as additional tasks and data are added, (3) the total amount of data and the total number of tasks both contribute significantly to multitask improvement, and (4) multitask networks afford limited transferability to tasks not in the training set. Our results underscore the need for greater data sharing and further algorithmic innovation to accelerate the drug discovery process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge