Lusann Yang
Crystal Structure Search with Random Relaxations Using Graph Networks
Dec 08, 2020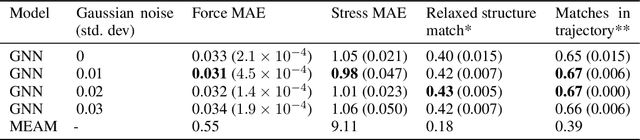
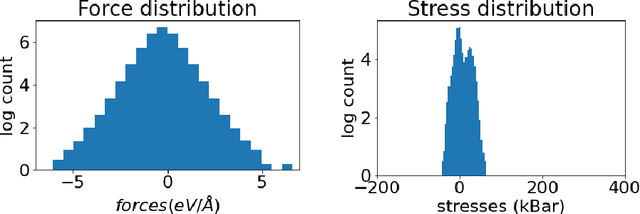
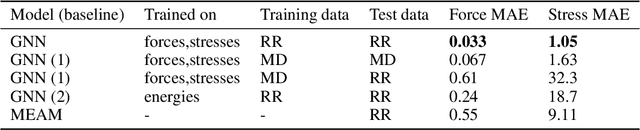
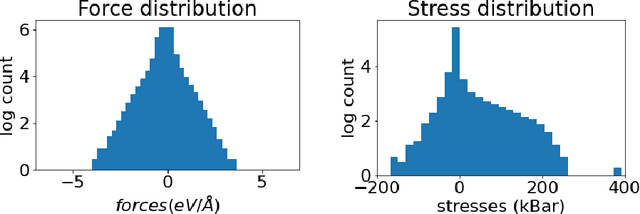
Abstract:Materials design enables technologies critical to humanity, including combating climate change with solar cells and batteries. Many properties of a material are determined by its atomic crystal structure. However, prediction of the atomic crystal structure for a given material's chemical formula is a long-standing grand challenge that remains a barrier in materials design. We investigate a data-driven approach to accelerating ab initio random structure search (AIRSS), a state-of-the-art method for crystal structure search. We build a novel dataset of random structure relaxations of Li-Si battery anode materials using high-throughput density functional theory calculations. We train graph neural networks to simulate relaxations of random structures. Our model is able to find an experimentally verified structure of Li15Si4 it was not trained on, and has potential for orders of magnitude speedup over AIRSS when searching large unit cells and searching over multiple chemical stoichiometries. Surprisingly, we find that data augmentation of adding Gaussian noise improves both the accuracy and out of domain generalization of our models.
Tensor field networks: Rotation- and translation-equivariant neural networks for 3D point clouds
May 18, 2018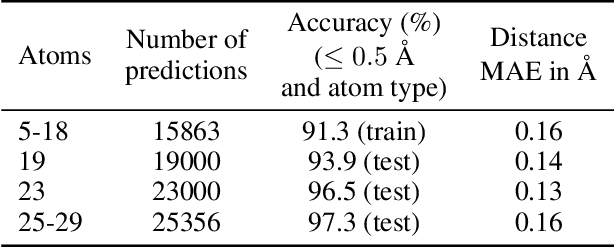
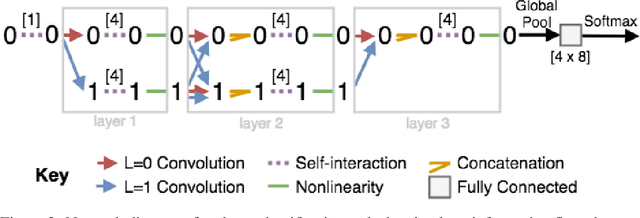
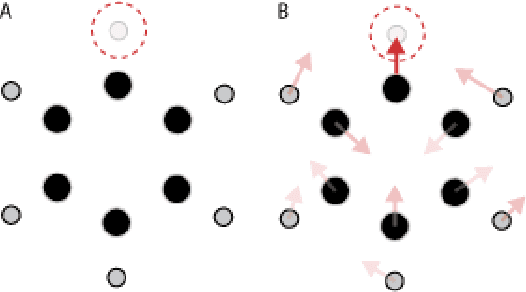
Abstract:We introduce tensor field neural networks, which are locally equivariant to 3D rotations, translations, and permutations of points at every layer. 3D rotation equivariance removes the need for data augmentation to identify features in arbitrary orientations. Our network uses filters built from spherical harmonics; due to the mathematical consequences of this filter choice, each layer accepts as input (and guarantees as output) scalars, vectors, and higher-order tensors, in the geometric sense of these terms. We demonstrate the capabilities of tensor field networks with tasks in geometry, physics, and chemistry.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge