Panagiotis Tsiotras
Distributed Event-Triggered Distance-Based Formation Control for Multi-Agent Systems
Sep 15, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of collaborative formation control for multi-agent systems with limited resources. We consider a team of robots tasked with achieving a desired formation from arbitrary initial configurations. To reduce unnecessary control updates and conserve resources, we propose a distributed event-triggered formation controller that relies on inter-agent distance measurements. Control updates are triggered only when the measurement error exceeds a predefined threshold, ensuring system stability. The proposed controller is validated through extensive simulations and real-world experiments involving different formations, communication topologies, scalability tests, and variations in design parameters, while also being compared against periodic triggering strategies. Results demonstrate that the event-triggered approach significantly reduces control efforts while preserving formation performance.
Delayed Expansion AGT: Kinodynamic Planning with Application to Tractor-Trailer Parking
Jun 16, 2025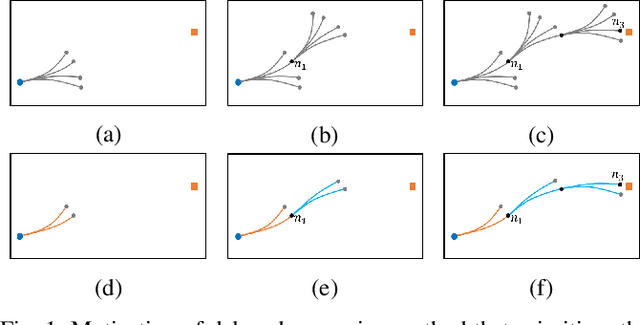
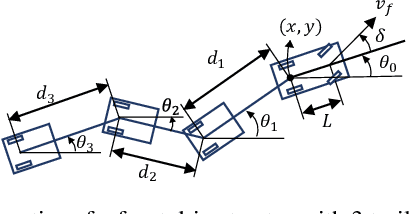
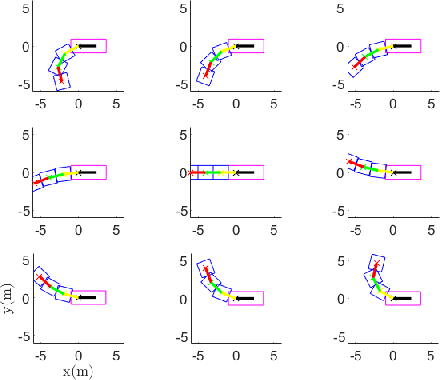
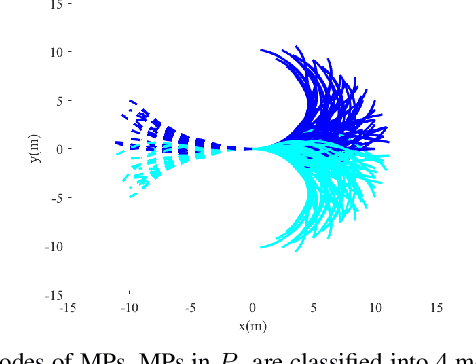
Abstract:Kinodynamic planning of articulated vehicles in cluttered environments faces additional challenges arising from high-dimensional state space and complex system dynamics. Built upon [1],[2], this work proposes the DE-AGT algorithm that grows a tree using pre-computed motion primitives (MPs) and A* heuristics. The first feature of DE-AGT is a delayed expansion of MPs. In particular, the MPs are divided into different modes, which are ranked online. With the MP classification and prioritization, DE-AGT expands the most promising mode of MPs first, which eliminates unnecessary computation and finds solutions faster. To obtain the cost-to-go heuristic for nonholonomic articulated vehicles, we rely on supervised learning and train neural networks for fast and accurate cost-to-go prediction. The learned heuristic is used for online mode ranking and node selection. Another feature of DE-AGT is the improved goal-reaching. Exactly reaching a goal state usually requires a constant connection checking with the goal by solving steering problems -- non-trivial and time-consuming for articulated vehicles. The proposed termination scheme overcomes this challenge by tightly integrating a light-weight trajectory tracking controller with the search process. DE-AGT is implemented for autonomous parking of a general car-like tractor with 3-trailer. Simulation results show an average of 10x acceleration compared to a previous method.
HCOA*: Hierarchical Class-ordered A* for Navigation in Semantic Environments
May 06, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of robot navigation in mixed geometric and semantic 3D environments. Given a hierarchical representation of the environment, the objective is to navigate from a start position to a goal while minimizing the computational cost. We introduce Hierarchical Class-ordered A* (HCOA*), an algorithm that leverages the environmental hierarchy for efficient path-planning in semantic graphs, significantly reducing computational effort. We use a total order over the semantic classes and prove theoretical performance guarantees for the algorithm. We propose two approaches for higher-layer node classification based on the node semantics of the lowest layer: a Graph Neural Network-based method and a Majority-Class method. We evaluate our approach through simulations on a 3D Scene Graph (3DSG), comparing it to the state-of-the-art and assessing its performance against our classification approaches. Results show that HCOA* can find the optimal path while reducing the number of expanded nodes by 25% and achieving a 16% reduction in computational time on the uHumans2 3DSG dataset.
Stereophotoclinometry Revisited
Apr 11, 2025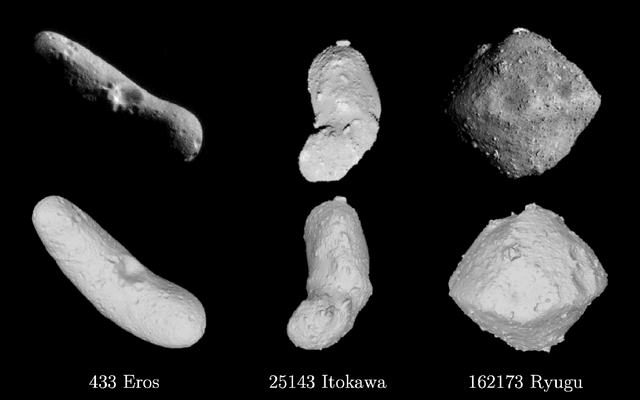
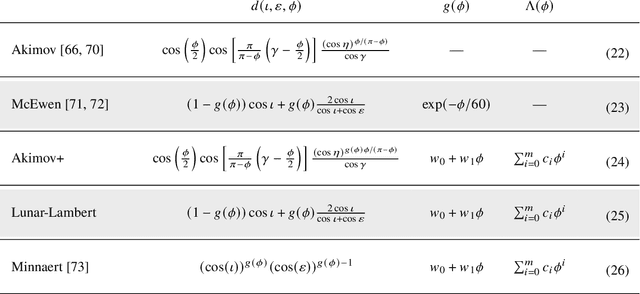
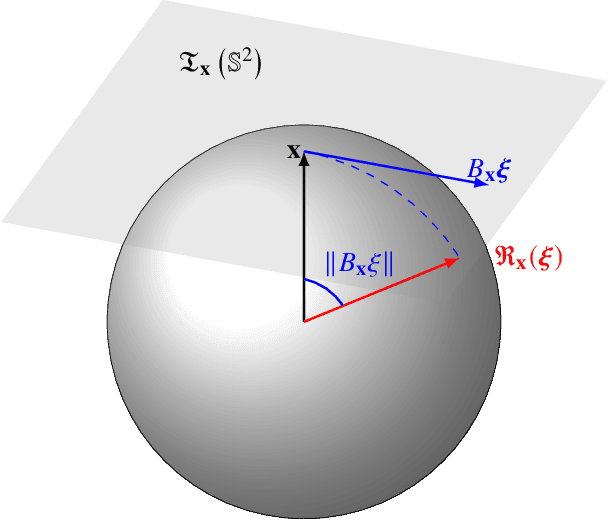
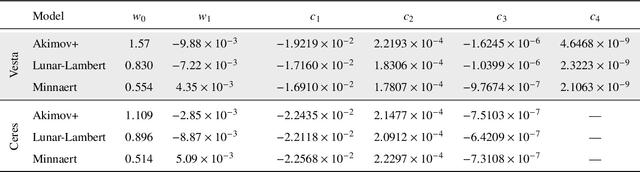
Abstract:Image-based surface reconstruction and characterization is crucial for missions to small celestial bodies, as it informs mission planning, navigation, and scientific analysis. However, current state-of-the-practice methods, such as stereophotoclinometry (SPC), rely heavily on human-in-the-loop verification and high-fidelity a priori information. This paper proposes Photoclinometry-from-Motion (PhoMo), a novel framework that incorporates photoclinometry techniques into a keypoint-based structure-from-motion (SfM) system to estimate the surface normal and albedo at detected landmarks to improve autonomous surface and shape characterization of small celestial bodies from in-situ imagery. In contrast to SPC, we forego the expensive maplet estimation step and instead use dense keypoint measurements and correspondences from an autonomous keypoint detection and matching method based on deep learning. Moreover, we develop a factor graph-based approach allowing for simultaneous optimization of the spacecraft's pose, landmark positions, Sun-relative direction, and surface normals and albedos via fusion of Sun vector measurements and image keypoint measurements. The proposed framework is validated on real imagery taken by the Dawn mission to the asteroid 4 Vesta and the minor planet 1 Ceres and compared against an SPC reconstruction, where we demonstrate superior rendering performance compared to an SPC solution and precise alignment to a stereophotogrammetry (SPG) solution without relying on any a priori camera pose and topography information or humans-in-the-loop.
Steering Large Agent Populations using Mean-Field Schrodinger Bridges with Gaussian Mixture Models
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:The Mean-Field Schrodinger Bridge (MFSB) problem is an optimization problem aiming to find the minimum effort control policy to drive a McKean-Vlassov stochastic differential equation from one probability measure to another. In the context of multiagent control, the objective is to control the configuration of a swarm of identical, interacting cooperative agents, as captured by the time-varying probability measure of their state. Available methods for solving this problem for distributions with continuous support rely either on spatial discretizations of the problem's domain or on approximating optimal solutions using neural networks trained through stochastic optimization schemes. For agents following Linear Time-Varying dynamics, and for Gaussian Mixture Model boundary distributions, we propose a highly efficient parameterization to approximate the solutions of the corresponding MFSB in closed form, without any learning steps. Our proposed approach consists of a mixture of elementary policies, each solving a Gaussian-to-Gaussian Covariance Steering problem from the components of the initial to the components of the terminal mixture. Leveraging the semidefinite formulation of the Covariance Steering problem, our proposed solver can handle probabilistic hard constraints on the system's state, while maintaining numerical tractability. We illustrate our approach on a variety of numerical examples.
Communication-Aware Iterative Map Compression for Online Path-Planning
Mar 13, 2025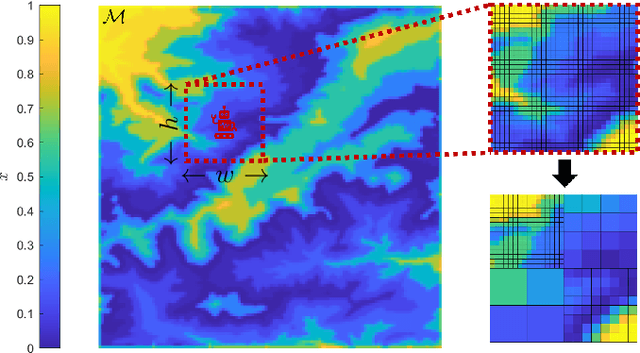
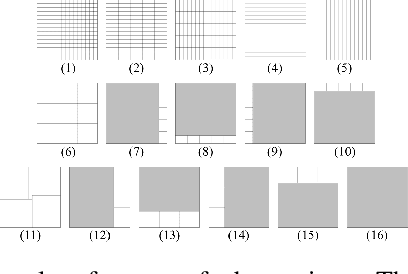
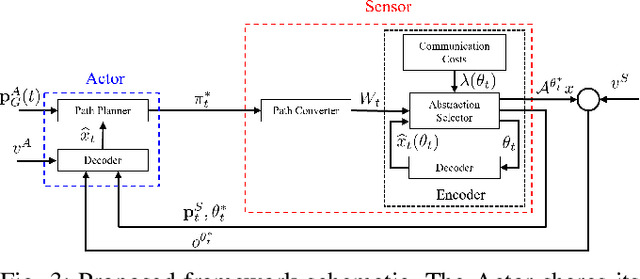
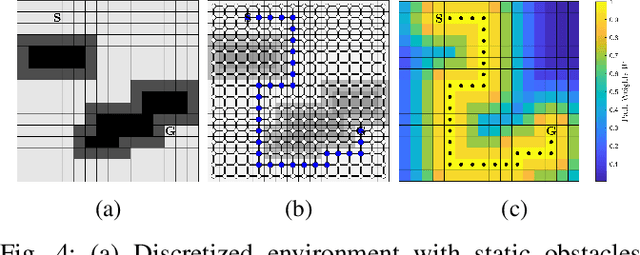
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of optimizing communicated information among heterogeneous, resource-aware robot teams to facilitate their navigation. In such operations, a mobile robot compresses its local map to assist another robot in reaching a target within an uncharted environment. The primary challenge lies in ensuring that the map compression step balances network load while transmitting only the most essential information for effective navigation. We propose a communication framework that sequentially selects the optimal map compression in a task-driven, communication-aware manner. It introduces a decoder capable of iterative map estimation, handling noise through Kalman filter techniques. The computational speed of our decoder allows for a larger compression template set compared to previous methods, and enables applications in more challenging environments. Specifically, our simulations demonstrate a remarkable 98% reduction in communicated information, compared to a framework that transmits the raw data, on a large Mars inclination map and an Earth map, all while maintaining similar planning costs. Furthermore, our method significantly reduces computational time compared to the state-of-the-art approach.
Safe Beyond the Horizon: Efficient Sampling-based MPC with Neural Control Barrier Functions
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:A common problem when using model predictive control (MPC) in practice is the satisfaction of safety specifications beyond the prediction horizon. While theoretical works have shown that safety can be guaranteed by enforcing a suitable terminal set constraint or a sufficiently long prediction horizon, these techniques are difficult to apply and thus are rarely used by practitioners, especially in the case of general nonlinear dynamics. To solve this problem, we impose a tradeoff between exact recursive feasibility, computational tractability, and applicability to ''black-box'' dynamics by learning an approximate discrete-time control barrier function and incorporating it into a variational inference MPC (VIMPC), a sampling-based MPC paradigm. To handle the resulting state constraints, we further propose a new sampling strategy that greatly reduces the variance of the estimated optimal control, improving the sample efficiency, and enabling real-time planning on a CPU. The resulting Neural Shield-VIMPC (NS-VIMPC) controller yields substantial safety improvements compared to existing sampling-based MPC controllers, even under badly designed cost functions. We validate our approach in both simulation and real-world hardware experiments.
Factor Graph-Based Active SLAM for Spacecraft Proximity Operations
Jan 19, 2025



Abstract:We investigate a scenario where a chaser spacecraft or satellite equipped with a monocular camera navigates in close proximity to a target spacecraft. The satellite's primary objective is to construct a representation of the operational environment and localize itself within it, utilizing the available image data. We frame the joint task of state trajectory and map estimation as an instance of smoothing-based simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), where the underlying structure of the problem is represented as a factor graph. Rather than considering estimation and planning as separate tasks, we propose to control the camera observations to actively reduce the uncertainty of the estimation variables, the spacecraft state, and the map landmarks. This is accomplished by adopting an information-theoretic metric to reason about the impact of candidate actions on the evolution of the belief state. Numerical simulations indicate that the proposed method successfully captures the interplay between planning and estimation, hence yielding reduced uncertainty and higher accuracy when compared to commonly adopted passive sensing strategies.
Go With the Flow: Fast Diffusion for Gaussian Mixture Models
Dec 12, 2024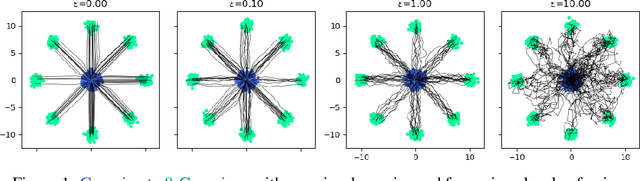
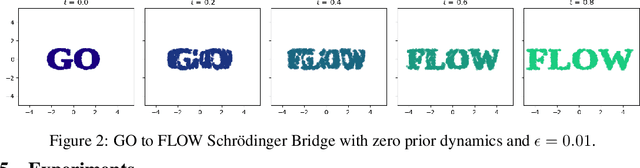


Abstract:Schr\"{o}dinger Bridges (SB) are diffusion processes that steer, in finite time, a given initial distribution to another final one while minimizing a suitable cost functional. Although various methods for computing SBs have recently been proposed in the literature, most of these approaches require computationally expensive training schemes, even for solving low-dimensional problems. In this work, we propose an analytic parametrization of a set of feasible policies for steering the distribution of a dynamical system from one Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) to another. Instead of relying on standard non-convex optimization techniques, the optimal policy within the set can be approximated as the solution of a low-dimensional linear program whose dimension scales linearly with the number of components in each mixture. Furthermore, our method generalizes naturally to more general classes of dynamical systems such as controllable Linear Time-Varying systems that cannot currently be solved using traditional neural SB approaches. We showcase the potential of this approach in low-to-moderate dimensional problems such as image-to-image translation in the latent space of an autoencoder, and various other examples. We also benchmark our approach on an Entropic Optimal Transport (EOT) problem and show that it outperforms state-of-the-art methods in cases where the boundary distributions are mixture models while requiring virtually no training.
SAVER: A Toolbox for Sampling-Based, Probabilistic Verification of Neural Networks
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:We present a neural network verification toolbox to 1) assess the probability of satisfaction of a constraint, and 2) synthesize a set expansion factor to achieve the probability of satisfaction. Specifically, the tool box establishes with a user-specified level of confidence whether the output of the neural network for a given input distribution is likely to be contained within a given set. Should the tool determine that the given set cannot satisfy the likelihood constraint, the tool also implements an approach outlined in this paper to alter the constraint set to ensure that the user-defined satisfaction probability is achieved. The toolbox is comprised of sampling-based approaches which exploit the properties of signed distance function to define set containment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge