George Rapakoulias
Steering Large Agent Populations using Mean-Field Schrodinger Bridges with Gaussian Mixture Models
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:The Mean-Field Schrodinger Bridge (MFSB) problem is an optimization problem aiming to find the minimum effort control policy to drive a McKean-Vlassov stochastic differential equation from one probability measure to another. In the context of multiagent control, the objective is to control the configuration of a swarm of identical, interacting cooperative agents, as captured by the time-varying probability measure of their state. Available methods for solving this problem for distributions with continuous support rely either on spatial discretizations of the problem's domain or on approximating optimal solutions using neural networks trained through stochastic optimization schemes. For agents following Linear Time-Varying dynamics, and for Gaussian Mixture Model boundary distributions, we propose a highly efficient parameterization to approximate the solutions of the corresponding MFSB in closed form, without any learning steps. Our proposed approach consists of a mixture of elementary policies, each solving a Gaussian-to-Gaussian Covariance Steering problem from the components of the initial to the components of the terminal mixture. Leveraging the semidefinite formulation of the Covariance Steering problem, our proposed solver can handle probabilistic hard constraints on the system's state, while maintaining numerical tractability. We illustrate our approach on a variety of numerical examples.
Go With the Flow: Fast Diffusion for Gaussian Mixture Models
Dec 12, 2024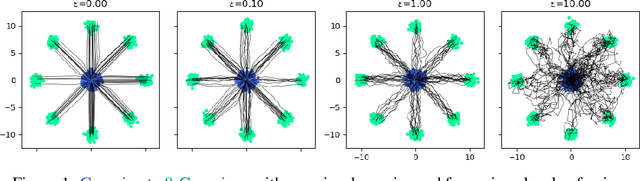
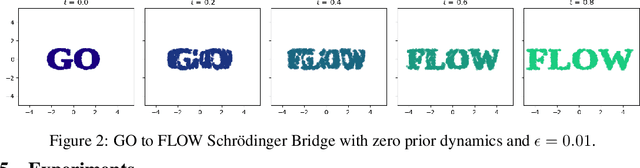


Abstract:Schr\"{o}dinger Bridges (SB) are diffusion processes that steer, in finite time, a given initial distribution to another final one while minimizing a suitable cost functional. Although various methods for computing SBs have recently been proposed in the literature, most of these approaches require computationally expensive training schemes, even for solving low-dimensional problems. In this work, we propose an analytic parametrization of a set of feasible policies for steering the distribution of a dynamical system from one Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) to another. Instead of relying on standard non-convex optimization techniques, the optimal policy within the set can be approximated as the solution of a low-dimensional linear program whose dimension scales linearly with the number of components in each mixture. Furthermore, our method generalizes naturally to more general classes of dynamical systems such as controllable Linear Time-Varying systems that cannot currently be solved using traditional neural SB approaches. We showcase the potential of this approach in low-to-moderate dimensional problems such as image-to-image translation in the latent space of an autoencoder, and various other examples. We also benchmark our approach on an Entropic Optimal Transport (EOT) problem and show that it outperforms state-of-the-art methods in cases where the boundary distributions are mixture models while requiring virtually no training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge