Pai Zheng
Logical Reasoning with Relation Network for Inductive Knowledge Graph Completion
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:Inductive knowledge graph completion (KGC) aims to infer the missing relation for a set of newly-coming entities that never appeared in the training set. Such a setting is more in line with reality, as real-world KGs are constantly evolving and introducing new knowledge. Recent studies have shown promising results using message passing over subgraphs to embed newly-coming entities for inductive KGC. However, the inductive capability of these methods is usually limited by two key issues. (i) KGC always suffers from data sparsity, and the situation is even exacerbated in inductive KGC where new entities often have few or no connections to the original KG. (ii) Cold-start problem. It is over coarse-grained for accurate KG reasoning to generate representations for new entities by gathering the local information from few neighbors. To this end, we propose a novel iNfOmax RelAtion Network, namely NORAN, for inductive KG completion. It aims to mine latent relation patterns for inductive KG completion. Specifically, by centering on relations, NORAN provides a hyper view towards KG modeling, where the correlations between relations can be naturally captured as entity-independent logical evidence to conduct inductive KGC. Extensive experiment results on five benchmarks show that our framework substantially outperforms the state-of-the-art KGC methods.
Revolutionizing Packaging: A Robotic Bagging Pipeline with Constraint-aware Structure-of-Interest Planning
Mar 15, 2024



Abstract:Bagging operations, common in packaging and assisted living applications, are challenging due to a bag's complex deformable properties. To address this, we develop a robotic system for automated bagging tasks using an adaptive structure-of-interest (SOI) manipulation approach. Our method relies on real-time visual feedback to dynamically adjust manipulation without requiring prior knowledge of bag materials or dynamics. We present a robust pipeline featuring state estimation for SOIs using Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM), SOI generation via optimization-based bagging techniques, SOI motion planning with Constrained Bidirectional Rapidly-exploring Random Trees (CBiRRT), and dual-arm manipulation coordinated by Model Predictive Control (MPC). Experiments demonstrate the system's ability to achieve precise, stable bagging of various objects using adaptive coordination of the manipulators. The proposed framework advances the capability of dual-arm robots to perform more sophisticated automation of common tasks involving interactions with deformable objects.
Modality-Aware Integration with Large Language Models for Knowledge-based Visual Question Answering
Feb 20, 2024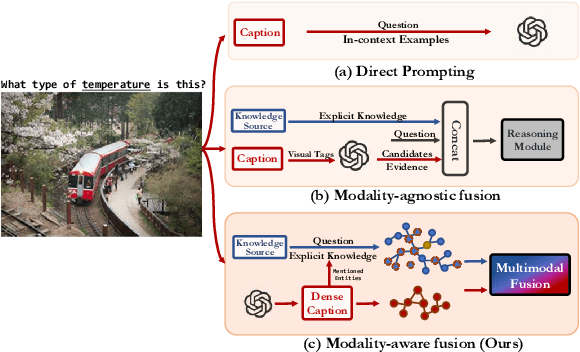
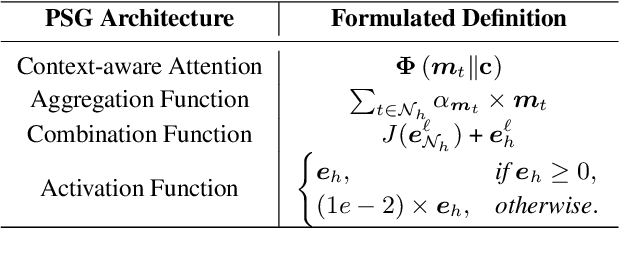
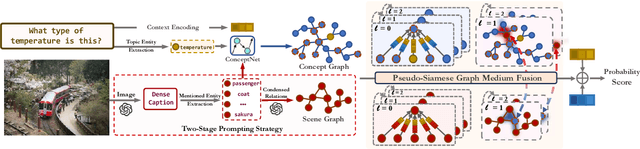
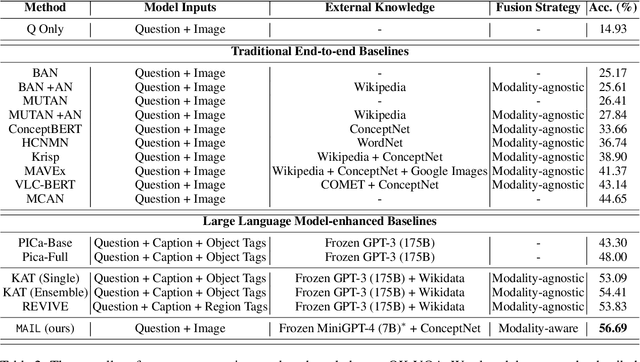
Abstract:Knowledge-based visual question answering (KVQA) has been extensively studied to answer visual questions with external knowledge, e.g., knowledge graphs (KGs). While several attempts have been proposed to leverage large language models (LLMs) as an implicit knowledge source, it remains challenging since LLMs may generate hallucinations. Moreover, multiple knowledge sources, e.g., images, KGs and LLMs, cannot be readily aligned for complex scenarios. To tackle these, we present a novel modality-aware integration with LLMs for KVQA (MAIL). It carefully leverages multimodal knowledge for both image understanding and knowledge reasoning. Specifically, (i) we propose a two-stage prompting strategy with LLMs to densely embody the image into a scene graph with detailed visual features; (ii) We construct a coupled concept graph by linking the mentioned entities with external facts. (iii) A tailored pseudo-siamese graph medium fusion is designed for sufficient multimodal fusion. We utilize the shared mentioned entities in two graphs as mediums to bridge a tight inter-modal exchange, while maximally preserving insightful intra-modal learning by constraining the fusion within mediums. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets show the superiority of MAIL with 24x less resources.
Bimanual Deformable Bag Manipulation Using a Structure-of-Interest Based Latent Dynamics Model
Jan 21, 2024Abstract:The manipulation of deformable objects by robotic systems presents a significant challenge due to their complex and infinite-dimensional configuration spaces. This paper introduces a novel approach to Deformable Object Manipulation (DOM) by emphasizing the identification and manipulation of Structures of Interest (SOIs) in deformable fabric bags. We propose a bimanual manipulation framework that leverages a Graph Neural Network (GNN)-based latent dynamics model to succinctly represent and predict the behavior of these SOIs. Our approach involves constructing a graph representation from partial point cloud data of the object and learning the latent dynamics model that effectively captures the essential deformations of the fabric bag within a reduced computational space. By integrating this latent dynamics model with Model Predictive Control (MPC), we empower robotic manipulators to perform precise and stable manipulation tasks focused on the SOIs. We have validated our framework through various empirical experiments demonstrating its efficacy in bimanual manipulation of fabric bags. Our contributions not only address the complexities inherent in DOM but also provide new perspectives and methodologies for enhancing robotic interactions with deformable objects by concentrating on their critical structural elements. Experimental videos can be obtained from https://sites.google.com/view/bagbot.
PSO-Based Optimal Coverage Path Planning for Surface Defect Inspection of 3C Components with a Robotic Line Scanner
Jul 10, 2023Abstract:The automatic inspection of surface defects is an important task for quality control in the computers, communications, and consumer electronics (3C) industry. Conventional devices for defect inspection (viz. line-scan sensors) have a limited field of view, thus, a robot-aided defect inspection system needs to scan the object from multiple viewpoints. Optimally selecting the robot's viewpoints and planning a path is regarded as coverage path planning (CPP), a problem that enables inspecting the object's complete surface while reducing the scanning time and avoiding misdetection of defects. However, the development of CPP strategies for robotic line scanners has not been sufficiently studied by researchers. To fill this gap in the literature, in this paper, we present a new approach for robotic line scanners to detect surface defects of 3C free-form objects automatically. Our proposed solution consists of generating a local path by a new hybrid region segmentation method and an adaptive planning algorithm to ensure the coverage of the complete object surface. An optimization method for the global path sequence is developed to maximize the scanning efficiency. To verify our proposed methodology, we conduct detailed simulation-based and experimental studies on various free-form workpieces, and compare its performance with a state-of-the-art solution. The reported results demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of our approach.
Performance evaluation of a foot-controlled human-robot interface
Mar 08, 2019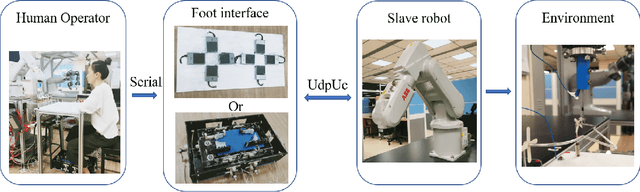
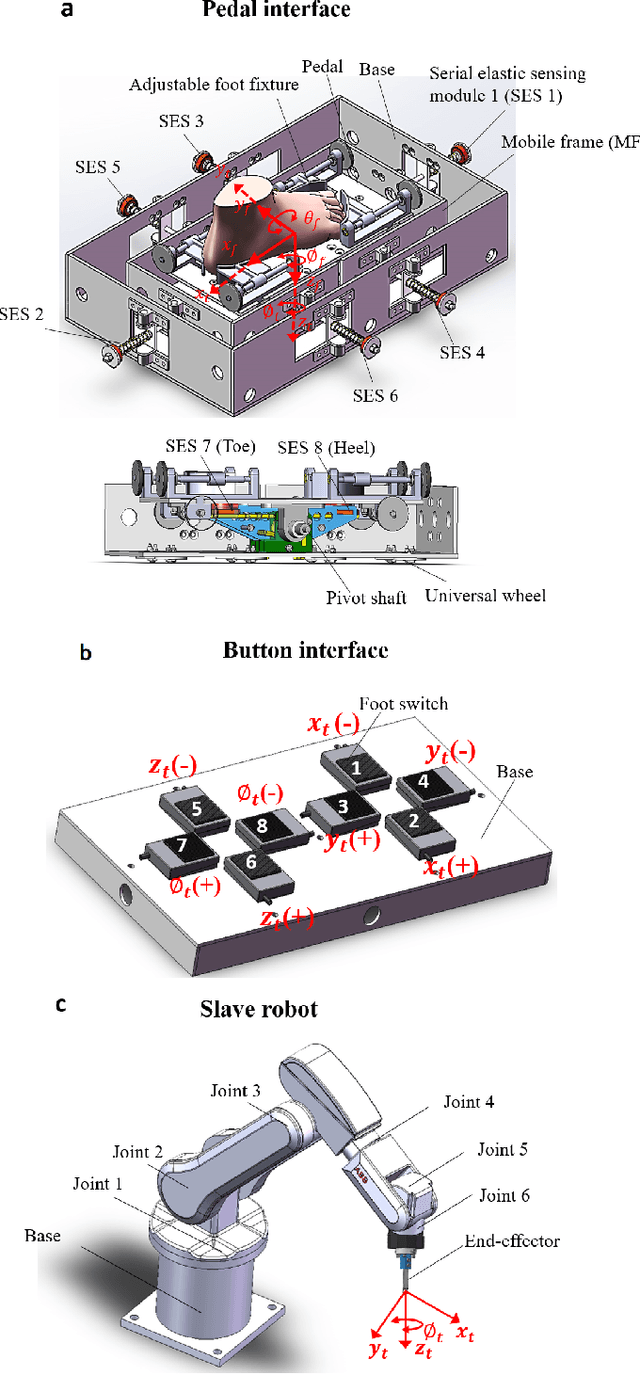
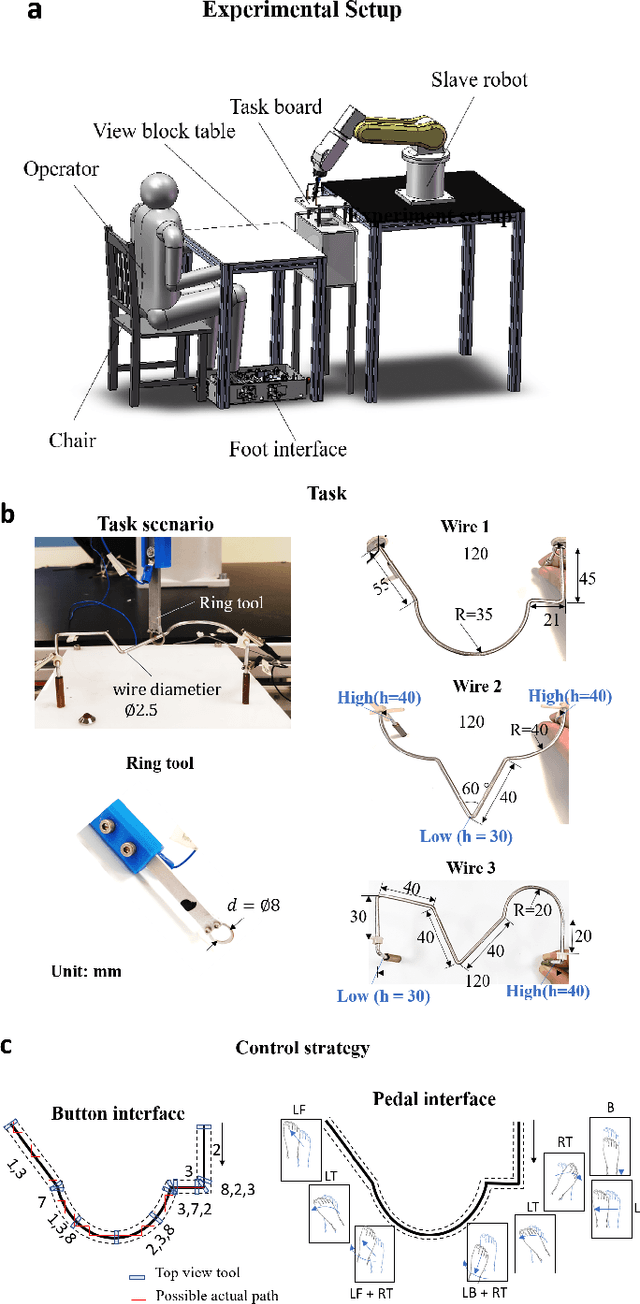
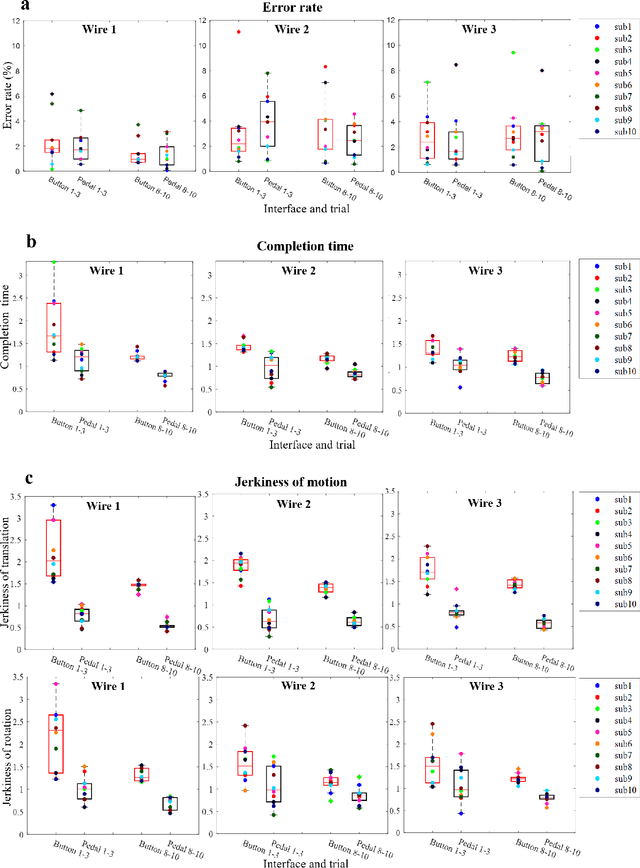
Abstract:Robotic minimally invasive interventions typically require using more than two instruments. We thus developed a foot pedal interface which allows the user to control a robotic arm (simultaneously to working with the hands) with four degrees of freedom in continuous directions and speeds. This paper evaluates and compares the performances of ten naive operators in using this new pedal interface and a traditional button interface in completing tasks. These tasks are geometrically complex path-following tasks similar to those in laparoscopic training, and the traditional button interface allows axis-by-axis control with constant speeds. Precision, time, and smoothness of the subjects' control movements for these tasks are analysed. The results demonstrate that the pedal interface can be used to control a robot for complex motion tasks. The subjects kept the average error rate at a low level of around 2.6% with both interfaces, but the pedal interface resulted in about 30% faster operation speed and 60% smoother movement, which indicates improved efficiency and user experience as compared with the button interface. The results of a questionnaire show that the operators found that controlling the robot with the pedal interface was more intuitive, comfortable, and less tiring than using the button interface.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge