Nikolas Martelaro
Facilitating Longitudinal Interaction Studies of AI Systems
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:UIST researchers develop tools to address user challenges. However, user interactions with AI evolve over time through learning, adaptation, and repurposing, making one time evaluations insufficient. Capturing these dynamics requires longer-term studies, but challenges in deployment, evaluation design, and data collection have made such longitudinal research difficult to implement. Our workshop aims to tackle these challenges and prepare researchers with practical strategies for longitudinal studies. The workshop includes a keynote, panel discussions, and interactive breakout groups for discussion and hands-on protocol design and tool prototyping sessions. We seek to foster a community around longitudinal system research and promote it as a more embraced method for designing, building, and evaluating UIST tools.
Exploring the Potential of Metacognitive Support Agents for Human-AI Co-Creation
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Despite the potential of generative AI (GenAI) design tools to enhance design processes, professionals often struggle to integrate AI into their workflows. Fundamental cognitive challenges include the need to specify all design criteria as distinct parameters upfront (intent formulation) and designers' reduced cognitive involvement in the design process due to cognitive offloading, which can lead to insufficient problem exploration, underspecification, and limited ability to evaluate outcomes. Motivated by these challenges, we envision novel metacognitive support agents that assist designers in working more reflectively with GenAI. To explore this vision, we conducted exploratory prototyping through a Wizard of Oz elicitation study with 20 mechanical designers probing multiple metacognitive support strategies. We found that agent-supported users created more feasible designs than non-supported users, with differing impacts between support strategies. Based on these findings, we discuss opportunities and tradeoffs of metacognitive support agents and considerations for future AI-based design tools.
Intent Tagging: Exploring Micro-Prompting Interactions for Supporting Granular Human-GenAI Co-Creation Workflows
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Despite Generative AI (GenAI) systems' potential for enhancing content creation, users often struggle to effectively integrate GenAI into their creative workflows. Core challenges include misalignment of AI-generated content with user intentions (intent elicitation and alignment), user uncertainty around how to best communicate their intents to the AI system (prompt formulation), and insufficient flexibility of AI systems to support diverse creative workflows (workflow flexibility). Motivated by these challenges, we created IntentTagger: a system for slide creation based on the notion of Intent Tags - small, atomic conceptual units that encapsulate user intent - for exploring granular and non-linear micro-prompting interactions for Human-GenAI co-creation workflows. Our user study with 12 participants provides insights into the value of flexibly expressing intent across varying levels of ambiguity, meta-intent elicitation, and the benefits and challenges of intent tag-driven workflows. We conclude by discussing the broader implications of our findings and design considerations for GenAI-supported content creation workflows.
Inkspire: Supporting Design Exploration with Generative AI through Analogical Sketching
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:With recent advancements in the capabilities of Text-to-Image (T2I) AI models, product designers have begun experimenting with them in their work. However, T2I models struggle to interpret abstract language and the current user experience of T2I tools can induce design fixation rather than a more iterative, exploratory process. To address these challenges, we developed Inkspire, a sketch-driven tool that supports designers in prototyping product design concepts with analogical inspirations and a complete sketch-to-design-to-sketch feedback loop. To inform the design of Inkspire, we conducted an exchange session with designers and distilled design goals for improving T2I interactions. In a within-subjects study comparing Inkspire to ControlNet, we found that Inkspire supported designers with more inspiration and exploration of design ideas, and improved aspects of the co-creative process by allowing designers to effectively grasp the current state of the AI to guide it towards novel design intentions.
"What's important here?": Opportunities and Challenges of Using LLMs in Retrieving Information from Web Interfaces
Dec 11, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) that have been trained on a corpus that includes large amount of code exhibit a remarkable ability to understand HTML code. As web interfaces are primarily constructed using HTML, we design an in-depth study to see how LLMs can be used to retrieve and locate important elements for a user given query (i.e. task description) in a web interface. In contrast with prior works, which primarily focused on autonomous web navigation, we decompose the problem as an even atomic operation - Can LLMs identify the important information in the web page for a user given query? This decomposition enables us to scrutinize the current capabilities of LLMs and uncover the opportunities and challenges they present. Our empirical experiments show that while LLMs exhibit a reasonable level of performance in retrieving important UI elements, there is still a substantial room for improvement. We hope our investigation will inspire follow-up works in overcoming the current challenges in this domain.
What Do I Hear? Generating Sounds for Visuals with ChatGPT
Nov 09, 2023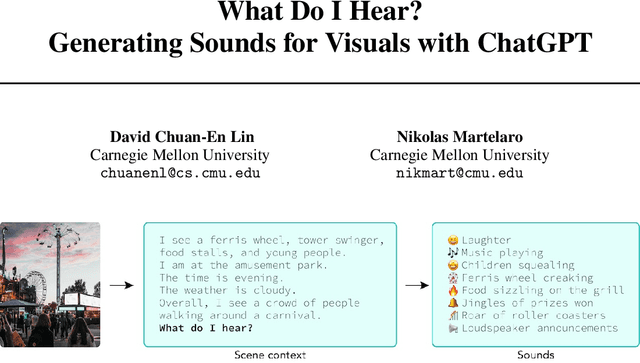
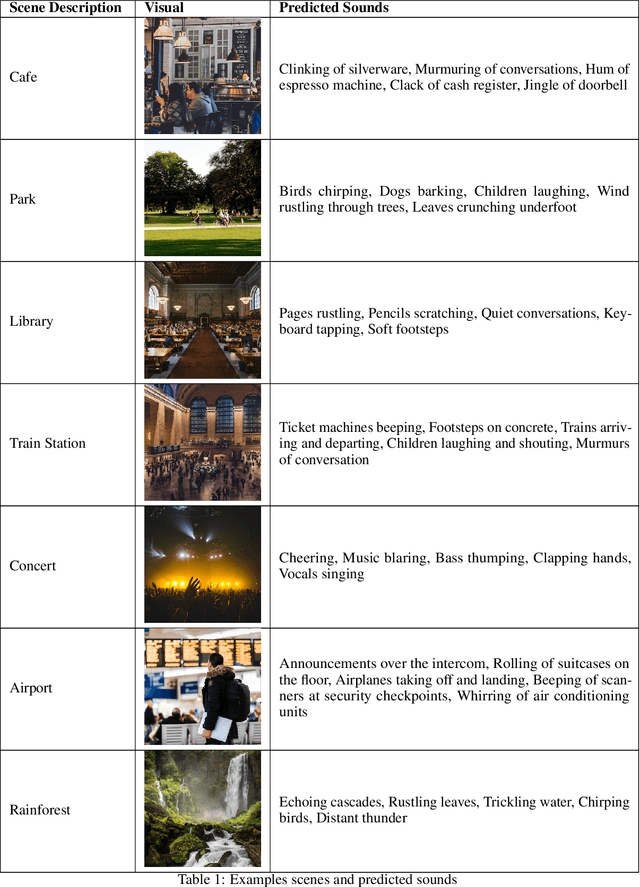
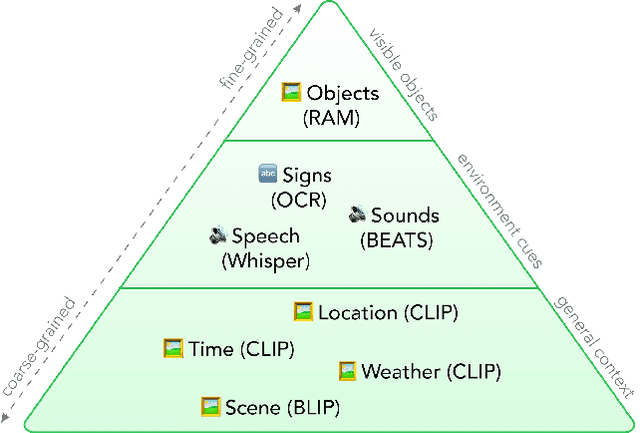

Abstract:This short paper introduces a workflow for generating realistic soundscapes for visual media. In contrast to prior work, which primarily focus on matching sounds for on-screen visuals, our approach extends to suggesting sounds that may not be immediately visible but are essential to crafting a convincing and immersive auditory environment. Our key insight is leveraging the reasoning capabilities of language models, such as ChatGPT. In this paper, we describe our workflow, which includes creating a scene context, brainstorming sounds, and generating the sounds.
Jigsaw: Supporting Designers in Prototyping Multimodal Applications by Assembling AI Foundation Models
Oct 12, 2023



Abstract:Recent advancements in AI foundation models have made it possible for them to be utilized off-the-shelf for creative tasks, including ideating design concepts or generating visual prototypes. However, integrating these models into the creative process can be challenging as they often exist as standalone applications tailored to specific tasks. To address this challenge, we introduce Jigsaw, a prototype system that employs puzzle pieces as metaphors to represent foundation models. Jigsaw allows designers to combine different foundation model capabilities across various modalities by assembling compatible puzzle pieces. To inform the design of Jigsaw, we interviewed ten designers and distilled design goals. In a user study, we showed that Jigsaw enhanced designers' understanding of available foundation model capabilities, provided guidance on combining capabilities across different modalities and tasks, and served as a canvas to support design exploration, prototyping, and documentation.
The AI Incident Database as an Educational Tool to Raise Awareness of AI Harms: A Classroom Exploration of Efficacy, Limitations, & Future Improvements
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:Prior work has established the importance of integrating AI ethics topics into computer and data sciences curricula. We provide evidence suggesting that one of the critical objectives of AI Ethics education must be to raise awareness of AI harms. While there are various sources to learn about such harms, The AI Incident Database (AIID) is one of the few attempts at offering a relatively comprehensive database indexing prior instances of harms or near harms stemming from the deployment of AI technologies in the real world. This study assesses the effectiveness of AIID as an educational tool to raise awareness regarding the prevalence and severity of AI harms in socially high-stakes domains. We present findings obtained through a classroom study conducted at an R1 institution as part of a course focused on the societal and ethical considerations around AI and ML. Our qualitative findings characterize students' initial perceptions of core topics in AI ethics and their desire to close the educational gap between their technical skills and their ability to think systematically about ethical and societal aspects of their work. We find that interacting with the database helps students better understand the magnitude and severity of AI harms and instills in them a sense of urgency around (a) designing functional and safe AI and (b) strengthening governance and accountability mechanisms. Finally, we compile students' feedback about the tool and our class activity into actionable recommendations for the database development team and the broader community to improve awareness of AI harms in AI ethics education.
Exploring Challenges and Opportunities to Support Designers in Learning to Co-create with AI-based Manufacturing Design Tools
Mar 01, 2023



Abstract:AI-based design tools are proliferating in professional software to assist engineering and industrial designers in complex manufacturing and design tasks. These tools take on more agentic roles than traditional computer-aided design tools and are often portrayed as "co-creators." Yet, working effectively with such systems requires different skills than working with complex CAD tools alone. To date, we know little about how engineering designers learn to work with AI-based design tools. In this study, we observed trained designers as they learned to work with two AI-based tools on a realistic design task. We find that designers face many challenges in learning to effectively co-create with current systems, including challenges in understanding and adjusting AI outputs and in communicating their design goals. Based on our findings, we highlight several design opportunities to better support designer-AI co-creation.
VideoMap: Video Editing in Latent Space
Nov 22, 2022



Abstract:Video has become a dominant form of media. However, video editing interfaces have remained largely unchanged over the past two decades. Such interfaces typically consist of a grid-like asset management panel and a linear editing timeline. When working with a large number of video clips, it can be difficult to sort through them all and identify patterns within (e.g. opportunities for smooth transitions and storytelling). In this work, we imagine a new paradigm for video editing by mapping videos into a 2D latent space and building a proof-of-concept interface.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge