Nana Fan
The 2nd Anti-UAV Workshop & Challenge: Methods and Results
Aug 25, 2021
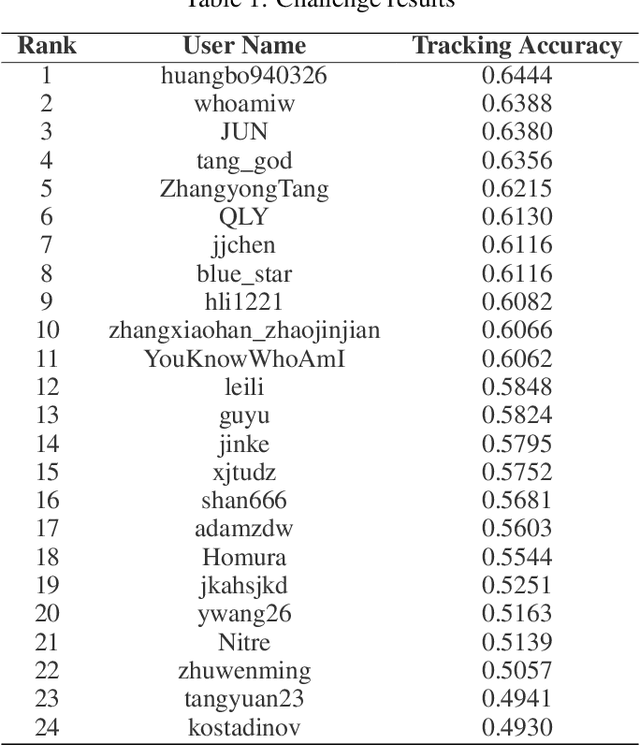
Abstract:The 2nd Anti-UAV Workshop \& Challenge aims to encourage research in developing novel and accurate methods for multi-scale object tracking. The Anti-UAV dataset used for the Anti-UAV Challenge has been publicly released. There are two subsets in the dataset, $i.e.$, the test-dev subset and test-challenge subset. Both subsets consist of 140 thermal infrared video sequences, spanning multiple occurrences of multi-scale UAVs. Around 24 participating teams from the globe competed in the 2nd Anti-UAV Challenge. In this paper, we provide a brief summary of the 2nd Anti-UAV Workshop \& Challenge including brief introductions to the top three methods.The submission leaderboard will be reopened for researchers that are interested in the Anti-UAV challenge. The benchmark dataset and other information can be found at: https://anti-uav.github.io/.
TCDesc: Learning Topology Consistent Descriptors for Image Matching
Sep 13, 2020



Abstract:The constraint of neighborhood consistency or local consistency is widely used for robust image matching. In this paper, we focus on learning neighborhood topology consistent descriptors (TCDesc), while former works of learning descriptors, such as HardNet and DSM, only consider point-to-point Euclidean distance among descriptors and totally neglect neighborhood information of descriptors. To learn topology consistent descriptors, first we propose the linear combination weights to depict the topological relationship between center descriptor and its kNN descriptors, where the difference between center descriptor and the linear combination of its kNN descriptors is minimized. Then we propose the global mapping function which maps the local linear combination weights to the global topology vector and define the topology distance of matching descriptors as l1 distance between their topology vectors. Last we employ adaptive weighting strategy to jointly minimize topology distance and Euclidean distance, which automatically adjust the weight or attention of two distances in triplet loss. Our method has the following two advantages: (1) We are the first to consider neighborhood information of descriptors, while former works mainly focus on neighborhood consistency of feature points; (2) Our method can be applied in any former work of learning descriptors by triplet loss. Experimental results verify the generalization of our method: We can improve the performances of both HardNet and DSM on several benchmarks.
LSOTB-TIR:A Large-Scale High-Diversity Thermal Infrared Object Tracking Benchmark
Aug 03, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we present a Large-Scale and high-diversity general Thermal InfraRed (TIR) Object Tracking Benchmark, called LSOTBTIR, which consists of an evaluation dataset and a training dataset with a total of 1,400 TIR sequences and more than 600K frames. We annotate the bounding box of objects in every frame of all sequences and generate over 730K bounding boxes in total. To the best of our knowledge, LSOTB-TIR is the largest and most diverse TIR object tracking benchmark to date. To evaluate a tracker on different attributes, we define 4 scenario attributes and 12 challenge attributes in the evaluation dataset. By releasing LSOTB-TIR, we encourage the community to develop deep learning based TIR trackers and evaluate them fairly and comprehensively. We evaluate and analyze more than 30 trackers on LSOTB-TIR to provide a series of baselines, and the results show that deep trackers achieve promising performance. Furthermore, we re-train several representative deep trackers on LSOTB-TIR, and their results demonstrate that the proposed training dataset significantly improves the performance of deep TIR trackers. Codes and dataset are available at https://github.com/QiaoLiuHit/LSOTB-TIR.
Multi-Task Driven Feature Models for Thermal Infrared Tracking
Nov 26, 2019



Abstract:Existing deep Thermal InfraRed (TIR) trackers usually use the feature models of RGB trackers for representation. However, these feature models learned on RGB images are neither effective in representing TIR objects nor taking fine-grained TIR information into consideration. To this end, we develop a multi-task framework to learn the TIR-specific discriminative features and fine-grained correlation features for TIR tracking. Specifically, we first use an auxiliary classification network to guide the generation of TIR-specific discriminative features for distinguishing the TIR objects belonging to different classes. Second, we design a fine-grained aware module to capture more subtle information for distinguishing the TIR objects belonging to the same class. These two kinds of features complement each other and recognize TIR objects in the levels of inter-class and intra-class respectively. These two feature models are learned using a multi-task matching framework and are jointly optimized on the TIR tracking task. In addition, we develop a large-scale TIR training dataset to train the network for adapting the model to the TIR domain. Extensive experimental results on three benchmarks show that the proposed algorithm achieves a relative gain of 10% over the baseline and performs favorably against the state-of-the-art methods. Codes and the proposed TIR dataset are available at {https://github.com/QiaoLiuHit/MMNet}.
Learning Deep Multi-Level Similarity for Thermal Infrared Object Tracking
Jun 09, 2019



Abstract:Existing deep Thermal InfraRed (TIR) trackers only use semantic features to describe the TIR object, which lack the sufficient discriminative capacity for handling distractors. This becomes worse when the feature extraction network is only trained on RGB images.To address this issue, we propose a multi-level similarity model under a Siamese framework for robust TIR object tracking. Specifically, we compute different pattern similarities on two convolutional layers using the proposed multi-level similarity network. One of them focuses on the global semantic similarity and the other computes the local structural similarity of the TIR object. These two similarities complement each other and hence enhance the discriminative capacity of the network for handling distractors. In addition, we design a simple while effective relative entropy based ensemble subnetwork to integrate the semantic and structural similarities. This subnetwork can adaptive learn the weights of the semantic and structural similarities at the training stage. To further enhance the discriminative capacity of the tracker, we construct the first large scale TIR video sequence dataset for training the proposed model. The proposed TIR dataset not only benefits the training for TIR tracking but also can be applied to numerous TIR vision tasks. Extensive experimental results on the VOT-TIR2015 and VOT-TIR2017 benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed algorithm performs favorably against the state-of-the-art methods.
Region-filtering Correlation Tracking
Mar 23, 2018



Abstract:Recently, correlation filters have demonstrated the excellent performance in visual tracking. However, the base training sample region is larger than the object region,including the Interference Region(IR). The IRs in training samples from cyclic shifts of the base training sample severely degrade the quality of a tracking model. In this paper, we propose the novel Region-filtering Correlation Tracking (RFCT) to address this problem. We immediately filter training samples by introducing a spatial map into the standard CF formulation. Compared with existing correlation filter trackers, our proposed tracker has the following advantages: (1) The correlation filter can be learned on a larger search region without the interference of the IR by a spatial map. (2) Due to processing training samples by a spatial map, it is more general way to control background information and target information in training samples. The values of the spatial map are not restricted, then a better spatial map can be explored. (3) The weight proportions of accurate filters are increased to alleviate model corruption. Experiments are performed on two benchmark datasets: OTB-2013 and OTB-2015. Quantitative evaluations on these benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed RFCT algorithm performs favorably against several state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge