Moin Nadeem
MosaicBERT: A Bidirectional Encoder Optimized for Fast Pretraining
Jan 16, 2024



Abstract:Although BERT-style encoder models are heavily used in NLP research, many researchers do not pretrain their own BERTs from scratch due to the high cost of training. In the past half-decade since BERT first rose to prominence, many advances have been made with other transformer architectures and training configurations that have yet to be systematically incorporated into BERT. Here, we introduce MosaicBERT, a BERT-style encoder architecture and training recipe that is empirically optimized for fast pretraining. This efficient architecture incorporates FlashAttention, Attention with Linear Biases (ALiBi), Gated Linear Units (GLU), a module to dynamically remove padded tokens, and low precision LayerNorm into the classic transformer encoder block. The training recipe includes a 30% masking ratio for the Masked Language Modeling (MLM) objective, bfloat16 precision, and vocabulary size optimized for GPU throughput, in addition to best-practices from RoBERTa and other encoder models. When pretrained from scratch on the C4 dataset, this base model achieves a downstream average GLUE (dev) score of 79.6 in 1.13 hours on 8 A100 80 GB GPUs at a cost of roughly $20. We plot extensive accuracy vs. pretraining speed Pareto curves and show that MosaicBERT base and large are consistently Pareto optimal when compared to a competitive BERT base and large. This empirical speed up in pretraining enables researchers and engineers to pretrain custom BERT-style models at low cost instead of finetune on existing generic models. We open source our model weights and code.
* 10 pages, 4 figures in main text. 25 pages total
The GEM Benchmark: Natural Language Generation, its Evaluation and Metrics
Feb 03, 2021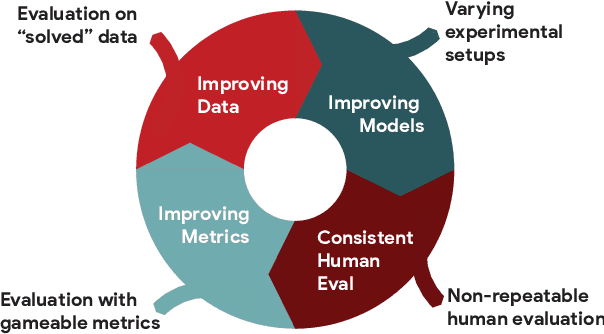
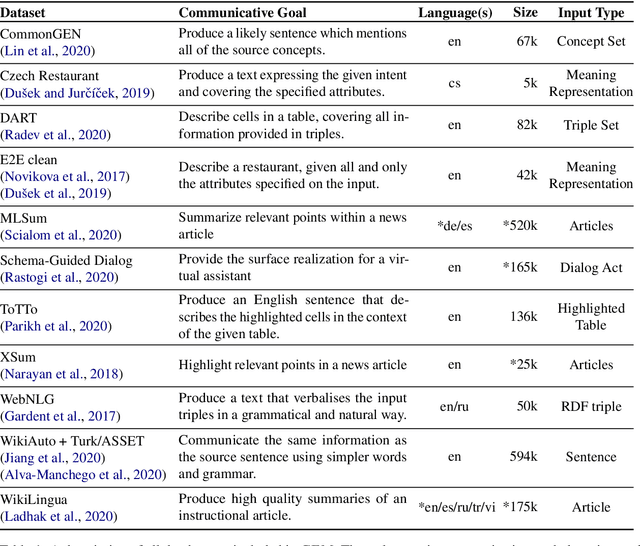
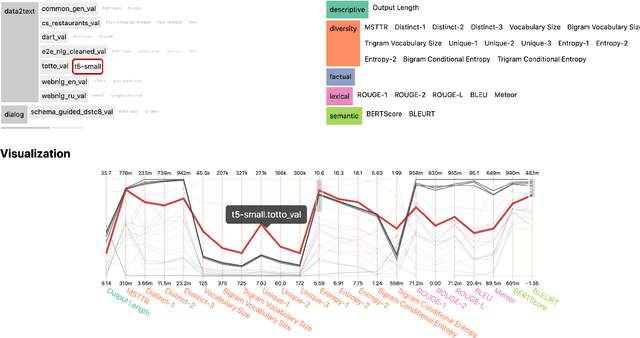
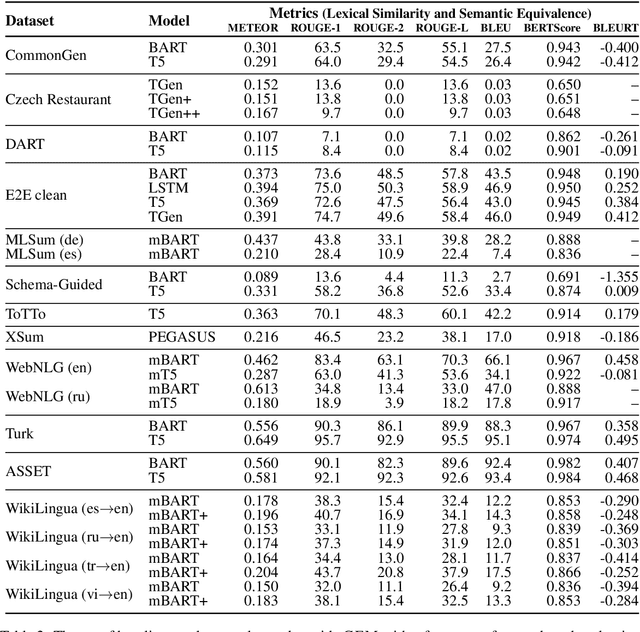
Abstract:We introduce GEM, a living benchmark for natural language Generation (NLG), its Evaluation, and Metrics. Measuring progress in NLG relies on a constantly evolving ecosystem of automated metrics, datasets, and human evaluation standards. However, due to this moving target, new models often still evaluate on divergent anglo-centric corpora with well-established, but flawed, metrics. This disconnect makes it challenging to identify the limitations of current models and opportunities for progress. Addressing this limitation, GEM provides an environment in which models can easily be applied to a wide set of corpora and evaluation strategies can be tested. Regular updates to the benchmark will help NLG research become more multilingual and evolve the challenge alongside models. This paper serves as the description of the initial release for which we are organizing a shared task at our ACL 2021 Workshop and to which we invite the entire NLG community to participate.
A Systematic Characterization of Sampling Algorithms for Open-ended Language Generation
Sep 15, 2020



Abstract:This work studies the widely adopted ancestral sampling algorithms for auto-regressive language models, which is not widely studied in the literature. We use the quality-diversity (Q-D) trade-off to investigate three popular sampling algorithms (top-k, nucleus and tempered sampling). We focus on the task of open-ended language generation. We first show that the existing sampling algorithms have similar performance. After carefully inspecting the transformations defined by different sampling algorithms, we identify three key properties that are shared among them: entropy reduction, order preservation, and slope preservation. To validate the importance of the identified properties, we design two sets of new sampling algorithms: one set in which each algorithm satisfies all three properties, and one set in which each algorithm violates at least one of the properties. We compare their performance with existing sampling algorithms, and find that violating the identified properties could lead to drastic performance degradation, as measured by the Q-D trade-off. On the other hand, we find that the set of sampling algorithms that satisfies these properties performs on par with the existing sampling algorithms. Our data and code are available at https://github.com/moinnadeem/characterizing-sampling-algorithms
StereoSet: Measuring stereotypical bias in pretrained language models
Apr 20, 2020



Abstract:A stereotype is an over-generalized belief about a particular group of people, e.g., Asians are good at math or Asians are bad drivers. Such beliefs (biases) are known to hurt target groups. Since pretrained language models are trained on large real world data, they are known to capture stereotypical biases. In order to assess the adverse effects of these models, it is important to quantify the bias captured in them. Existing literature on quantifying bias evaluates pretrained language models on a small set of artificially constructed bias-assessing sentences. We present StereoSet, a large-scale natural dataset in English to measure stereotypical biases in four domains: gender, profession, race, and religion. We evaluate popular models like BERT, GPT-2, RoBERTa, and XLNet on our dataset and show that these models exhibit strong stereotypical biases. We also present a leaderboard with a hidden test set to track the bias of future language models at https://stereoset.mit.edu
FAKTA: An Automatic End-to-End Fact Checking System
Jun 07, 2019



Abstract:We present FAKTA which is a unified framework that integrates various components of a fact checking process: document retrieval from media sources with various types of reliability, stance detection of documents with respect to given claims, evidence extraction, and linguistic analysis. FAKTA predicts the factuality of given claims and provides evidence at the document and sentence level to explain its predictions
Neural Educational Recommendation Engine (NERE)
Sep 21, 2018



Abstract:Quizlet is the most popular online learning tool in the United States, and is used by over 2/3 of high school students, and 1/2 of college students. With more than 95% of Quizlet users reporting improved grades as a result, the platform has become the de-facto tool used in millions of classrooms. In this paper, we explore the task of recommending suitable content for a student to study, given their prior interests, as well as what their peers are studying. We propose a novel approach, i.e. Neural Educational Recommendation Engine (NERE), to recommend educational content by leveraging student behaviors rather than ratings. We have found that this approach better captures social factors that are more aligned with learning. NERE is based on a recurrent neural network that includes collaborative and content-based approaches for recommendation, and takes into account any particular student's speed, mastery, and experience to recommend the appropriate task. We train NERE by jointly learning the user embeddings and content embeddings, and attempt to predict the content embedding for the final timestamp. We also develop a confidence estimator for our neural network, which is a crucial requirement for productionizing this model. We apply NERE to Quizlet's proprietary dataset, and present our results. We achieved an R^2 score of 0.81 in the content embedding space, and a recall score of 54% on our 100 nearest neighbors. This vastly exceeds the recall@100 score of 12% that a standard matrix-factorization approach provides. We conclude with a discussion on how NERE will be deployed, and position our work as one of the first educational recommender systems for the K-12 space.
Identifying Depression on Twitter
Jul 25, 2016



Abstract:Social media has recently emerged as a premier method to disseminate information online. Through these online networks, tens of millions of individuals communicate their thoughts, personal experiences, and social ideals. We therefore explore the potential of social media to predict, even prior to onset, Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) in online personas. We employ a crowdsourced method to compile a list of Twitter users who profess to being diagnosed with depression. Using up to a year of prior social media postings, we utilize a Bag of Words approach to quantify each tweet. Lastly, we leverage several statistical classifiers to provide estimates to the risk of depression. Our work posits a new methodology for constructing our classifier by treating social as a text-classification problem, rather than a behavioral one on social media platforms. By using a corpus of 2.5M tweets, we achieved an 81% accuracy rate in classification, with a precision score of .86. We believe that this method may be helpful in developing tools that estimate the risk of an individual being depressed, can be employed by physicians, concerned individuals, and healthcare agencies to aid in diagnosis, even possibly enabling those suffering from depression to be more proactive about recovering from their mental health.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge