Miriam Bellver
Human Body Measurement Estimation with Adversarial Augmentation
Oct 11, 2022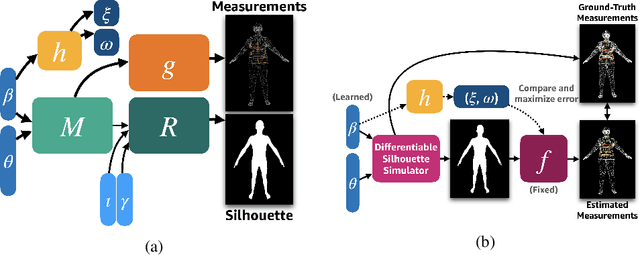
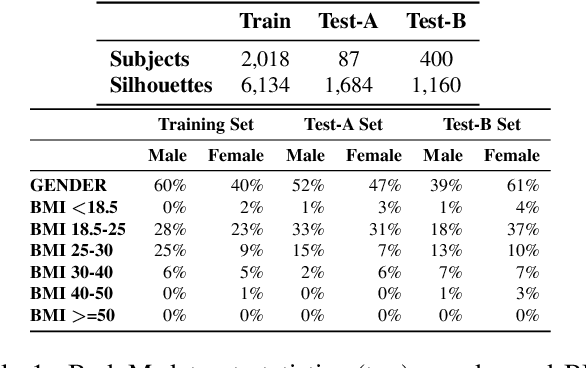
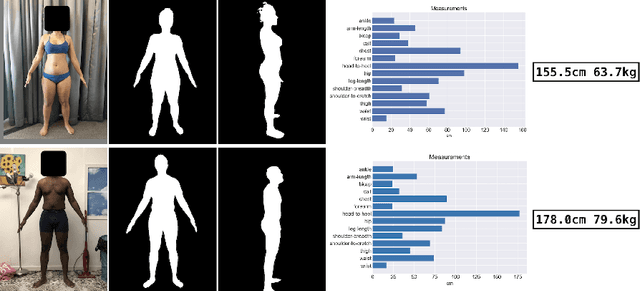
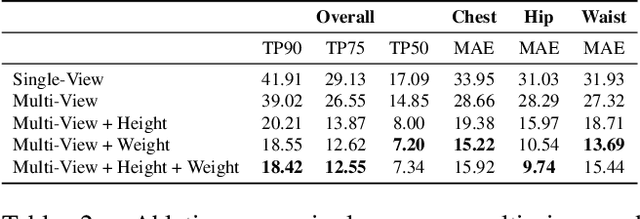
Abstract:We present a Body Measurement network (BMnet) for estimating 3D anthropomorphic measurements of the human body shape from silhouette images. Training of BMnet is performed on data from real human subjects, and augmented with a novel adversarial body simulator (ABS) that finds and synthesizes challenging body shapes. ABS is based on the skinned multiperson linear (SMPL) body model, and aims to maximize BMnet measurement prediction error with respect to latent SMPL shape parameters. ABS is fully differentiable with respect to these parameters, and trained end-to-end via backpropagation with BMnet in the loop. Experiments show that ABS effectively discovers adversarial examples, such as bodies with extreme body mass indices (BMI), consistent with the rarity of extreme-BMI bodies in BMnet's training set. Thus ABS is able to reveal gaps in training data and potential failures in predicting under-represented body shapes. Results show that training BMnet with ABS improves measurement prediction accuracy on real bodies by up to 10%, when compared to no augmentation or random body shape sampling. Furthermore, our method significantly outperforms SOTA measurement estimation methods by as much as 3x. Finally, we release BodyM, the first challenging, large-scale dataset of photo silhouettes and body measurements of real human subjects, to further promote research in this area. Project website: https://adversarialbodysim.github.io
SynthRef: Generation of Synthetic Referring Expressions for Object Segmentation
Jun 09, 2021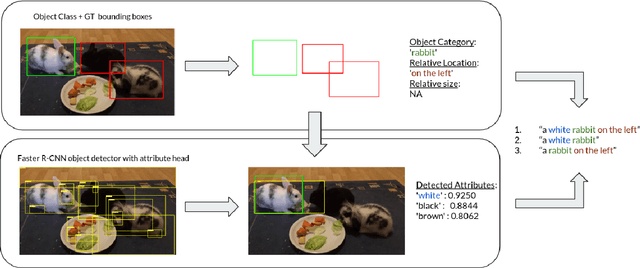



Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning have brought significant progress in visual grounding tasks such as language-guided video object segmentation. However, collecting large datasets for these tasks is expensive in terms of annotation time, which represents a bottleneck. To this end, we propose a novel method, namely SynthRef, for generating synthetic referring expressions for target objects in an image (or video frame), and we also present and disseminate the first large-scale dataset with synthetic referring expressions for video object segmentation. Our experiments demonstrate that by training with our synthetic referring expressions one can improve the ability of a model to generalize across different datasets, without any additional annotation cost. Moreover, our formulation allows its application to any object detection or segmentation dataset.
RefVOS: A Closer Look at Referring Expressions for Video Object Segmentation
Oct 01, 2020

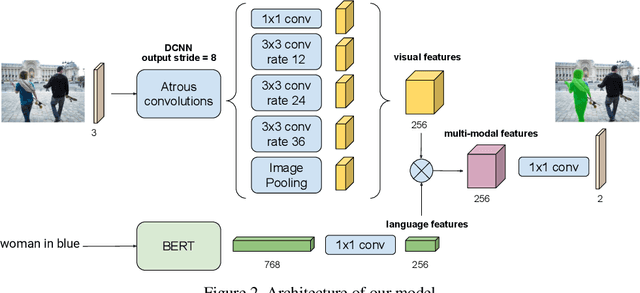
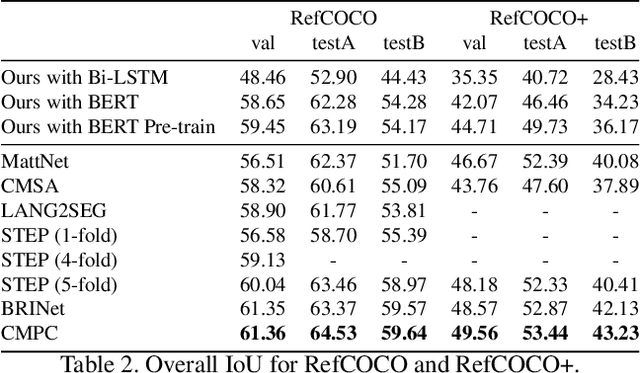
Abstract:The task of video object segmentation with referring expressions (language-guided VOS) is to, given a linguistic phrase and a video, generate binary masks for the object to which the phrase refers. Our work argues that existing benchmarks used for this task are mainly composed of trivial cases, in which referents can be identified with simple phrases. Our analysis relies on a new categorization of the phrases in the DAVIS-2017 and Actor-Action datasets into trivial and non-trivial REs, with the non-trivial REs annotated with seven RE semantic categories. We leverage this data to analyze the results of RefVOS, a novel neural network that obtains competitive results for the task of language-guided image segmentation and state of the art results for language-guided VOS. Our study indicates that the major challenges for the task are related to understanding motion and static actions.
Mask-guided sample selection for Semi-Supervised Instance Segmentation
Aug 25, 2020



Abstract:Image segmentation methods are usually trained with pixel-level annotations, which require significant human effort to collect. The most common solution to address this constraint is to implement weakly-supervised pipelines trained with lower forms of supervision, such as bounding boxes or scribbles. Another option are semi-supervised methods, which leverage a large amount of unlabeled data and a limited number of strongly-labeled samples. In this second setup, samples to be strongly-annotated can be selected randomly or with an active learning mechanism that chooses the ones that will maximize the model performance. In this work, we propose a sample selection approach to decide which samples to annotate for semi-supervised instance segmentation. Our method consists in first predicting pseudo-masks for the unlabeled pool of samples, together with a score predicting the quality of the mask. This score is an estimate of the Intersection Over Union (IoU) of the segment with the ground truth mask. We study which samples are better to annotate given the quality score, and show how our approach outperforms a random selection, leading to improved performance for semi-supervised instance segmentation with low annotation budgets.
Budget-aware Semi-Supervised Semantic and Instance Segmentation
May 23, 2019


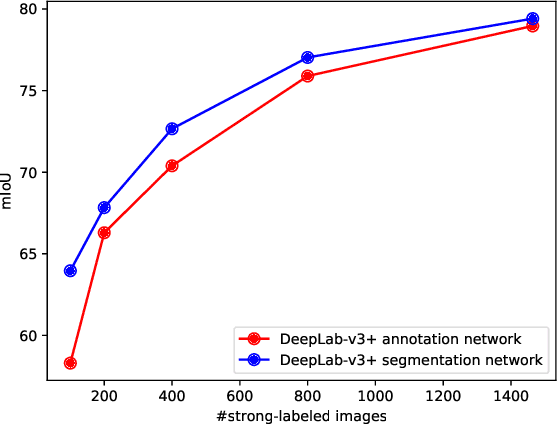
Abstract:Methods that move towards less supervised scenarios are key for image segmentation, as dense labels demand significant human intervention. Generally, the annotation burden is mitigated by labeling datasets with weaker forms of supervision, e.g. image-level labels or bounding boxes. Another option are semi-supervised settings, that commonly leverage a few strong annotations and a huge number of unlabeled/weakly-labeled data. In this paper, we revisit semi-supervised segmentation schemes and narrow down significantly the annotation budget (in terms of total labeling time of the training set) compared to previous approaches. With a very simple pipeline, we demonstrate that at low annotation budgets, semi-supervised methods outperform by a wide margin weakly-supervised ones for both semantic and instance segmentation. Our approach also outperforms previous semi-supervised works at a much reduced labeling cost. We present results for the Pascal VOC benchmark and unify weakly and semi-supervised approaches by considering the total annotation budget, thus allowing a fairer comparison between methods.
RVOS: End-to-End Recurrent Network for Video Object Segmentation
Mar 13, 2019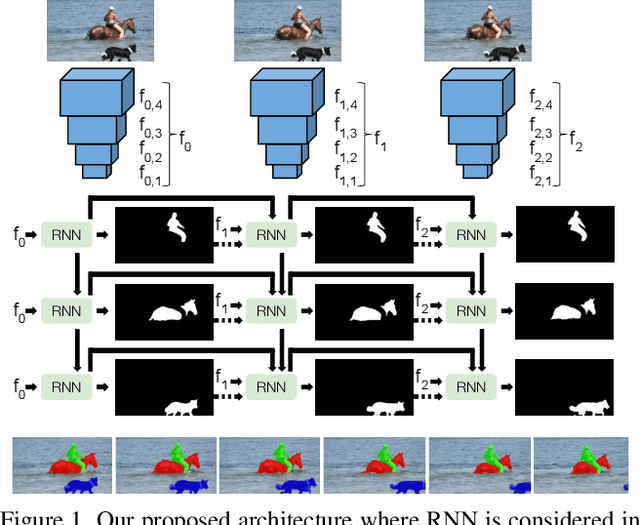

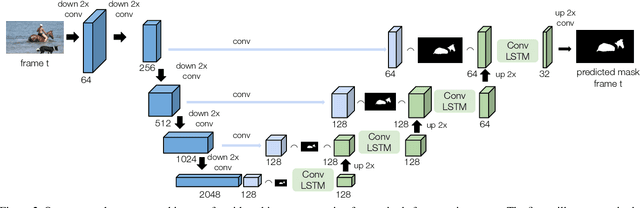
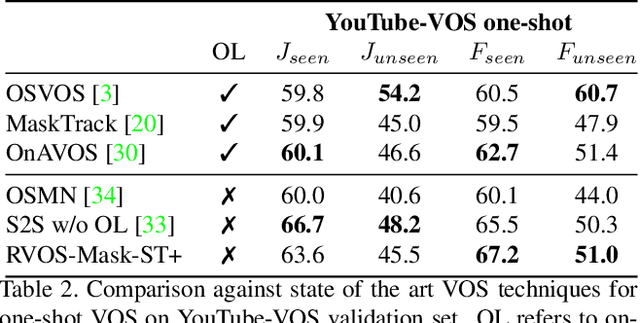
Abstract:Multiple object video object segmentation is a challenging task, specially for the zero-shot case, when no object mask is given at the initial frame and the model has to find the objects to be segmented along the sequence. In our work, we propose a Recurrent network for multiple object Video Object Segmentation (RVOS) that is fully end-to-end trainable. Our model incorporates recurrence on two different domains: (i) the spatial, which allows to discover the different object instances within a frame, and (ii) the temporal, which allows to keep the coherence of the segmented objects along time. We train RVOS for zero-shot video object segmentation and are the first ones to report quantitative results for DAVIS-2017 and YouTube-VOS benchmarks. Further, we adapt RVOS for one-shot video object segmentation by using the masks obtained in previous time steps as inputs to be processed by the recurrent module. Our model reaches comparable results to state-of-the-art techniques in YouTube-VOS benchmark and outperforms all previous video object segmentation methods not using online learning in the DAVIS-2017 benchmark. Moreover, our model achieves faster inference runtimes than previous methods, reaching 44ms/frame on a P100 GPU.
Recurrent Neural Networks for Semantic Instance Segmentation
Sep 03, 2018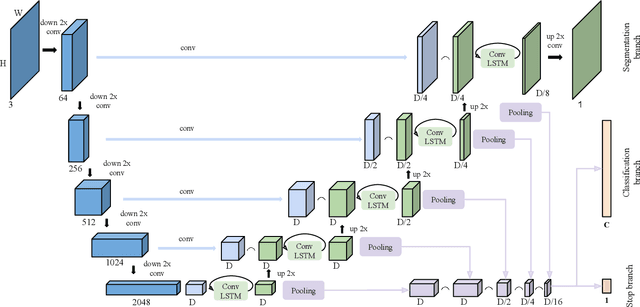
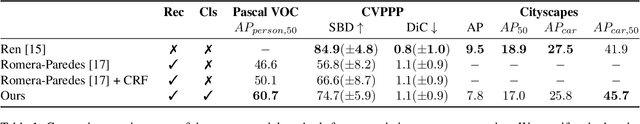
Abstract:We present a recurrent model for semantic instance segmentation that sequentially generates binary masks and their associated class probabilities for every object in an image. Our proposed system is trainable end-to-end from an input image to a sequence of labeled masks and, compared to methods relying on object proposals, does not require post-processing steps on its output. We study the suitability of our recurrent model on three different instance segmentation benchmarks, namely Pascal VOC 2012, CVPPP Plant Leaf Segmentation and Cityscapes. Further, we analyze the object sorting patterns generated by our model and observe that it learns to follow a consistent pattern, which correlates with the activations learned in the encoder part of our network. Source code and models are available at https://imatge-upc.github.io/rsis/
Detection-aided liver lesion segmentation using deep learning
Nov 29, 2017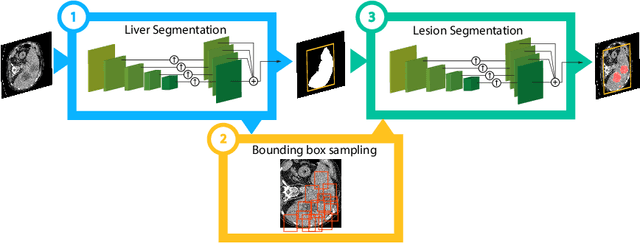


Abstract:A fully automatic technique for segmenting the liver and localizing its unhealthy tissues is a convenient tool in order to diagnose hepatic diseases and assess the response to the according treatments. In this work we propose a method to segment the liver and its lesions from Computed Tomography (CT) scans using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), that have proven good results in a variety of computer vision tasks, including medical imaging. The network that segments the lesions consists of a cascaded architecture, which first focuses on the region of the liver in order to segment the lesions on it. Moreover, we train a detector to localize the lesions, and mask the results of the segmentation network with the positive detections. The segmentation architecture is based on DRIU, a Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) with side outputs that work on feature maps of different resolutions, to finally benefit from the multi-scale information learned by different stages of the network. The main contribution of this work is the use of a detector to localize the lesions, which we show to be beneficial to remove false positives triggered by the segmentation network. Source code and models are available at https://imatge-upc.github.io/liverseg-2017-nipsws/ .
Hierarchical Object Detection with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Nov 25, 2016



Abstract:We present a method for performing hierarchical object detection in images guided by a deep reinforcement learning agent. The key idea is to focus on those parts of the image that contain richer information and zoom on them. We train an intelligent agent that, given an image window, is capable of deciding where to focus the attention among five different predefined region candidates (smaller windows). This procedure is iterated providing a hierarchical image analysis.We compare two different candidate proposal strategies to guide the object search: with and without overlap. Moreover, our work compares two different strategies to extract features from a convolutional neural network for each region proposal: a first one that computes new feature maps for each region proposal, and a second one that computes the feature maps for the whole image to later generate crops for each region proposal. Experiments indicate better results for the overlapping candidate proposal strategy and a loss of performance for the cropped image features due to the loss of spatial resolution. We argue that, while this loss seems unavoidable when working with large amounts of object candidates, the much more reduced amount of region proposals generated by our reinforcement learning agent allows considering to extract features for each location without sharing convolutional computation among regions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge