Minjung Shin
Laboratory for Natural and Artificial Kinästhese, Convergence Research Center for Artificial Intelligence
ASemConsist: Adaptive Semantic Feature Control for Training-Free Identity-Consistent Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Recent text-to-image diffusion models have significantly improved visual quality and text alignment. However, generating a sequence of images while preserving consistent character identity across diverse scene descriptions remains a challenging task. Existing methods often struggle with a trade-off between maintaining identity consistency and ensuring per-image prompt alignment. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework, ASemconsist, that addresses this challenge through selective text embedding modification, enabling explicit semantic control over character identity without sacrificing prompt alignment. Furthermore, based on our analysis of padding embeddings in FLUX, we propose a semantic control strategy that repurposes padding embeddings as semantic containers. Additionally, we introduce an adaptive feature-sharing strategy that automatically evaluates textual ambiguity and applies constraints only to the ambiguous identity prompt. Finally, we propose a unified evaluation protocol, the Consistency Quality Score (CQS), which integrates identity preservation and per-image text alignment into a single comprehensive metric, explicitly capturing performance imbalances between the two metrics. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance, effectively overcoming prior trade-offs. Project page: https://minjung-s.github.io/asemconsist
"There Is No Such Thing as a Dumb Question," But There Are Good Ones
May 15, 2025Abstract:Questioning has become increasingly crucial for both humans and artificial intelligence, yet there remains limited research comprehensively assessing question quality. In response, this study defines good questions and presents a systematic evaluation framework. We propose two key evaluation dimensions: appropriateness (sociolinguistic competence in context) and effectiveness (strategic competence in goal achievement). Based on these foundational dimensions, a rubric-based scoring system was developed. By incorporating dynamic contextual variables, our evaluation framework achieves structure and flexibility through semi-adaptive criteria. The methodology was validated using the CAUS and SQUARE datasets, demonstrating the ability of the framework to access both well-formed and problematic questions while adapting to varied contexts. As we establish a flexible and comprehensive framework for question evaluation, this study takes a significant step toward integrating questioning behavior with structured analytical methods grounded in the intrinsic nature of questioning.
Eye-for-an-eye: Appearance Transfer with Semantic Correspondence in Diffusion Models
Jun 11, 2024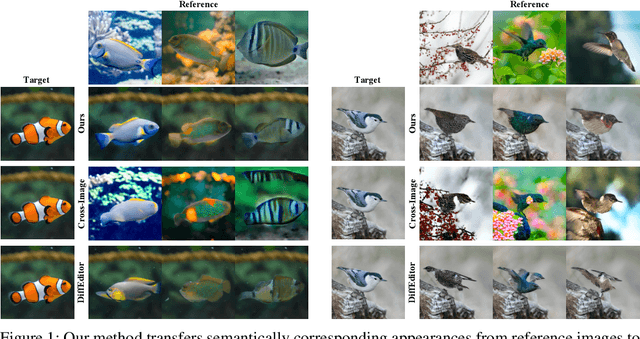
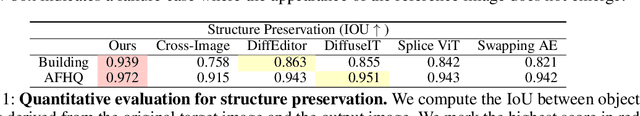
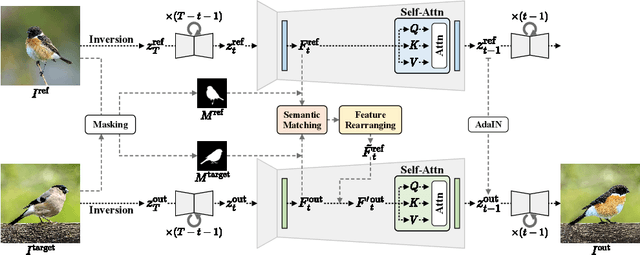

Abstract:As pretrained text-to-image diffusion models have become a useful tool for image synthesis, people want to specify the results in various ways. In this paper, we introduce a method to produce results with the same structure of a target image but painted with colors from a reference image, i.e., appearance transfer, especially following the semantic correspondence between the result and the reference. E.g., the result wing takes color from the reference wing, not the reference head. Existing methods rely on the query-key similarity within self-attention layer, usually producing defective results. To this end, we propose to find semantic correspondences and explicitly rearrange the features according to the semantic correspondences. Extensive experiments show the superiority of our method in various aspects: preserving the structure of the target and reflecting the color from the reference according to the semantic correspondences, even when the two images are not aligned.
CAUS: A Dataset for Question Generation based on Human Cognition Leveraging Large Language Models
Apr 18, 2024



Abstract:We introduce the CAUS (Curious About Uncertain Scene) dataset, designed to enable Large Language Models, specifically GPT-4, to emulate human cognitive processes for resolving uncertainties. Leveraging this dataset, we investigate the potential of LLMs to engage in questioning effectively. Our approach involves providing scene descriptions embedded with uncertainties to stimulate the generation of reasoning and queries. The queries are then classified according to multi-dimensional criteria. All procedures are facilitated by a collaborative system involving both LLMs and human researchers. Our results demonstrate that GPT-4 can effectively generate pertinent questions and grasp their nuances, particularly when given appropriate context and instructions. The study suggests that incorporating human-like questioning into AI models improves their ability to manage uncertainties, paving the way for future advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Chain of Empathy: Enhancing Empathetic Response of Large Language Models Based on Psychotherapy Models
Nov 02, 2023


Abstract:We present a novel method, the Chain of Empathy (CoE) prompting, that utilizes insights from psychotherapy to induce Large Language Models (LLMs) to reason about human emotional states. This method is inspired by various psychotherapy approaches including Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), Person Centered Therapy (PCT), and Reality Therapy (RT), each leading to different patterns of interpreting clients' mental states. LLMs without reasoning generated predominantly exploratory responses. However, when LLMs used CoE reasoning, we found a more comprehensive range of empathetic responses aligned with the different reasoning patterns of each psychotherapy model. The CBT based CoE resulted in the most balanced generation of empathetic responses. The findings underscore the importance of understanding the emotional context and how it affects human and AI communication. Our research contributes to understanding how psychotherapeutic models can be incorporated into LLMs, facilitating the development of context-specific, safer, and empathetic AI.
BallGAN: 3D-aware Image Synthesis with a Spherical Background
Jan 22, 2023



Abstract:3D-aware GANs aim to synthesize realistic 3D scenes such that they can be rendered in arbitrary perspectives to produce images. Although previous methods produce realistic images, they suffer from unstable training or degenerate solutions where the 3D geometry is unnatural. We hypothesize that the 3D geometry is underdetermined due to the insufficient constraint, i.e., being classified as real image to the discriminator is not enough. To solve this problem, we propose to approximate the background as a spherical surface and represent a scene as a union of the foreground placed in the sphere and the thin spherical background. It reduces the degree of freedom in the background field. Accordingly, we modify the volume rendering equation and incorporate dedicated constraints to design a novel 3D-aware GAN framework named BallGAN. BallGAN has multiple advantages as follows. 1) It produces more reasonable 3D geometry; the images of a scene across different viewpoints have better photometric consistency and fidelity than the state-of-the-art methods. 2) The training becomes much more stable. 3) The foreground can be separately rendered on top of different arbitrary backgrounds.
Source-free Subject Adaptation for EEG-based Visual Recognition
Jan 20, 2023



Abstract:This paper focuses on subject adaptation for EEG-based visual recognition. It aims at building a visual stimuli recognition system customized for the target subject whose EEG samples are limited, by transferring knowledge from abundant data of source subjects. Existing approaches consider the scenario that samples of source subjects are accessible during training. However, it is often infeasible and problematic to access personal biological data like EEG signals due to privacy issues. In this paper, we introduce a novel and practical problem setup, namely source-free subject adaptation, where the source subject data are unavailable and only the pre-trained model parameters are provided for subject adaptation. To tackle this challenging problem, we propose classifier-based data generation to simulate EEG samples from source subjects using classifier responses. Using the generated samples and target subject data, we perform subject-independent feature learning to exploit the common knowledge shared across different subjects. Notably, our framework is generalizable and can adopt any subject-independent learning method. In the experiments on the EEG-ImageNet40 benchmark, our model brings consistent improvements regardless of the choice of subject-independent learning. Also, our method shows promising performance, recording top-1 test accuracy of 74.6% under the 5-shot setting even without relying on source data. Our code can be found at https://github.com/DeepBCI/Deep-BCI/tree/master/1_Intelligent_BCI/Source_Free_Subject_Adaptation_for_EEG.
Inter-subject Contrastive Learning for Subject Adaptive EEG-based Visual Recognition
Feb 07, 2022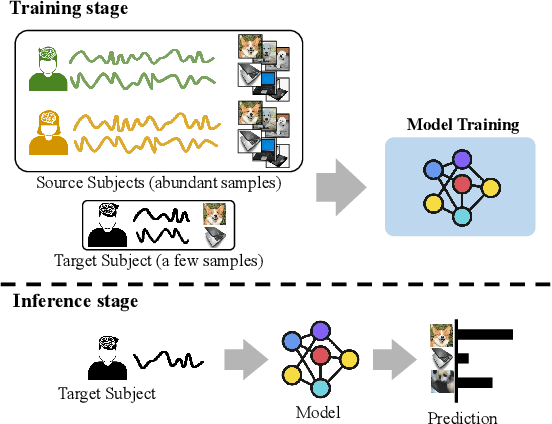
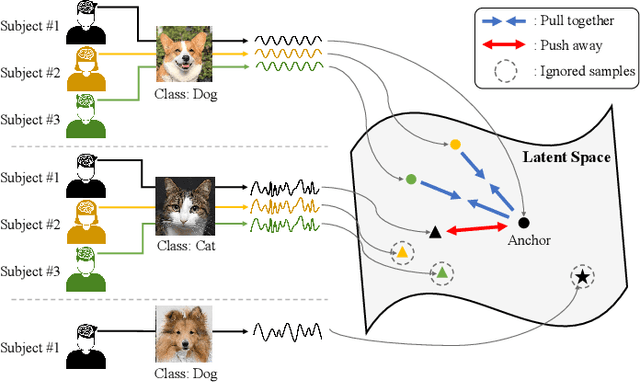
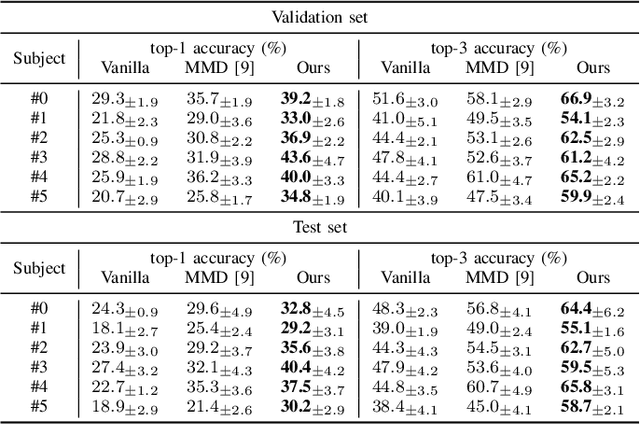
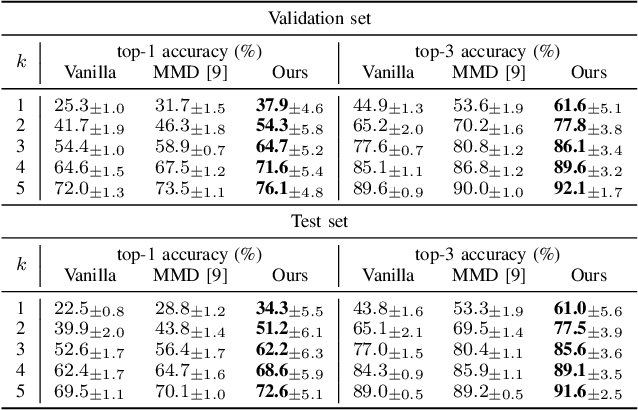
Abstract:This paper tackles the problem of subject adaptive EEG-based visual recognition. Its goal is to accurately predict the categories of visual stimuli based on EEG signals with only a handful of samples for the target subject during training. The key challenge is how to appropriately transfer the knowledge obtained from abundant data of source subjects to the subject of interest. To this end, we introduce a novel method that allows for learning subject-independent representation by increasing the similarity of features sharing the same class but coming from different subjects. With the dedicated sampling principle, our model effectively captures the common knowledge shared across different subjects, thereby achieving promising performance for the target subject even under harsh problem settings with limited data. Specifically, on the EEG-ImageNet40 benchmark, our model records the top-1 / top-3 test accuracy of 72.6% / 91.6% when using only five EEG samples per class for the target subject. Our code is available at https://github.com/DeepBCI/Deep-BCI/tree/master/1_Intelligent_BCI/Inter_Subject_Contrastive_Learning_for_EEG.
Toward a Human-Level Video Understanding Intelligence
Oct 18, 2021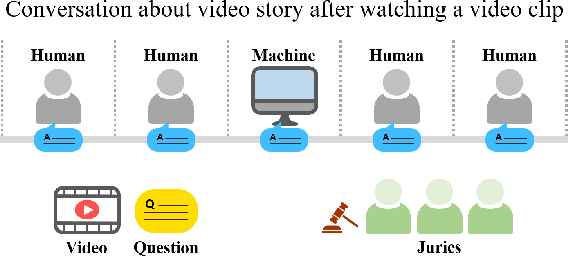

Abstract:We aim to develop an AI agent that can watch video clips and have a conversation with human about the video story. Developing video understanding intelligence is a significantly challenging task, and evaluation methods for adequately measuring and analyzing the progress of AI agent are lacking as well. In this paper, we propose the Video Turing Test to provide effective and practical assessments of video understanding intelligence as well as human-likeness evaluation of AI agents. We define a general format and procedure of the Video Turing Test and present a case study to confirm the effectiveness and usefulness of the proposed test.
CogME: A Novel Evaluation Metric for Video Understanding Intelligence
Jul 21, 2021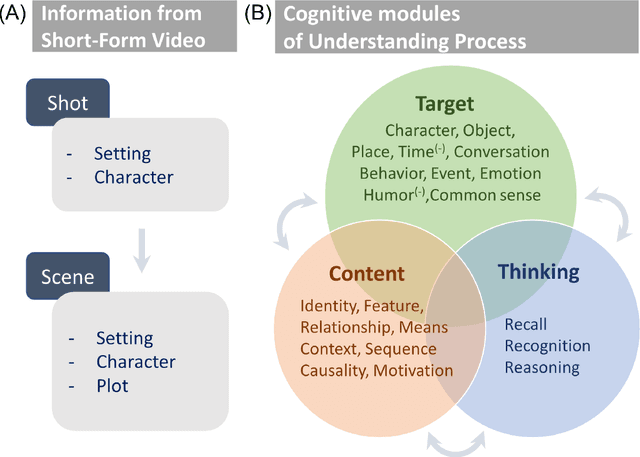
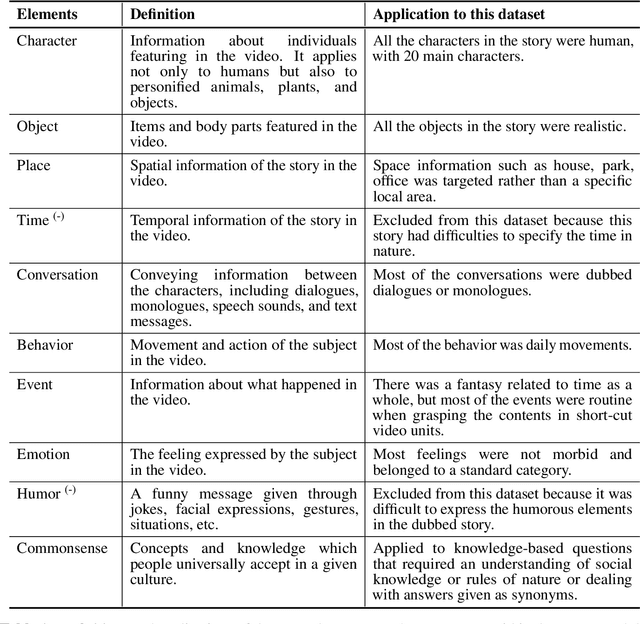
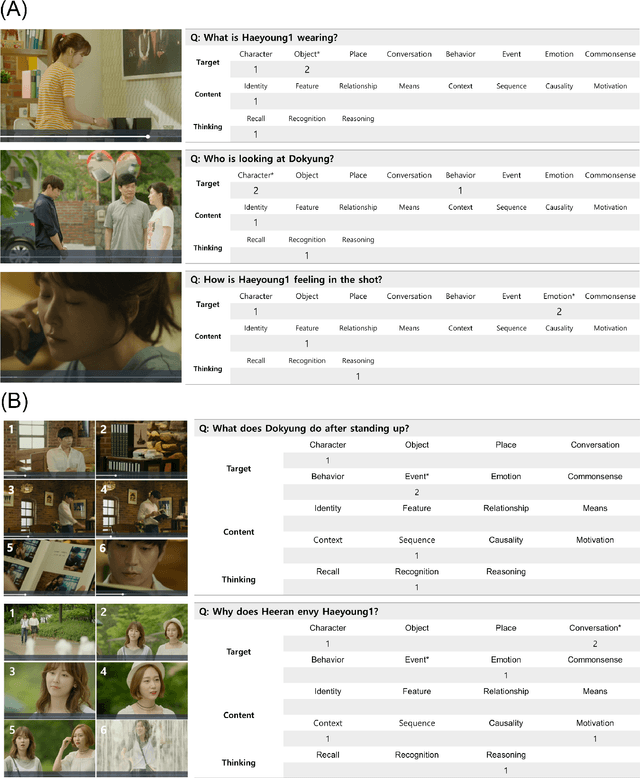
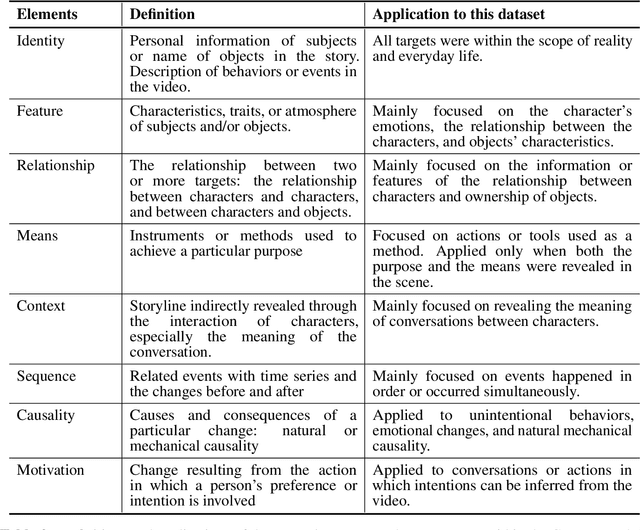
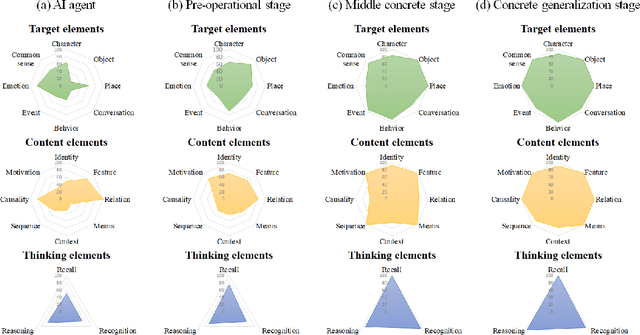
Abstract:Developing video understanding intelligence is quite challenging because it requires holistic integration of images, scripts, and sounds based on natural language processing, temporal dependency, and reasoning. Recently, substantial attempts have been made on several video datasets with associated question answering (QA) on a large scale. However, existing evaluation metrics for video question answering (VideoQA) do not provide meaningful analysis. To make progress, we argue that a well-made framework, established on the way humans understand, is required to explain and evaluate the performance of understanding in detail. Then we propose a top-down evaluation system for VideoQA, based on the cognitive process of humans and story elements: Cognitive Modules for Evaluation (CogME). CogME is composed of three cognitive modules: targets, contents, and thinking. The interaction among the modules in the understanding procedure can be expressed in one sentence as follows: "I understand the CONTENT of the TARGET through a way of THINKING." Each module has sub-components derived from the story elements. We can specify the required aspects of understanding by annotating the sub-components to individual questions. CogME thus provides a framework for an elaborated specification of VideoQA datasets. To examine the suitability of a VideoQA dataset for validating video understanding intelligence, we evaluated the baseline model of the DramaQA dataset by applying CogME. The evaluation reveals that story elements are unevenly reflected in the existing dataset, and the model based on the dataset may cause biased predictions. Although this study has only been able to grasp a narrow range of stories, we expect that it offers the first step in considering the cognitive process of humans on the video understanding intelligence of humans and AI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge