Jewook Lee
Fair Contrastive Learning for Facial Attribute Classification
Mar 30, 2022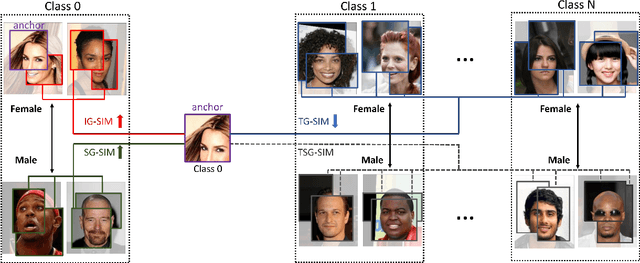
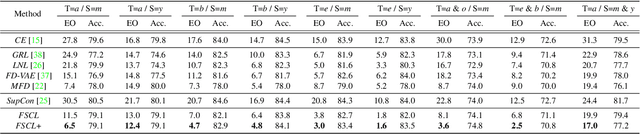
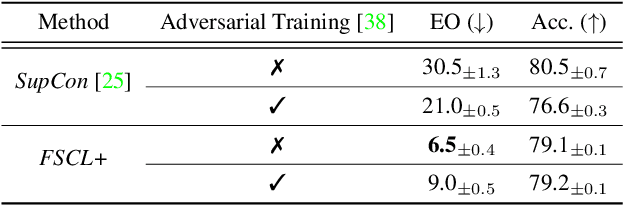
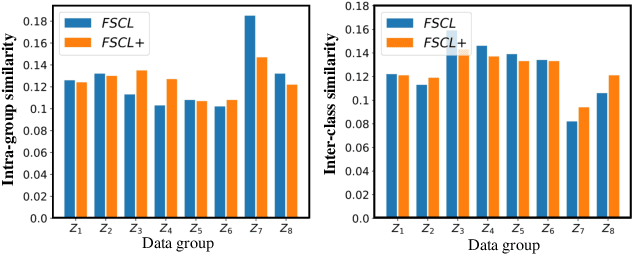
Abstract:Learning visual representation of high quality is essential for image classification. Recently, a series of contrastive representation learning methods have achieved preeminent success. Particularly, SupCon outperformed the dominant methods based on cross-entropy loss in representation learning. However, we notice that there could be potential ethical risks in supervised contrastive learning. In this paper, we for the first time analyze unfairness caused by supervised contrastive learning and propose a new Fair Supervised Contrastive Loss (FSCL) for fair visual representation learning. Inheriting the philosophy of supervised contrastive learning, it encourages representation of the same class to be closer to each other than that of different classes, while ensuring fairness by penalizing the inclusion of sensitive attribute information in representation. In addition, we introduce a group-wise normalization to diminish the disparities of intra-group compactness and inter-class separability between demographic groups that arouse unfair classification. Through extensive experiments on CelebA and UTK Face, we validate that the proposed method significantly outperforms SupCon and existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of the trade-off between top-1 accuracy and fairness. Moreover, our method is robust to the intensity of data bias and effectively works in incomplete supervised settings. Our code is available at https://github.com/sungho-CoolG/FSCL.
Inter-subject Contrastive Learning for Subject Adaptive EEG-based Visual Recognition
Feb 07, 2022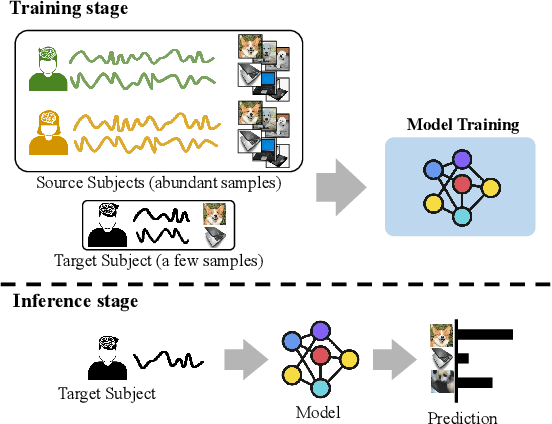
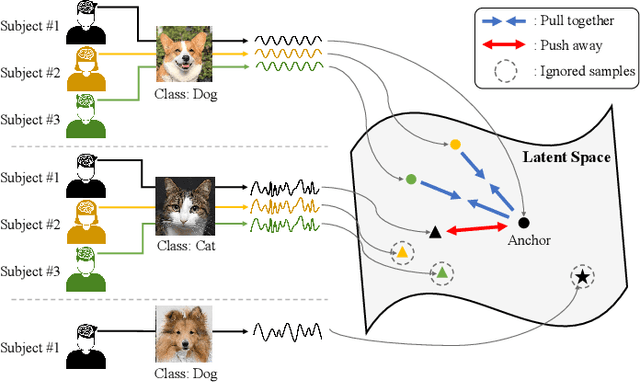
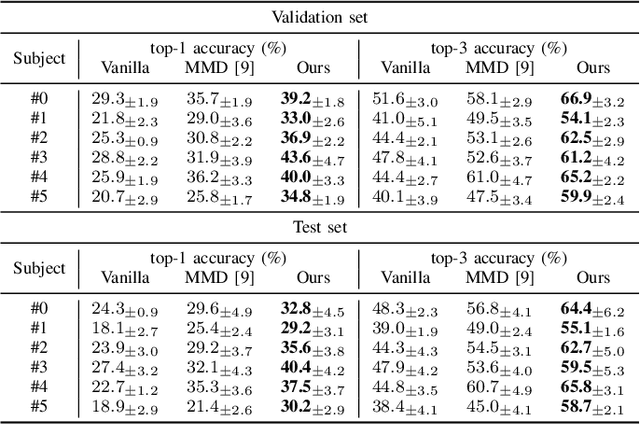
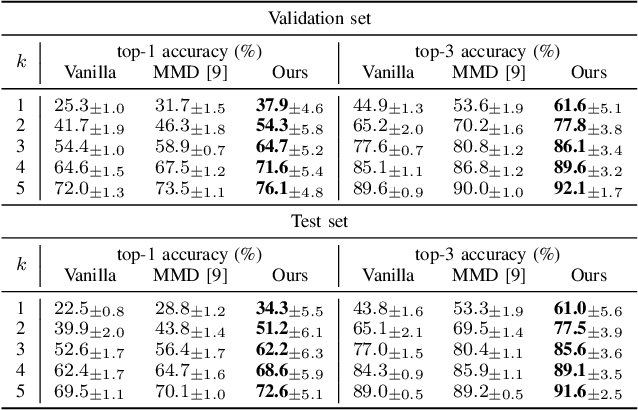
Abstract:This paper tackles the problem of subject adaptive EEG-based visual recognition. Its goal is to accurately predict the categories of visual stimuli based on EEG signals with only a handful of samples for the target subject during training. The key challenge is how to appropriately transfer the knowledge obtained from abundant data of source subjects to the subject of interest. To this end, we introduce a novel method that allows for learning subject-independent representation by increasing the similarity of features sharing the same class but coming from different subjects. With the dedicated sampling principle, our model effectively captures the common knowledge shared across different subjects, thereby achieving promising performance for the target subject even under harsh problem settings with limited data. Specifically, on the EEG-ImageNet40 benchmark, our model records the top-1 / top-3 test accuracy of 72.6% / 91.6% when using only five EEG samples per class for the target subject. Our code is available at https://github.com/DeepBCI/Deep-BCI/tree/master/1_Intelligent_BCI/Inter_Subject_Contrastive_Learning_for_EEG.
Feature Stylization and Domain-aware Contrastive Learning for Domain Generalization
Aug 19, 2021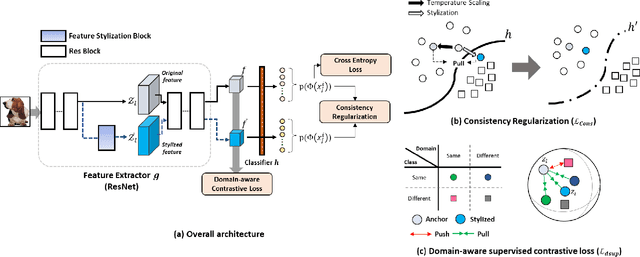
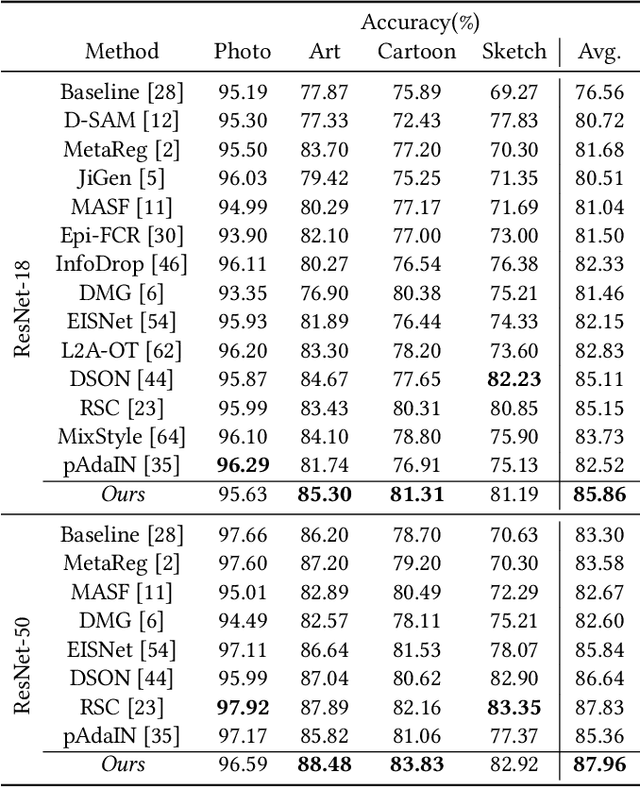
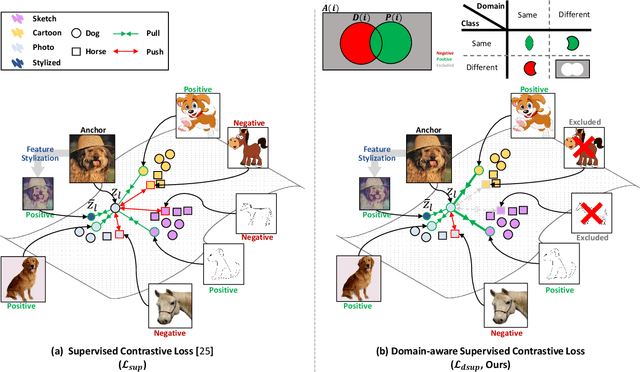
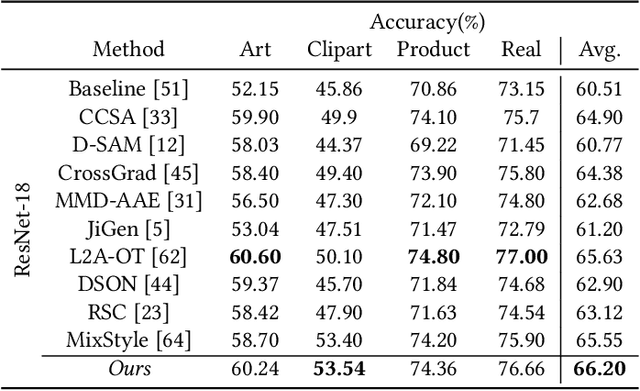
Abstract:Domain generalization aims to enhance the model robustness against domain shift without accessing the target domain. Since the available source domains for training are limited, recent approaches focus on generating samples of novel domains. Nevertheless, they either struggle with the optimization problem when synthesizing abundant domains or cause the distortion of class semantics. To these ends, we propose a novel domain generalization framework where feature statistics are utilized for stylizing original features to ones with novel domain properties. To preserve class information during stylization, we first decompose features into high and low frequency components. Afterward, we stylize the low frequency components with the novel domain styles sampled from the manipulated statistics, while preserving the shape cues in high frequency ones. As the final step, we re-merge both components to synthesize novel domain features. To enhance domain robustness, we utilize the stylized features to maintain the model consistency in terms of features as well as outputs. We achieve the feature consistency with the proposed domain-aware supervised contrastive loss, which ensures domain invariance while increasing class discriminability. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed feature stylization and the domain-aware contrastive loss. Through quantitative comparisons, we verify the lead of our method upon existing state-of-the-art methods on two benchmarks, PACS and Office-Home.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge