Min Hyun Han
FADEL: Uncertainty-aware Fake Audio Detection with Evidential Deep Learning
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Recently, fake audio detection has gained significant attention, as advancements in speech synthesis and voice conversion have increased the vulnerability of automatic speaker verification (ASV) systems to spoofing attacks. A key challenge in this task is generalizing models to detect unseen, out-of-distribution (OOD) attacks. Although existing approaches have shown promising results, they inherently suffer from overconfidence issues due to the usage of softmax for classification, which can produce unreliable predictions when encountering unpredictable spoofing attempts. To deal with this limitation, we propose a novel framework called fake audio detection with evidential learning (FADEL). By modeling class probabilities with a Dirichlet distribution, FADEL incorporates model uncertainty into its predictions, thereby leading to more robust performance in OOD scenarios. Experimental results on the ASVspoof2019 Logical Access (LA) and ASVspoof2021 LA datasets indicate that the proposed method significantly improves the performance of baseline models. Furthermore, we demonstrate the validity of uncertainty estimation by analyzing a strong correlation between average uncertainty and equal error rate (EER) across different spoofing algorithms.
HILCodec: High Fidelity and Lightweight Neural Audio Codec
May 08, 2024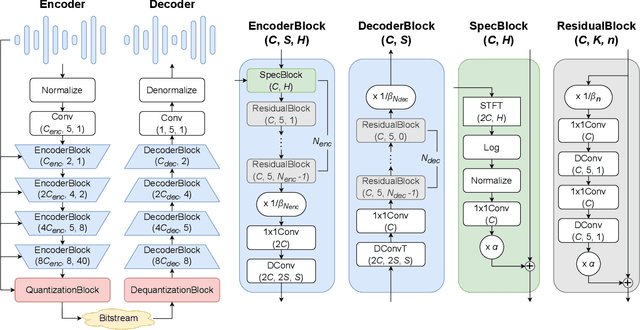
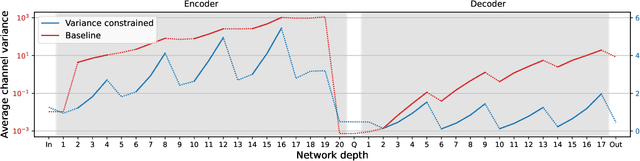
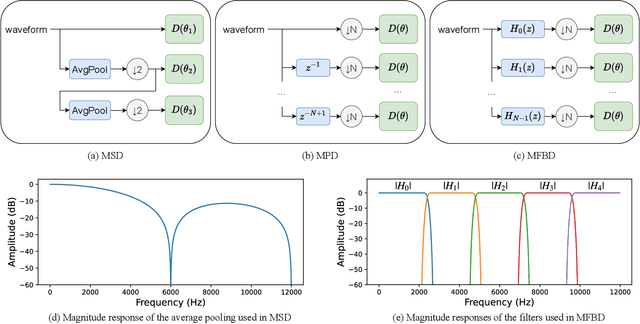
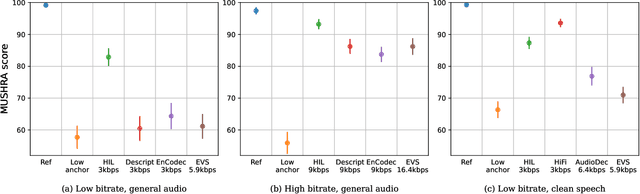
Abstract:The recent advancement of end-to-end neural audio codecs enables compressing audio at very low bitrates while reconstructing the output audio with high fidelity. Nonetheless, such improvements often come at the cost of increased model complexity. In this paper, we identify and address the problems of existing neural audio codecs. We show that the performance of Wave-U-Net does not increase consistently as the network depth increases. We analyze the root cause of such a phenomenon and suggest a variance-constrained design. Also, we reveal various distortions in previous waveform domain discriminators and propose a novel distortion-free discriminator. The resulting model, \textit{HILCodec}, is a real-time streaming audio codec that demonstrates state-of-the-art quality across various bitrates and audio types.
EEND-DEMUX: End-to-End Neural Speaker Diarization via Demultiplexed Speaker Embeddings
Dec 11, 2023Abstract:In recent years, there have been studies to further improve the end-to-end neural speaker diarization (EEND) systems. This letter proposes the EEND-DEMUX model, a novel framework utilizing demultiplexed speaker embeddings. In this work, we focus on disentangling speaker-relevant information in the latent space and then transform each separated latent variable into its corresponding speech activity. EEND-DEMUX can directly obtain separated speaker embeddings through the demultiplexing operation in the inference phase without an external speaker diarization system, an embedding extractor, or a heuristic decoding technique. Furthermore, we employ a multi-head cross-attention mechanism to capture the correlation between mixture and separated speaker embeddings effectively. We formulate three loss functions based on matching, orthogonality, and sparsity constraints to learn robust demultiplexed speaker embeddings. The experimental results on the LibriMix dataset show consistently improved performance in both a fixed and flexible number of speakers scenarios.
Towards single integrated spoofing-aware speaker verification embeddings
Jun 01, 2023



Abstract:This study aims to develop a single integrated spoofing-aware speaker verification (SASV) embeddings that satisfy two aspects. First, rejecting non-target speakers' input as well as target speakers' spoofed inputs should be addressed. Second, competitive performance should be demonstrated compared to the fusion of automatic speaker verification (ASV) and countermeasure (CM) embeddings, which outperformed single embedding solutions by a large margin in the SASV2022 challenge. We analyze that the inferior performance of single SASV embeddings comes from insufficient amount of training data and distinct nature of ASV and CM tasks. To this end, we propose a novel framework that includes multi-stage training and a combination of loss functions. Copy synthesis, combined with several vocoders, is also exploited to address the lack of spoofed data. Experimental results show dramatic improvements, achieving a SASV-EER of 1.06% on the evaluation protocol of the SASV2022 challenge.
Fully Unsupervised Training of Few-shot Keyword Spotting
Oct 07, 2022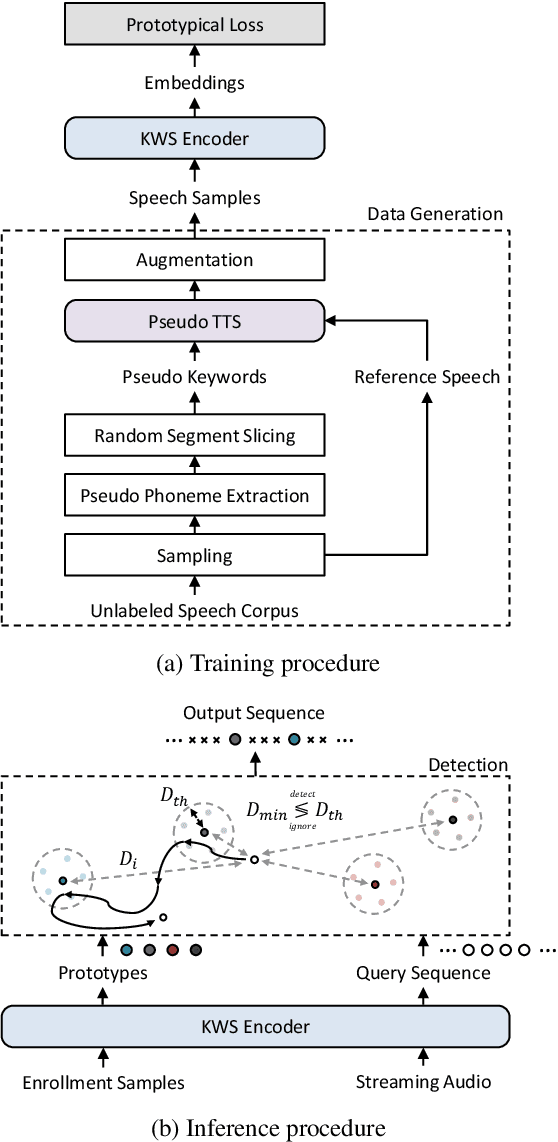
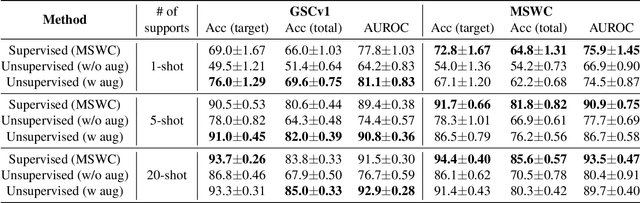
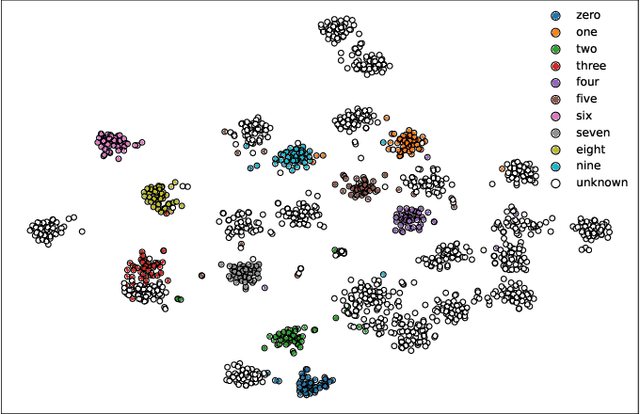
Abstract:For training a few-shot keyword spotting (FS-KWS) model, a large labeled dataset containing massive target keywords has known to be essential to generalize to arbitrary target keywords with only a few enrollment samples. To alleviate the expensive data collection with labeling, in this paper, we propose a novel FS-KWS system trained only on synthetic data. The proposed system is based on metric learning enabling target keywords to be detected using distance metrics. Exploiting the speech synthesis model that generates speech with pseudo phonemes instead of texts, we easily obtain a large collection of multi-view samples with the same semantics. These samples are sufficient for training, considering metric learning does not intrinsically necessitate labeled data. All of the components in our framework do not require any supervision, making our method unsupervised. Experimental results on real datasets show our proposed method is competitive even without any labeled and real datasets.
Disentangled Speaker Representation Learning via Mutual Information Minimization
Aug 17, 2022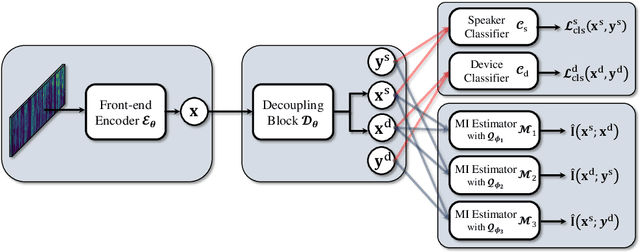
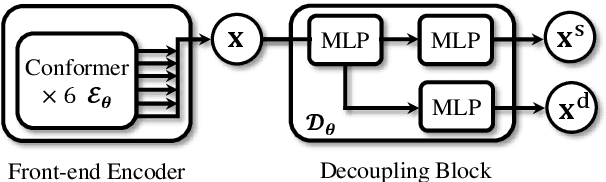
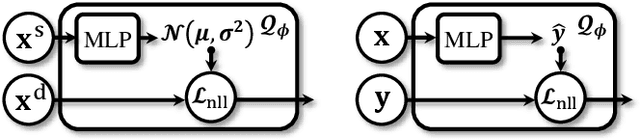
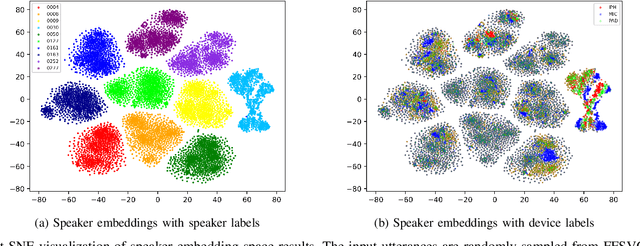
Abstract:Domain mismatch problem caused by speaker-unrelated feature has been a major topic in speaker recognition. In this paper, we propose an explicit disentanglement framework to unravel speaker-relevant features from speaker-unrelated features via mutual information (MI) minimization. To achieve our goal of minimizing MI between speaker-related and speaker-unrelated features, we adopt a contrastive log-ratio upper bound (CLUB), which exploits the upper bound of MI. Our framework is constructed in a 3-stage structure. First, in the front-end encoder, input speech is encoded into shared initial embedding. Next, in the decoupling block, shared initial embedding is split into separate speaker-related and speaker-unrelated embeddings. Finally, disentanglement is conducted by MI minimization in the last stage. Experiments on Far-Field Speaker Verification Challenge 2022 (FFSVC2022) demonstrate that our proposed framework is effective for disentanglement. Also, to utilize domain-unknown datasets containing numerous speakers, we pre-trained the front-end encoder with VoxCeleb datasets. We then fine-tuned the speaker embedding model in the disentanglement framework with FFSVC 2022 dataset. The experimental results show that fine-tuning with a disentanglement framework on a existing pre-trained model is valid and can further improve performance.
Bootstrap Equilibrium and Probabilistic Speaker Representation Learning for Self-supervised Speaker Verification
Dec 24, 2021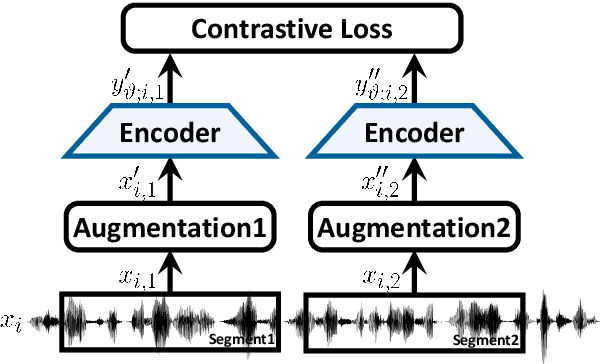
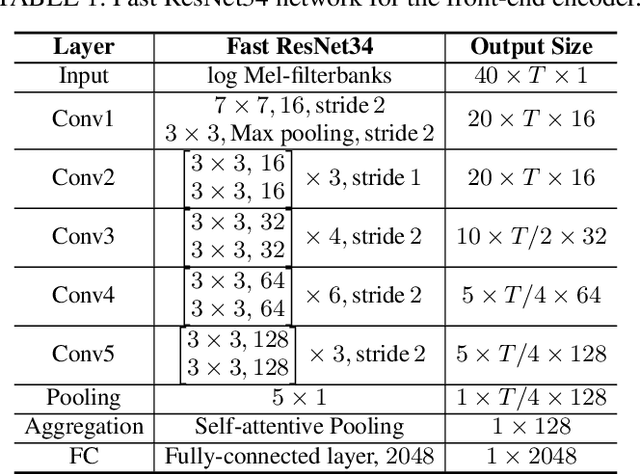
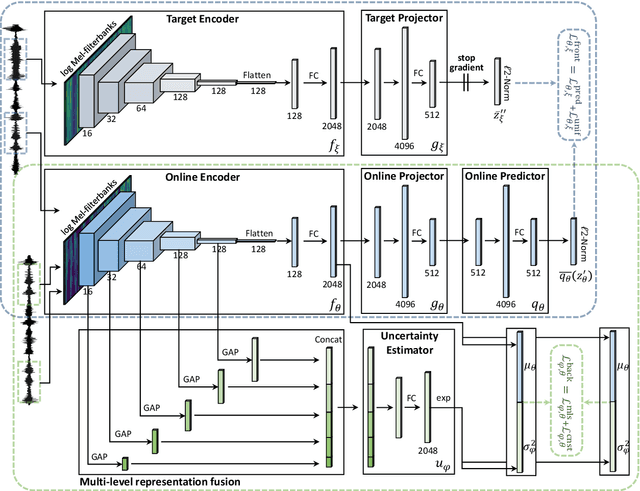
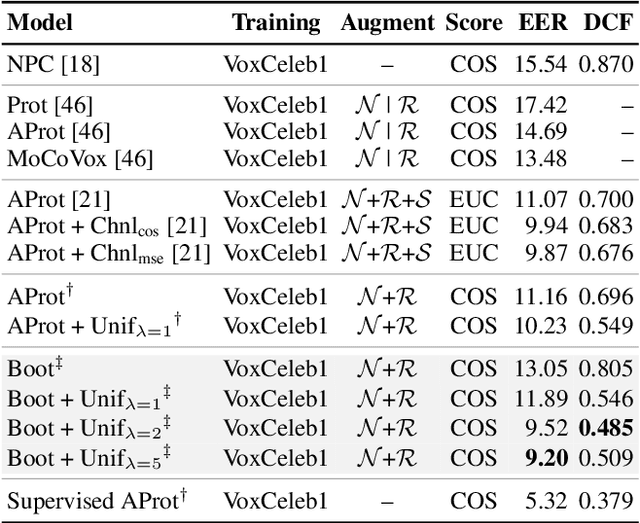
Abstract:In this paper, we propose self-supervised speaker representation learning strategies, which comprise of a bootstrap equilibrium speaker representation learning in the front-end and an uncertainty-aware probabilistic speaker embedding training in the back-end. In the front-end stage, we learn the speaker representations via the bootstrap training scheme with the uniformity regularization term. In the back-end stage, the probabilistic speaker embeddings are estimated by maximizing the mutual likelihood score between the speech samples belonging to the same speaker, which provide not only speaker representations but also data uncertainty. Experimental results show that the proposed bootstrap equilibrium training strategy can effectively help learn the speaker representations and outperforms the conventional methods based on contrastive learning. Also, we demonstrate that the integrated two-stage framework further improves the speaker verification performance on the VoxCeleb1 test set in terms of EER and MinDCF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge