Michael Oechsle
AnyUp: Universal Feature Upsampling
Oct 14, 2025
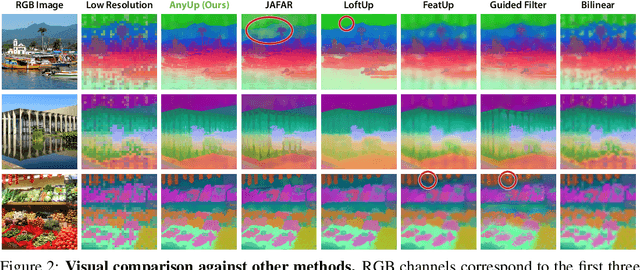

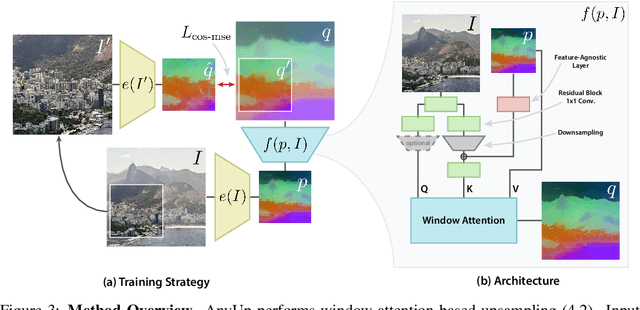
Abstract:We introduce AnyUp, a method for feature upsampling that can be applied to any vision feature at any resolution, without encoder-specific training. Existing learning-based upsamplers for features like DINO or CLIP need to be re-trained for every feature extractor and thus do not generalize to different feature types at inference time. In this work, we propose an inference-time feature-agnostic upsampling architecture to alleviate this limitation and improve upsampling quality. In our experiments, AnyUp sets a new state of the art for upsampled features, generalizes to different feature types, and preserves feature semantics while being efficient and easy to apply to a wide range of downstream tasks.
CubeDiff: Repurposing Diffusion-Based Image Models for Panorama Generation
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:We introduce a novel method for generating 360{\deg} panoramas from text prompts or images. Our approach leverages recent advances in 3D generation by employing multi-view diffusion models to jointly synthesize the six faces of a cubemap. Unlike previous methods that rely on processing equirectangular projections or autoregressive generation, our method treats each face as a standard perspective image, simplifying the generation process and enabling the use of existing multi-view diffusion models. We demonstrate that these models can be adapted to produce high-quality cubemaps without requiring correspondence-aware attention layers. Our model allows for fine-grained text control, generates high resolution panorama images and generalizes well beyond its training set, whilst achieving state-of-the-art results, both qualitatively and quantitatively. Project page: https://cubediff.github.io/
Gaussians-to-Life: Text-Driven Animation of 3D Gaussian Splatting Scenes
Nov 28, 2024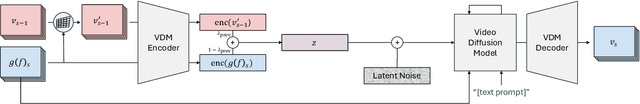
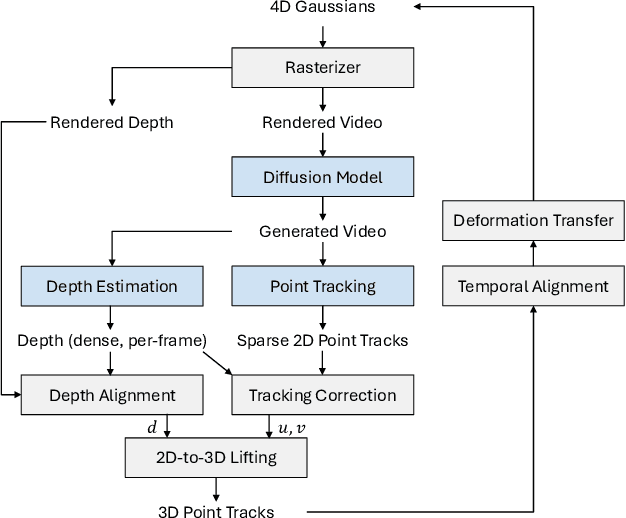
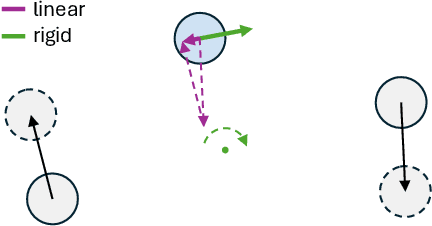
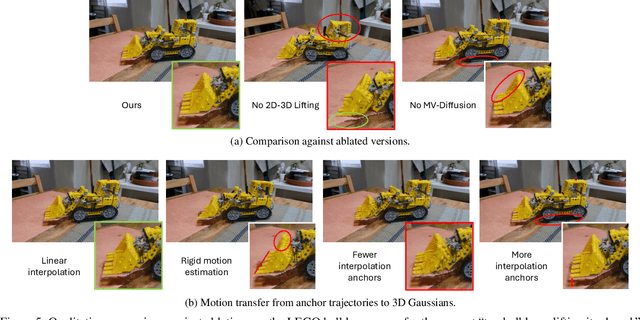
Abstract:State-of-the-art novel view synthesis methods achieve impressive results for multi-view captures of static 3D scenes. However, the reconstructed scenes still lack "liveliness," a key component for creating engaging 3D experiences. Recently, novel video diffusion models generate realistic videos with complex motion and enable animations of 2D images, however they cannot naively be used to animate 3D scenes as they lack multi-view consistency. To breathe life into the static world, we propose Gaussians2Life, a method for animating parts of high-quality 3D scenes in a Gaussian Splatting representation. Our key idea is to leverage powerful video diffusion models as the generative component of our model and to combine these with a robust technique to lift 2D videos into meaningful 3D motion. We find that, in contrast to prior work, this enables realistic animations of complex, pre-existing 3D scenes and further enables the animation of a large variety of object classes, while related work is mostly focused on prior-based character animation, or single 3D objects. Our model enables the creation of consistent, immersive 3D experiences for arbitrary scenes.
Evolutive Rendering Models
May 27, 2024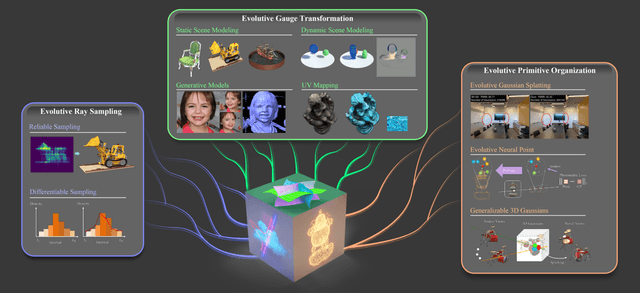
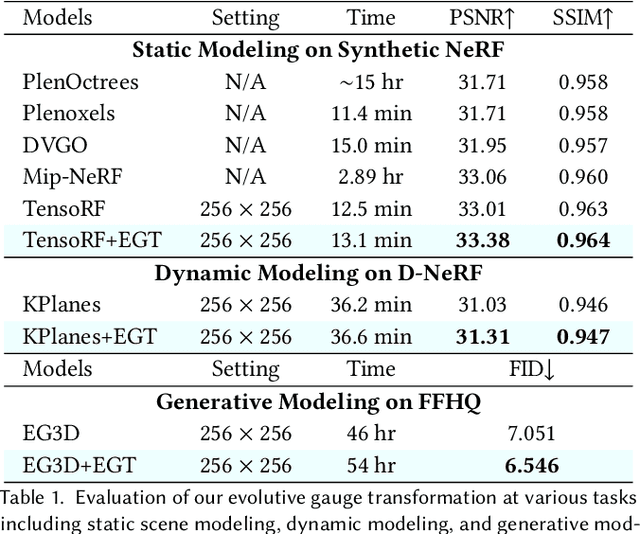
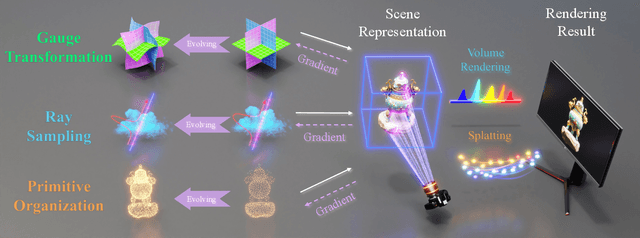
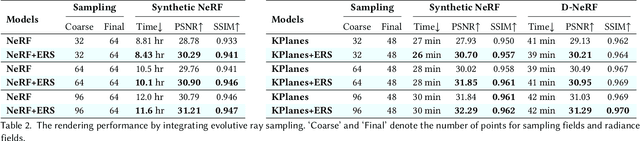
Abstract:The landscape of computer graphics has undergone significant transformations with the recent advances of differentiable rendering models. These rendering models often rely on heuristic designs that may not fully align with the final rendering objectives. We address this gap by pioneering \textit{evolutive rendering models}, a methodology where rendering models possess the ability to evolve and adapt dynamically throughout the rendering process. In particular, we present a comprehensive learning framework that enables the optimization of three principal rendering elements, including the gauge transformations, the ray sampling mechanisms, and the primitive organization. Central to this framework is the development of differentiable versions of these rendering elements, allowing for effective gradient backpropagation from the final rendering objectives. A detailed analysis of gradient characteristics is performed to facilitate a stable and goal-oriented elements evolution. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the large potential of evolutive rendering models for enhancing the rendering performance across various domains, including static and dynamic scene representations, generative modeling, and texture mapping.
Splat-SLAM: Globally Optimized RGB-only SLAM with 3D Gaussians
May 26, 2024



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting has emerged as a powerful representation of geometry and appearance for RGB-only dense Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), as it provides a compact dense map representation while enabling efficient and high-quality map rendering. However, existing methods show significantly worse reconstruction quality than competing methods using other 3D representations, e.g. neural points clouds, since they either do not employ global map and pose optimization or make use of monocular depth. In response, we propose the first RGB-only SLAM system with a dense 3D Gaussian map representation that utilizes all benefits of globally optimized tracking by adapting dynamically to keyframe pose and depth updates by actively deforming the 3D Gaussian map. Moreover, we find that refining the depth updates in inaccurate areas with a monocular depth estimator further improves the accuracy of the 3D reconstruction. Our experiments on the Replica, TUM-RGBD, and ScanNet datasets indicate the effectiveness of globally optimized 3D Gaussians, as the approach achieves superior or on par performance with existing RGB-only SLAM methods methods in tracking, mapping and rendering accuracy while yielding small map sizes and fast runtimes. The source code is available at https://github.com/eriksandstroem/Splat-SLAM.
RadSplat: Radiance Field-Informed Gaussian Splatting for Robust Real-Time Rendering with 900+ FPS
Mar 20, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in view synthesis and real-time rendering have achieved photorealistic quality at impressive rendering speeds. While Radiance Field-based methods achieve state-of-the-art quality in challenging scenarios such as in-the-wild captures and large-scale scenes, they often suffer from excessively high compute requirements linked to volumetric rendering. Gaussian Splatting-based methods, on the other hand, rely on rasterization and naturally achieve real-time rendering but suffer from brittle optimization heuristics that underperform on more challenging scenes. In this work, we present RadSplat, a lightweight method for robust real-time rendering of complex scenes. Our main contributions are threefold. First, we use radiance fields as a prior and supervision signal for optimizing point-based scene representations, leading to improved quality and more robust optimization. Next, we develop a novel pruning technique reducing the overall point count while maintaining high quality, leading to smaller and more compact scene representations with faster inference speeds. Finally, we propose a novel test-time filtering approach that further accelerates rendering and allows to scale to larger, house-sized scenes. We find that our method enables state-of-the-art synthesis of complex captures at 900+ FPS.
UNISURF: Unifying Neural Implicit Surfaces and Radiance Fields for Multi-View Reconstruction
Apr 20, 2021
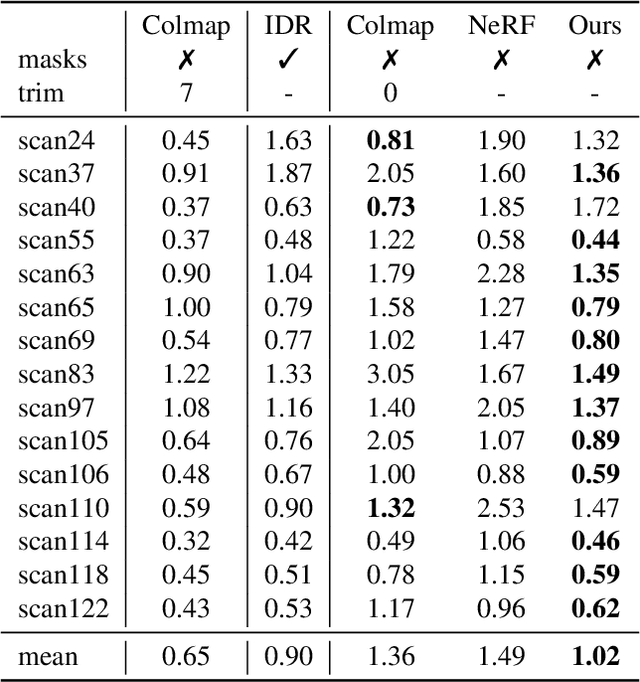


Abstract:Neural implicit 3D representations have emerged as a powerful paradigm for reconstructing surfaces from multi-view images and synthesizing novel views. Unfortunately, existing methods such as DVR or IDR require accurate per-pixel object masks as supervision. At the same time, neural radiance fields have revolutionized novel view synthesis. However, NeRF's estimated volume density does not admit accurate surface reconstruction. Our key insight is that implicit surface models and radiance fields can be formulated in a unified way, enabling both surface and volume rendering using the same model. This unified perspective enables novel, more efficient sampling procedures and the ability to reconstruct accurate surfaces without input masks. We compare our method on the DTU, BlendedMVS, and a synthetic indoor dataset. Our experiments demonstrate that we outperform NeRF in terms of reconstruction quality while performing on par with IDR without requiring masks.
Learning Implicit Surface Light Fields
Mar 27, 2020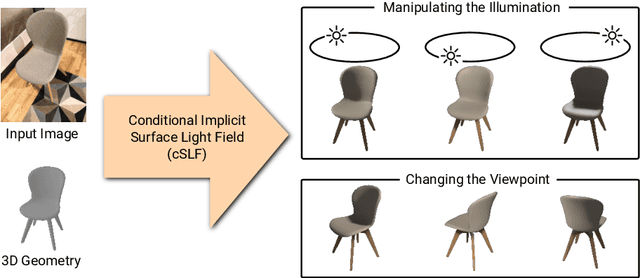
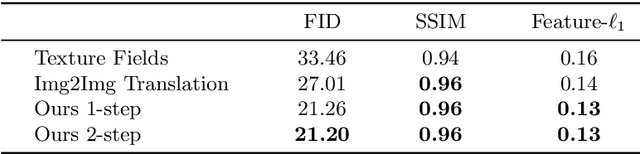
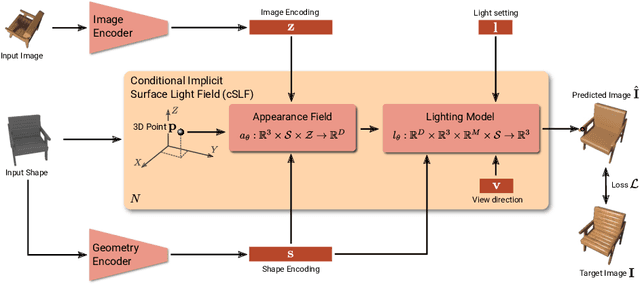
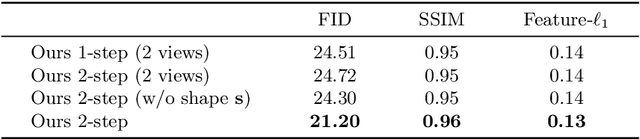
Abstract:Implicit representations of 3D objects have recently achieved impressive results on learning-based 3D reconstruction tasks. While existing works use simple texture models to represent object appearance, photo-realistic image synthesis requires reasoning about the complex interplay of light, geometry and surface properties. In this work, we propose a novel implicit representation for capturing the visual appearance of an object in terms of its surface light field. In contrast to existing representations, our implicit model represents surface light fields in a continuous fashion and independent of the geometry. Moreover, we condition the surface light field with respect to the location and color of a small light source. Compared to traditional surface light field models, this allows us to manipulate the light source and relight the object using environment maps. We further demonstrate the capabilities of our model to predict the visual appearance of an unseen object from a single real RGB image and corresponding 3D shape information. As evidenced by our experiments, our model is able to infer rich visual appearance including shadows and specular reflections. Finally, we show that the proposed representation can be embedded into a variational auto-encoder for generating novel appearances that conform to the specified illumination conditions.
Differentiable Volumetric Rendering: Learning Implicit 3D Representations without 3D Supervision
Dec 16, 2019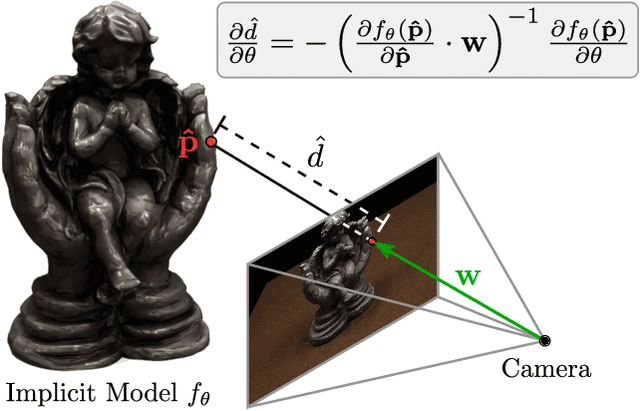
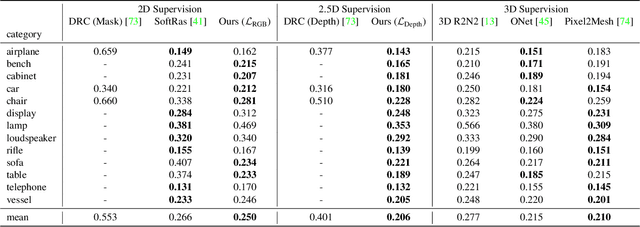
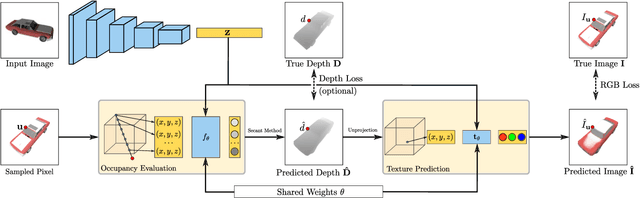
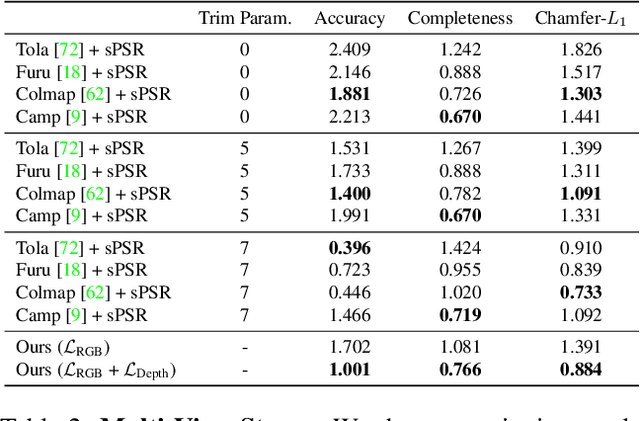
Abstract:Learning-based 3D reconstruction methods have shown impressive results. However, most methods require 3D supervision which is often hard to obtain for real world datasets. Recently, several works have proposed differentiable rendering techniques to train reconstruction models from RGB images. Unfortunately, these approaches are currently restricted to voxel- and mesh-based representations, suffering from discretization or low resolution. In this work, we propose a differentiable rendering formulation for implicit shape and texture representations. Implicit representations have recently gained popularity as they are able to represent shape and texture continuously. Our key insight is that depth gradients can be derived analytically using the concept of implicit differentiation. This allows us to learn implicit shape and texture representations directly from RGB images. We experimentally show that our single-view reconstructions rival those learned with full 3D supervision. Moreover, we find that our method can be used for multi-view 3D reconstruction, directly resulting in watertight meshes.
Texture Fields: Learning Texture Representations in Function Space
May 17, 2019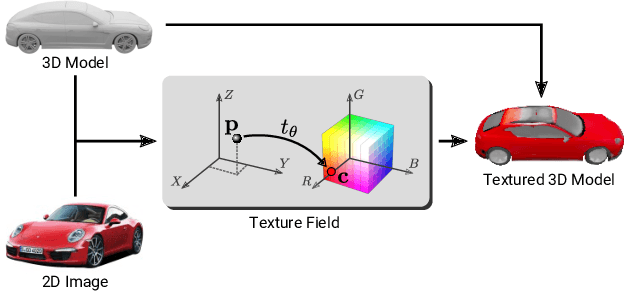
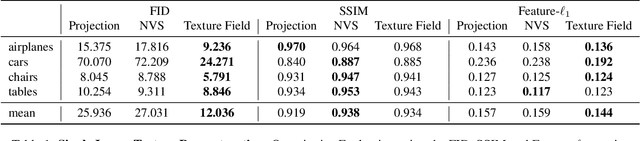
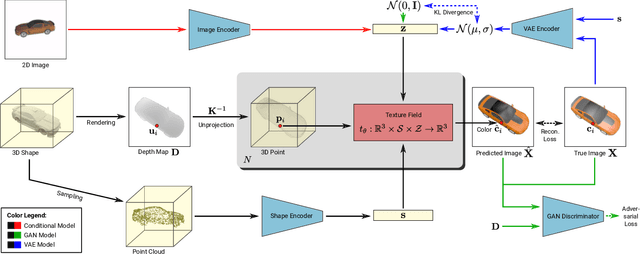
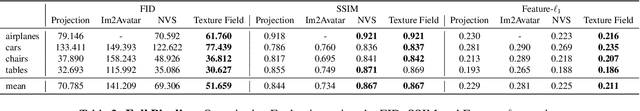
Abstract:In recent years, substantial progress has been achieved in learning-based reconstruction of 3D objects. At the same time, generative models were proposed that can generate highly realistic images. However, despite this success in these closely related tasks, texture reconstruction of 3D objects has received little attention from the research community and state-of-the-art methods are either limited to comparably low resolution or constrained experimental setups. A major reason for these limitations is that common representations of texture are inefficient or hard to interface for modern deep learning techniques. In this paper, we propose Texture Fields, a novel texture representation which is based on regressing a continuous 3D function parameterized with a neural network. Our approach circumvents limiting factors like shape discretization and parameterization, as the proposed texture representation is independent of the shape representation of the 3D object. We show that Texture Fields are able to represent high frequency texture and naturally blend with modern deep learning techniques. Experimentally, we find that Texture Fields compare favorably to state-of-the-art methods for conditional texture reconstruction of 3D objects and enable learning of probabilistic generative models for texturing unseen 3D models. We believe that Texture Fields will become an important building block for the next generation of generative 3D models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge