Michael Mock
Fraunhofer Institute for Intelligent Analysis and Information Systems IAIS Sankt Augustin, Germany
Textual Data Bias Detection and Mitigation -- An Extensible Pipeline with Experimental Evaluation
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Textual data used to train large language models (LLMs) exhibits multifaceted bias manifestations encompassing harmful language and skewed demographic distributions. Regulations such as the European AI Act require identifying and mitigating biases against protected groups in data, with the ultimate goal of preventing unfair model outputs. However, practical guidance and operationalization are lacking. We propose a comprehensive data bias detection and mitigation pipeline comprising four components that address two data bias types, namely representation bias and (explicit) stereotypes for a configurable sensitive attribute. First, we leverage LLM-generated word lists created based on quality criteria to detect relevant group labels. Second, representation bias is quantified using the Demographic Representation Score. Third, we detect and mitigate stereotypes using sociolinguistically informed filtering. Finally, we compensate representation bias through Grammar- and Context-Aware Counterfactual Data Augmentation. We conduct a two-fold evaluation using the examples of gender, religion and age. First, the effectiveness of each individual component on data debiasing is evaluated through human validation and baseline comparison. The findings demonstrate that we successfully reduce representation bias and (explicit) stereotypes in a text dataset. Second, the effect of data debiasing on model bias reduction is evaluated by bias benchmarking of several models (0.6B-8B parameters), fine-tuned on the debiased text dataset. This evaluation reveals that LLMs fine-tuned on debiased data do not consistently show improved performance on bias benchmarks, exposing critical gaps in current evaluation methodologies and highlighting the need for targeted data manipulation to address manifested model bias.
Detecting Linguistic Indicators for Stereotype Assessment with Large Language Models
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Social categories and stereotypes are embedded in language and can introduce data bias into Large Language Models (LLMs). Despite safeguards, these biases often persist in model behavior, potentially leading to representational harm in outputs. While sociolinguistic research provides valuable insights into the formation of stereotypes, NLP approaches for stereotype detection rarely draw on this foundation and often lack objectivity, precision, and interpretability. To fill this gap, in this work we propose a new approach that detects and quantifies the linguistic indicators of stereotypes in a sentence. We derive linguistic indicators from the Social Category and Stereotype Communication (SCSC) framework which indicate strong social category formulation and stereotyping in language, and use them to build a categorization scheme. To automate this approach, we instruct different LLMs using in-context learning to apply the approach to a sentence, where the LLM examines the linguistic properties and provides a basis for a fine-grained assessment. Based on an empirical evaluation of the importance of different linguistic indicators, we learn a scoring function that measures the linguistic indicators of a stereotype. Our annotations of stereotyped sentences show that these indicators are present in these sentences and explain the strength of a stereotype. In terms of model performance, our results show that the models generally perform well in detecting and classifying linguistic indicators of category labels used to denote a category, but sometimes struggle to correctly evaluate the associated behaviors and characteristics. Using more few-shot examples within the prompts, significantly improves performance. Model performance increases with size, as Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct and GPT-4 achieve comparable results that surpass those of Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct, GPT-4-mini and Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct.
Detecting Systematic Weaknesses in Vision Models along Predefined Human-Understandable Dimensions
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Studying systematic weaknesses of DNNs has gained prominence in the last few years with the rising focus on building safe AI systems. Slice discovery methods (SDMs) are prominent algorithmic approaches for finding such systematic weaknesses. They identify top-k semantically coherent slices/subsets of data where a DNN-under-test has low performance. For being directly useful, e.g., as evidences in a safety argumentation, slices should be aligned with human-understandable (safety-relevant) dimensions, which, for example, are defined by safety and domain experts as parts of the operational design domain (ODD). While straightforward for structured data, the lack of semantic metadata makes these investigations challenging for unstructured data. Therefore, we propose a complete workflow which combines contemporary foundation models with algorithms for combinatorial search that consider structured data and DNN errors for finding systematic weaknesses in images. In contrast to existing approaches, ours identifies weak slices that are in line with predefined human-understandable dimensions. As the workflow includes foundation models, its intermediate and final results may not always be exact. Therefore, we build into our workflow an approach to address the impact of noisy metadata. We evaluate our approach w.r.t. its quality on four popular computer vision datasets, including autonomous driving datasets like Cityscapes, BDD100k, and RailSem19, while using multiple state-of-the-art models as DNNs-under-test.
Developing trustworthy AI applications with foundation models
May 08, 2024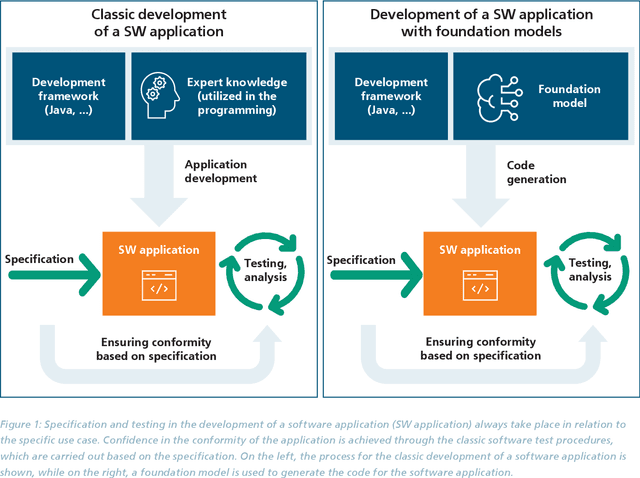
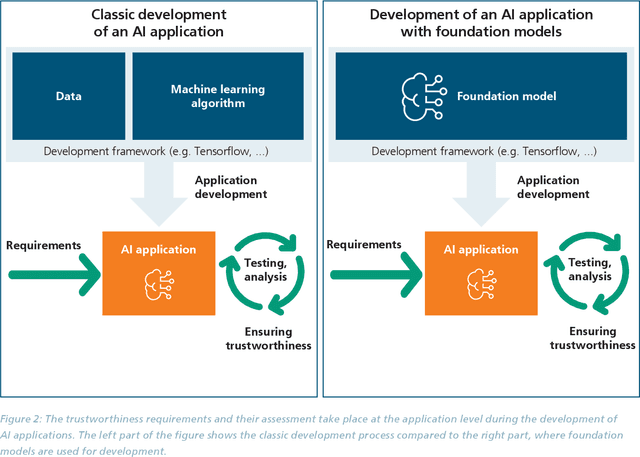

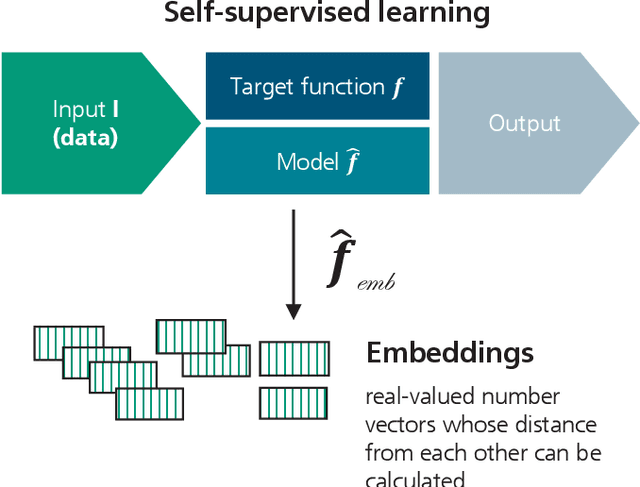
Abstract:The trustworthiness of AI applications has been the subject of recent research and is also addressed in the EU's recently adopted AI Regulation. The currently emerging foundation models in the field of text, speech and image processing offer completely new possibilities for developing AI applications. This whitepaper shows how the trustworthiness of an AI application developed with foundation models can be evaluated and ensured. For this purpose, the application-specific, risk-based approach for testing and ensuring the trustworthiness of AI applications, as developed in the 'AI Assessment Catalog - Guideline for Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence' by Fraunhofer IAIS, is transferred to the context of foundation models. Special consideration is given to the fact that specific risks of foundation models can have an impact on the AI application and must also be taken into account when checking trustworthiness. Chapter 1 of the white paper explains the fundamental relationship between foundation models and AI applications based on them in terms of trustworthiness. Chapter 2 provides an introduction to the technical construction of foundation models and Chapter 3 shows how AI applications can be developed based on them. Chapter 4 provides an overview of the resulting risks regarding trustworthiness. Chapter 5 shows which requirements for AI applications and foundation models are to be expected according to the draft of the European Union's AI Regulation and Chapter 6 finally shows the system and procedure for meeting trustworthiness requirements.
Assessing Systematic Weaknesses of DNNs using Counterfactuals
Aug 03, 2023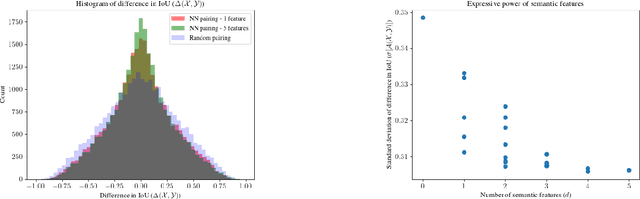
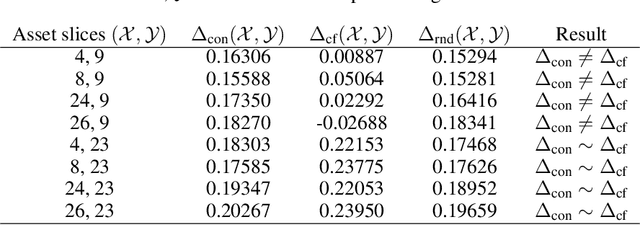
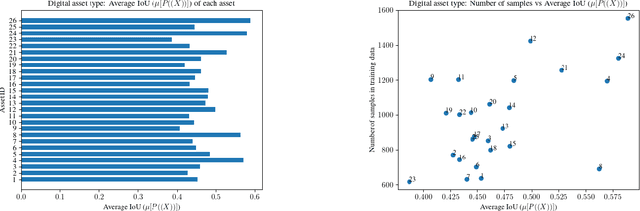

Abstract:With the advancement of DNNs into safety-critical applications, testing approaches for such models have gained more attention. A current direction is the search for and identification of systematic weaknesses that put safety assumptions based on average performance values at risk. Such weaknesses can take on the form of (semantically coherent) subsets or areas in the input space where a DNN performs systematically worse than its expected average. However, it is non-trivial to attribute the reason for such observed low performances to the specific semantic features that describe the subset. For instance, inhomogeneities within the data w.r.t. other (non-considered) attributes might distort results. However, taking into account all (available) attributes and their interaction is often computationally highly expensive. Inspired by counterfactual explanations, we propose an effective and computationally cheap algorithm to validate the semantic attribution of existing subsets, i.e., to check whether the identified attribute is likely to have caused the degraded performance. We demonstrate this approach on an example from the autonomous driving domain using highly annotated simulated data, where we show for a semantic segmentation model that (i) performance differences among the different pedestrian assets exist, but (ii) only in some cases is the asset type itself the reason for this reduction in the performance.
Using ScrutinAI for Visual Inspection of DNN Performance in a Medical Use Case
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:Our Visual Analytics (VA) tool ScrutinAI supports human analysts to investigate interactively model performanceand data sets. Model performance depends on labeling quality to a large extent. In particular in medical settings, generation of high quality labels requires in depth expert knowledge and is very costly. Often, data sets are labeled by collecting opinions of groups of experts. We use our VA tool to analyse the influence of label variations between different experts on the model performance. ScrutinAI facilitates to perform a root cause analysis that distinguishes weaknesses of deep neural network (DNN) models caused by varying or missing labeling quality from true weaknesses. We scrutinize the overall detection of intracranial hemorrhages and the more subtle differentiation between subtypes in a publicly available data set.
Guideline for Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence -- AI Assessment Catalog
Jun 20, 2023Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has made impressive progress in recent years and represents a key technology that has a crucial impact on the economy and society. However, it is clear that AI and business models based on it can only reach their full potential if AI applications are developed according to high quality standards and are effectively protected against new AI risks. For instance, AI bears the risk of unfair treatment of individuals when processing personal data e.g., to support credit lending or staff recruitment decisions. The emergence of these new risks is closely linked to the fact that the behavior of AI applications, particularly those based on Machine Learning (ML), is essentially learned from large volumes of data and is not predetermined by fixed programmed rules. Thus, the issue of the trustworthiness of AI applications is crucial and is the subject of numerous major publications by stakeholders in politics, business and society. In addition, there is mutual agreement that the requirements for trustworthy AI, which are often described in an abstract way, must now be made clear and tangible. One challenge to overcome here relates to the fact that the specific quality criteria for an AI application depend heavily on the application context and possible measures to fulfill them in turn depend heavily on the AI technology used. Lastly, practical assessment procedures are needed to evaluate whether specific AI applications have been developed according to adequate quality standards. This AI assessment catalog addresses exactly this point and is intended for two target groups: Firstly, it provides developers with a guideline for systematically making their AI applications trustworthy. Secondly, it guides assessors and auditors on how to examine AI applications for trustworthiness in a structured way.
Inspect, Understand, Overcome: A Survey of Practical Methods for AI Safety
Apr 29, 2021Abstract:The use of deep neural networks (DNNs) in safety-critical applications like mobile health and autonomous driving is challenging due to numerous model-inherent shortcomings. These shortcomings are diverse and range from a lack of generalization over insufficient interpretability to problems with malicious inputs. Cyber-physical systems employing DNNs are therefore likely to suffer from safety concerns. In recent years, a zoo of state-of-the-art techniques aiming to address these safety concerns has emerged. This work provides a structured and broad overview of them. We first identify categories of insufficiencies to then describe research activities aiming at their detection, quantification, or mitigation. Our paper addresses both machine learning experts and safety engineers: The former ones might profit from the broad range of machine learning topics covered and discussions on limitations of recent methods. The latter ones might gain insights into the specifics of modern ML methods. We moreover hope that our contribution fuels discussions on desiderata for ML systems and strategies on how to propel existing approaches accordingly.
Patch Shortcuts: Interpretable Proxy Models Efficiently Find Black-Box Vulnerabilities
Apr 22, 2021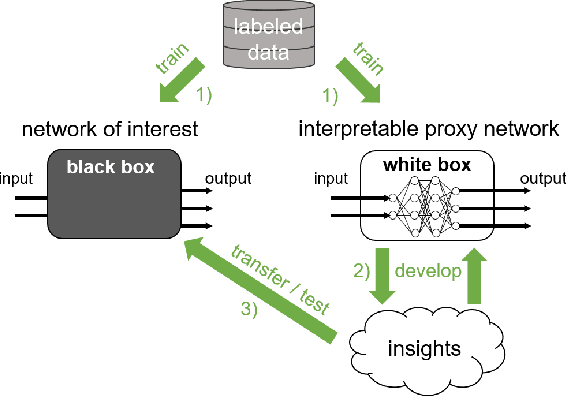
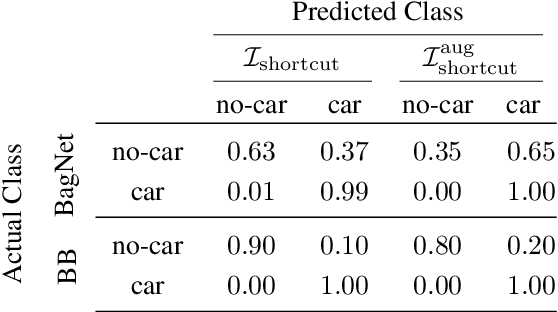

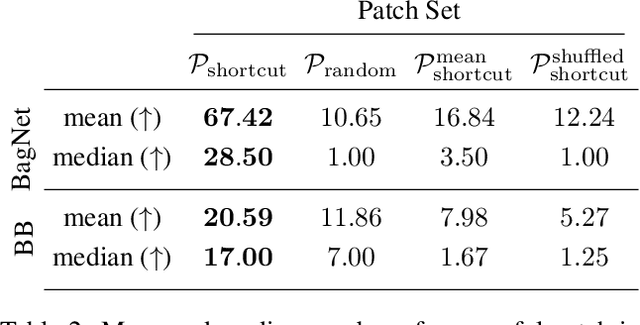
Abstract:An important pillar for safe machine learning (ML) is the systematic mitigation of weaknesses in neural networks to afford their deployment in critical applications. An ubiquitous class of safety risks are learned shortcuts, i.e. spurious correlations a network exploits for its decisions that have no semantic connection to the actual task. Networks relying on such shortcuts bear the risk of not generalizing well to unseen inputs. Explainability methods help to uncover such network vulnerabilities. However, many of these techniques are not directly applicable if access to the network is constrained, in so-called black-box setups. These setups are prevalent when using third-party ML components. To address this constraint, we present an approach to detect learned shortcuts using an interpretable-by-design network as a proxy to the black-box model of interest. Leveraging the proxy's guarantees on introspection we automatically extract candidates for learned shortcuts. Their transferability to the black box is validated in a systematic fashion. Concretely, as proxy model we choose a BagNet, which bases its decisions purely on local image patches. We demonstrate on the autonomous driving dataset A2D2 that extracted patch shortcuts significantly influence the black box model. By efficiently identifying such patch-based vulnerabilities, we contribute to safer ML models.
Communication-Efficient Distributed Online Learning with Kernels
Nov 28, 2019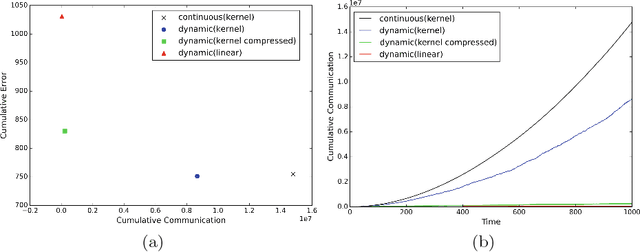
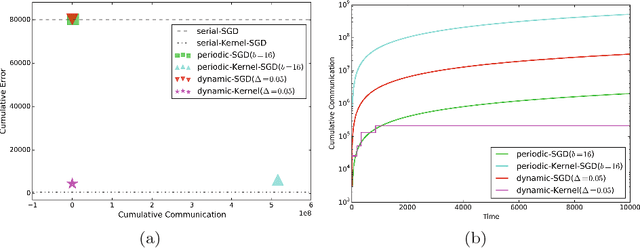
Abstract:We propose an efficient distributed online learning protocol for low-latency real-time services. It extends a previously presented protocol to kernelized online learners that represent their models by a support vector expansion. While such learners often achieve higher predictive performance than their linear counterparts, communicating the support vector expansions becomes inefficient for large numbers of support vectors. The proposed extension allows for a larger class of online learning algorithms---including those alleviating the problem above through model compression. In addition, we characterize the quality of the proposed protocol by introducing a novel criterion that requires the communication to be bounded by the loss suffered.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge