Rebekka Görge
Fraunhofer Institute for Intelligent Analysis and Information Systems IAIS Sankt Augustin, Germany
Textual Data Bias Detection and Mitigation -- An Extensible Pipeline with Experimental Evaluation
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Textual data used to train large language models (LLMs) exhibits multifaceted bias manifestations encompassing harmful language and skewed demographic distributions. Regulations such as the European AI Act require identifying and mitigating biases against protected groups in data, with the ultimate goal of preventing unfair model outputs. However, practical guidance and operationalization are lacking. We propose a comprehensive data bias detection and mitigation pipeline comprising four components that address two data bias types, namely representation bias and (explicit) stereotypes for a configurable sensitive attribute. First, we leverage LLM-generated word lists created based on quality criteria to detect relevant group labels. Second, representation bias is quantified using the Demographic Representation Score. Third, we detect and mitigate stereotypes using sociolinguistically informed filtering. Finally, we compensate representation bias through Grammar- and Context-Aware Counterfactual Data Augmentation. We conduct a two-fold evaluation using the examples of gender, religion and age. First, the effectiveness of each individual component on data debiasing is evaluated through human validation and baseline comparison. The findings demonstrate that we successfully reduce representation bias and (explicit) stereotypes in a text dataset. Second, the effect of data debiasing on model bias reduction is evaluated by bias benchmarking of several models (0.6B-8B parameters), fine-tuned on the debiased text dataset. This evaluation reveals that LLMs fine-tuned on debiased data do not consistently show improved performance on bias benchmarks, exposing critical gaps in current evaluation methodologies and highlighting the need for targeted data manipulation to address manifested model bias.
Detecting Linguistic Indicators for Stereotype Assessment with Large Language Models
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Social categories and stereotypes are embedded in language and can introduce data bias into Large Language Models (LLMs). Despite safeguards, these biases often persist in model behavior, potentially leading to representational harm in outputs. While sociolinguistic research provides valuable insights into the formation of stereotypes, NLP approaches for stereotype detection rarely draw on this foundation and often lack objectivity, precision, and interpretability. To fill this gap, in this work we propose a new approach that detects and quantifies the linguistic indicators of stereotypes in a sentence. We derive linguistic indicators from the Social Category and Stereotype Communication (SCSC) framework which indicate strong social category formulation and stereotyping in language, and use them to build a categorization scheme. To automate this approach, we instruct different LLMs using in-context learning to apply the approach to a sentence, where the LLM examines the linguistic properties and provides a basis for a fine-grained assessment. Based on an empirical evaluation of the importance of different linguistic indicators, we learn a scoring function that measures the linguistic indicators of a stereotype. Our annotations of stereotyped sentences show that these indicators are present in these sentences and explain the strength of a stereotype. In terms of model performance, our results show that the models generally perform well in detecting and classifying linguistic indicators of category labels used to denote a category, but sometimes struggle to correctly evaluate the associated behaviors and characteristics. Using more few-shot examples within the prompts, significantly improves performance. Model performance increases with size, as Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct and GPT-4 achieve comparable results that surpass those of Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct, GPT-4-mini and Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct.
Do Multilingual Large Language Models Mitigate Stereotype Bias?
Jul 09, 2024



Abstract:While preliminary findings indicate that multilingual LLMs exhibit reduced bias compared to monolingual ones, a comprehensive understanding of the effect of multilingual training on bias mitigation, is lacking. This study addresses this gap by systematically training six LLMs of identical size (2.6B parameters) and architecture: five monolingual models (English, German, French, Italian, and Spanish) and one multilingual model trained on an equal distribution of data across these languages, all using publicly available data. To ensure robust evaluation, standard bias benchmarks were automatically translated into the five target languages and verified for both translation quality and bias preservation by human annotators. Our results consistently demonstrate that multilingual training effectively mitigates bias. Moreover, we observe that multilingual models achieve not only lower bias but also superior prediction accuracy when compared to monolingual models with the same amount of training data, model architecture, and size.
LLMs and Memorization: On Quality and Specificity of Copyright Compliance
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Memorization in large language models (LLMs) is a growing concern. LLMs have been shown to easily reproduce parts of their training data, including copyrighted work. This is an important problem to solve, as it may violate existing copyright laws as well as the European AI Act. In this work, we propose a systematic analysis to quantify the extent of potential copyright infringements in LLMs using European law as an example. Unlike previous work, we evaluate instruction-finetuned models in a realistic end-user scenario. Our analysis builds on a proposed threshold of 160 characters, which we borrow from the German Copyright Service Provider Act and a fuzzy text matching algorithm to identify potentially copyright-infringing textual reproductions. The specificity of countermeasures against copyright infringement is analyzed by comparing model behavior on copyrighted and public domain data. We investigate what behaviors models show instead of producing protected text (such as refusal or hallucination) and provide a first legal assessment of these behaviors. We find that there are huge differences in copyright compliance, specificity, and appropriate refusal among popular LLMs. Alpaca, GPT 4, GPT 3.5, and Luminous perform best in our comparison, with OpenGPT-X, Alpaca, and Luminous producing a particularly low absolute number of potential copyright violations. Code will be published soon.
Developing trustworthy AI applications with foundation models
May 08, 2024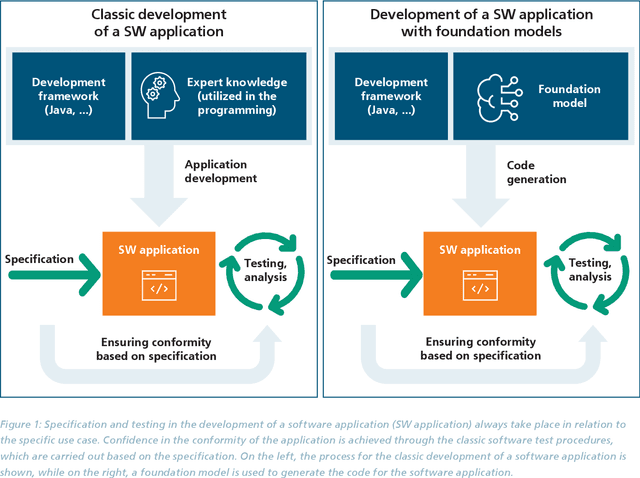
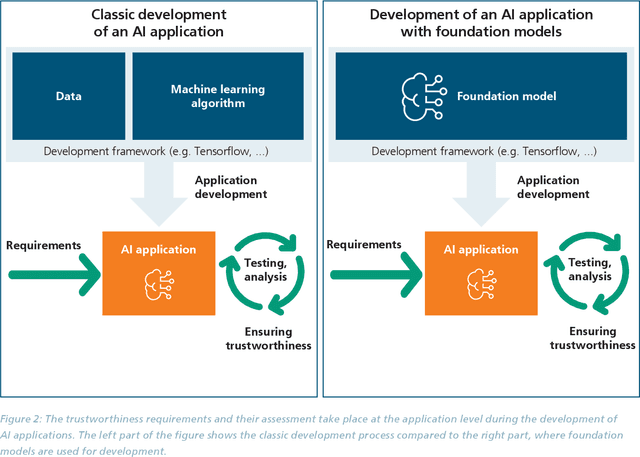

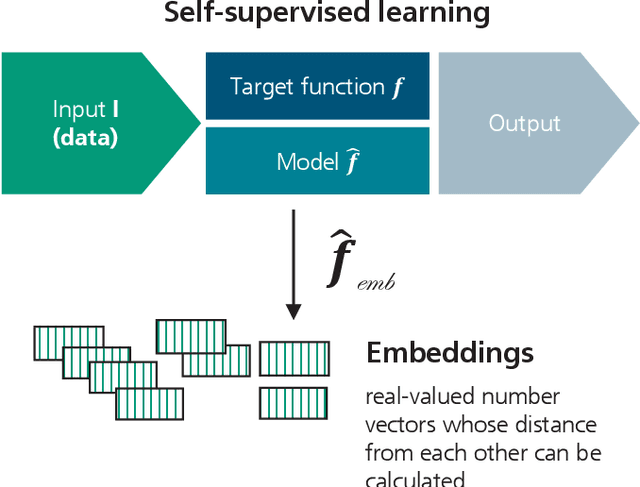
Abstract:The trustworthiness of AI applications has been the subject of recent research and is also addressed in the EU's recently adopted AI Regulation. The currently emerging foundation models in the field of text, speech and image processing offer completely new possibilities for developing AI applications. This whitepaper shows how the trustworthiness of an AI application developed with foundation models can be evaluated and ensured. For this purpose, the application-specific, risk-based approach for testing and ensuring the trustworthiness of AI applications, as developed in the 'AI Assessment Catalog - Guideline for Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence' by Fraunhofer IAIS, is transferred to the context of foundation models. Special consideration is given to the fact that specific risks of foundation models can have an impact on the AI application and must also be taken into account when checking trustworthiness. Chapter 1 of the white paper explains the fundamental relationship between foundation models and AI applications based on them in terms of trustworthiness. Chapter 2 provides an introduction to the technical construction of foundation models and Chapter 3 shows how AI applications can be developed based on them. Chapter 4 provides an overview of the resulting risks regarding trustworthiness. Chapter 5 shows which requirements for AI applications and foundation models are to be expected according to the draft of the European Union's AI Regulation and Chapter 6 finally shows the system and procedure for meeting trustworthiness requirements.
Using ScrutinAI for Visual Inspection of DNN Performance in a Medical Use Case
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:Our Visual Analytics (VA) tool ScrutinAI supports human analysts to investigate interactively model performanceand data sets. Model performance depends on labeling quality to a large extent. In particular in medical settings, generation of high quality labels requires in depth expert knowledge and is very costly. Often, data sets are labeled by collecting opinions of groups of experts. We use our VA tool to analyse the influence of label variations between different experts on the model performance. ScrutinAI facilitates to perform a root cause analysis that distinguishes weaknesses of deep neural network (DNN) models caused by varying or missing labeling quality from true weaknesses. We scrutinize the overall detection of intracranial hemorrhages and the more subtle differentiation between subtypes in a publicly available data set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge