Akbar Karimi
IMP Lab, Department of Engineering and Architecture, University of Parma, Parma, Italy
Encoder Fine-tuning with Stochastic Sampling Outperforms Open-weight GPT in Astronomy Knowledge Extraction
Nov 11, 2025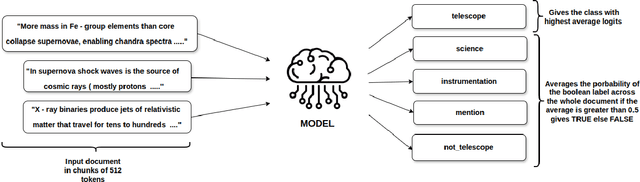
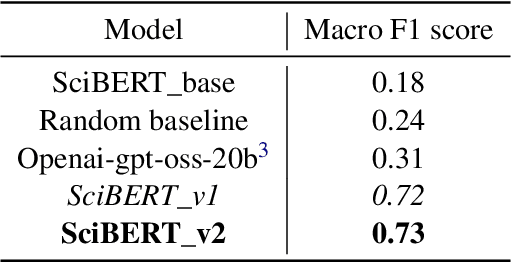
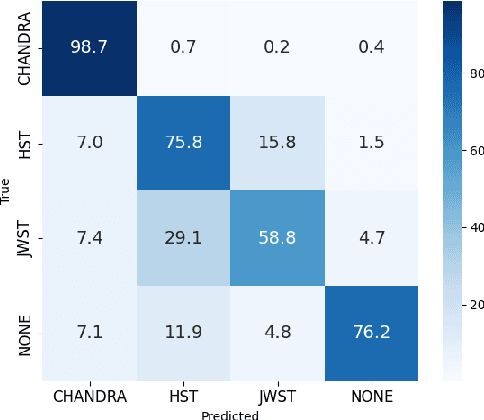
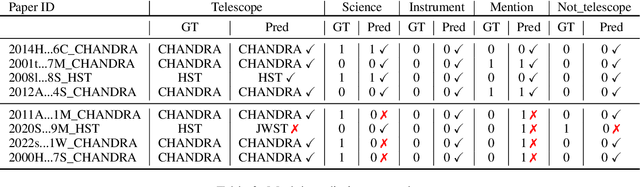
Abstract:Scientific literature in astronomy is rapidly expanding, making it increasingly important to automate the extraction of key entities and contextual information from research papers. In this paper, we present an encoder-based system for extracting knowledge from astronomy articles. Our objective is to develop models capable of classifying telescope references, detecting auxiliary semantic attributes, and recognizing instrument mentions from textual content. To this end, we implement a multi-task transformer-based system built upon the SciBERT model and fine-tuned for astronomy corpora classification. To carry out the fine-tuning, we stochastically sample segments from the training data and use majority voting over the test segments at inference time. Our system, despite its simplicity and low-cost implementation, significantly outperforms the open-weight GPT baseline.
More Agents Helps but Adversarial Robustness Gap Persists
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:When LLM agents work together, they seem to be more powerful than a single LLM in mathematical question answering. However, are they also more robust to adversarial inputs? We investigate this question using adversarially perturbed math questions. These perturbations include punctuation noise with three intensities (10, 30, and 50 percent), plus real-world and human-like typos (WikiTypo, R2ATA). Using a unified sampling-and-voting framework (Agent Forest), we evaluate six open-source models (Qwen3-4B/14B, Llama3.1-8B, Mistral-7B, Gemma3-4B/12B) across four benchmarks (GSM8K, MATH, MMLU-Math, MultiArith), with various numbers of agents n from one to 25 (1, 2, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25). Our findings show that (1) Noise type matters: punctuation noise harm scales with its severity, and the human typos remain the dominant bottleneck, yielding the largest gaps to Clean accuracy and the highest ASR even with a large number of agents. And (2) Collaboration reliably improves accuracy as the number of agents, n, increases, with the largest gains from one to five agents and diminishing returns beyond 10 agents. However, the adversarial robustness gap persists regardless of the agent count.
ArithmAttack: Evaluating Robustness of LLMs to Noisy Context in Math Problem Solving
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive capabilities in math problem-solving tasks, their robustness to noisy inputs is not well-studied. In this work, we propose ArithmAttack to examine how robust the LLMs are when they encounter noisy prompts that contain extra noise in the form of punctuation marks. While being easy to implement, ArithmAttack does not cause any information loss since words are not added or deleted from the context. We evaluate the robustness of seven LLMs, including LLama3, Mistral, and Mathstral, on noisy GSM8K and MultiArith datasets. Our experiments suggest that all the studied models show vulnerability to such noise, with more noise leading to poorer performances.
Exploring Robustness of LLMs to Sociodemographically-Conditioned Paraphrasing
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive performance in various NLP tasks. However, there are concerns about their reliability in different domains of linguistic variations. Many works have proposed robustness evaluation measures for local adversarial attacks, but we need globally robust models unbiased to different language styles. We take a broader approach to explore a wider range of variations across sociodemographic dimensions to perform structured reliability tests on the reasoning capacity of language models. We extend the SocialIQA dataset to create diverse paraphrased sets conditioned on sociodemographic styles. The assessment aims to provide a deeper understanding of LLMs in (a) their capability of generating demographic paraphrases with engineered prompts and (b) their reasoning capabilities in real-world, complex language scenarios. We also explore measures such as perplexity, explainability, and ATOMIC performance of paraphrases for fine-grained reliability analysis of LLMs on these sets. We find that demographic-specific paraphrasing significantly impacts the performance of language models, indicating that the subtleties of language variations remain a significant challenge. The code and dataset will be made available for reproducibility and future research.
Exploring Robustness of Multilingual LLMs on Real-World Noisy Data
Jan 14, 2025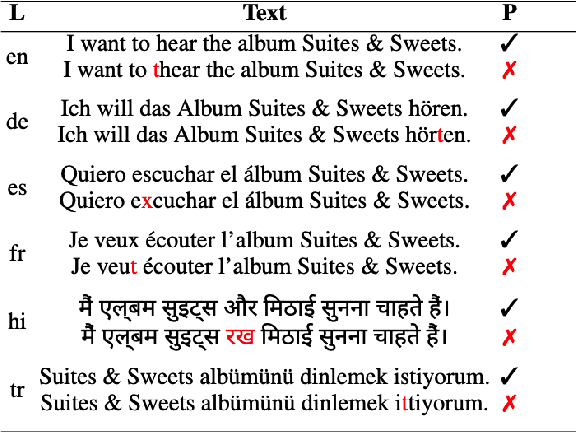
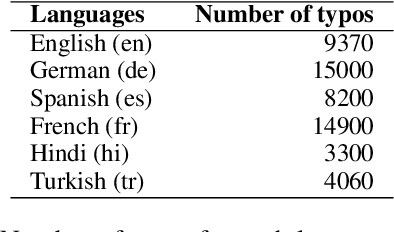
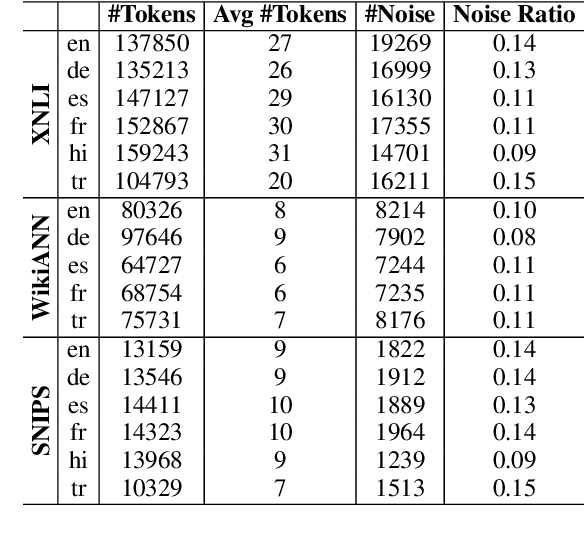
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on Web data that might contain spelling errors made by humans. But do they become robust to similar real-world noise? In this paper, we investigate the effect of real-world spelling mistakes on the performance of 9 language models, with parameters ranging from 0.2B to 13B, in 3 different NLP tasks, namely Natural Language Inference (NLI), Name Entity Recognition (NER), and Intent Classification (IC). We perform our experiments on 6 different languages and build a dictionary of real-world noise for them using the Wikipedia edit history. We show that the performance gap of the studied models on the clean and noisy test data averaged across all the datasets and languages ranges from 2.3 to 4.3 absolute percentage points. In addition, mT5 models, in general, show more robustness compared to BLOOM, Falcon, and BERT-like models. In particular, mT5 (13B), was the most robust on average overall, across the 3 tasks, and in 4 of the 6 languages.
Enforcing Fundamental Relations via Adversarial Attacks on Input Parameter Correlations
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:Correlations between input parameters play a crucial role in many scientific classification tasks, since these are often related to fundamental laws of nature. For example, in high energy physics, one of the common deep learning use-cases is the classification of signal and background processes in particle collisions. In many such cases, the fundamental principles of the correlations between observables are often better understood than the actual distributions of the observables themselves. In this work, we present a new adversarial attack algorithm called Random Distribution Shuffle Attack (RDSA), emphasizing the correlations between observables in the network rather than individual feature characteristics. Correct application of the proposed novel attack can result in a significant improvement in classification performance - particularly in the context of data augmentation - when using the generated adversaries within adversarial training. Given that correlations between input features are also crucial in many other disciplines. We demonstrate the RDSA effectiveness on six classification tasks, including two particle collision challenges (using CERN Open Data), hand-written digit recognition (MNIST784), human activity recognition (HAR), weather forecasting (Rain in Australia), and ICU patient mortality (MIMIC-IV), demonstrating a general use case beyond fundamental physics for this new type of adversarial attack algorithms.
Do Multilingual Large Language Models Mitigate Stereotype Bias?
Jul 09, 2024



Abstract:While preliminary findings indicate that multilingual LLMs exhibit reduced bias compared to monolingual ones, a comprehensive understanding of the effect of multilingual training on bias mitigation, is lacking. This study addresses this gap by systematically training six LLMs of identical size (2.6B parameters) and architecture: five monolingual models (English, German, French, Italian, and Spanish) and one multilingual model trained on an equal distribution of data across these languages, all using publicly available data. To ensure robust evaluation, standard bias benchmarks were automatically translated into the five target languages and verified for both translation quality and bias preservation by human annotators. Our results consistently demonstrate that multilingual training effectively mitigates bias. Moreover, we observe that multilingual models achieve not only lower bias but also superior prediction accuracy when compared to monolingual models with the same amount of training data, model architecture, and size.
Self-Balanced R-CNN for Instance Segmentation
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Current state-of-the-art two-stage models on instance segmentation task suffer from several types of imbalances. In this paper, we address the Intersection over the Union (IoU) distribution imbalance of positive input Regions of Interest (RoIs) during the training of the second stage. Our Self-Balanced R-CNN (SBR-CNN), an evolved version of the Hybrid Task Cascade (HTC) model, brings brand new loop mechanisms of bounding box and mask refinements. With an improved Generic RoI Extraction (GRoIE), we also address the feature-level imbalance at the Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) level, originated by a non-uniform integration between low- and high-level features from the backbone layers. In addition, the redesign of the architecture heads toward a fully convolutional approach with FCC further reduces the number of parameters and obtains more clues to the connection between the task to solve and the layers used. Moreover, our SBR-CNN model shows the same or even better improvements if adopted in conjunction with other state-of-the-art models. In fact, with a lightweight ResNet-50 as backbone, evaluated on COCO minival 2017 dataset, our model reaches 45.3% and 41.5% AP for object detection and instance segmentation, with 12 epochs and without extra tricks. The code is available at https://github.com/IMPLabUniPr/mmdetection/tree/sbr_cnn
CAISA at SemEval-2023 Task 8: Counterfactual Data Augmentation for Mitigating Class Imbalance in Causal Claim Identification
Jun 01, 2023



Abstract:The class imbalance problem can cause machine learning models to produce an undesirable performance on the minority class as well as the whole dataset. Using data augmentation techniques to increase the number of samples is one way to tackle this problem. We introduce a novel counterfactual data augmentation by verb replacement for the identification of medical claims. In addition, we investigate the impact of this method and compare it with 3 other data augmentation techniques, showing that the proposed method can result in a significant (relative) improvement in the minority class.
Improving Localization for Semi-Supervised Object Detection
Jun 21, 2022Abstract:Nowadays, Semi-Supervised Object Detection (SSOD) is a hot topic, since, while it is rather easy to collect images for creating a new dataset, labeling them is still an expensive and time-consuming task. One of the successful methods to take advantage of raw images on a Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) setting is the Mean Teacher technique, where the operations of pseudo-labeling by the Teacher and the Knowledge Transfer from the Student to the Teacher take place simultaneously. However, the pseudo-labeling by thresholding is not the best solution since the confidence value is not strictly related to the prediction uncertainty, not permitting to safely filter predictions. In this paper, we introduce an additional classification task for bounding box localization to improve the filtering of the predicted bounding boxes and obtain higher quality on Student training. Furthermore, we empirically prove that bounding box regression on the unsupervised part can equally contribute to the training as much as category classification. Our experiments show that our IL-net (Improving Localization net) increases SSOD performance by 1.14% AP on COCO dataset in limited-annotation regime. The code is available at https://github.com/IMPLabUniPr/unbiased-teacher/tree/ilnet
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge