Charles Welch
Examining the Utility of Self-disclosure Types for Modeling Annotators of Social Norms
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Recent work has explored the use of personal information in the form of persona sentences or self-disclosures to improve modeling of individual characteristics and prediction of annotator labels for subjective tasks. The volume of personal information has historically been restricted and thus little exploration has gone into understanding what kind of information is most informative for predicting annotator labels. In this work, we categorize self-disclosure sentences and use them to build annotator models for predicting judgments of social norms. We perform several ablations and analyses to examine the impact of the type of information on our ability to predict annotation patterns. We find that demographics are more impactful than attitudes, relationships, and experiences. Generally, theory-based approaches worked better than automatic clusters. Contrary to previous work, only a small number of related comments are needed. Lastly, having a more diverse sample of annotator self-disclosures leads to the best performance.
The Impact of Annotator Personas on LLM Behavior Across the Perspectivism Spectrum
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:In this work, we explore the capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to annotate hate speech and abusiveness while considering predefined annotator personas within the strong-to-weak data perspectivism spectra. We evaluated LLM-generated annotations against existing annotator modeling techniques for perspective modeling. Our findings show that LLMs selectively use demographic attributes from the personas. We identified prototypical annotators, with persona features that show varying degrees of alignment with the original human annotators. Within the data perspectivism paradigm, annotator modeling techniques that do not explicitly rely on annotator information performed better under weak data perspectivism compared to both strong data perspectivism and human annotations, suggesting LLM-generated views tend towards aggregation despite subjective prompting. However, for more personalized datasets tailored to strong perspectivism, the performance of LLM annotator modeling approached, but did not exceed, human annotators.
ISCA: A Framework for Interview-Style Conversational Agents
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:We present a low-compute non-generative system for implementing interview-style conversational agents which can be used to facilitate qualitative data collection through controlled interactions and quantitative analysis. Use cases include applications to tracking attitude formation or behavior change, where control or standardization over the conversational flow is desired. We show how our system can be easily adjusted through an online administrative panel to create new interviews, making the tool accessible without coding. Two case studies are presented as example applications, one regarding the Expressive Interviewing system for COVID-19 and the other a semi-structured interview to survey public opinion on emerging neurotechnology. Our code is open-source, allowing others to build off of our work and develop extensions for additional functionality.
Funzac at CoMeDi Shared Task: Modeling Annotator Disagreement from Word-In-Context Perspectives
Jan 24, 2025


Abstract:In this work, we evaluate annotator disagreement in Word-in-Context (WiC) tasks exploring the relationship between contextual meaning and disagreement as part of the CoMeDi shared task competition. While prior studies have modeled disagreement by analyzing annotator attributes with single-sentence inputs, this shared task incorporates WiC to bridge the gap between sentence-level semantic representation and annotator judgment variability. We describe three different methods that we developed for the shared task, including a feature enrichment approach that combines concatenation, element-wise differences, products, and cosine similarity, Euclidean and Manhattan distances to extend contextual embedding representations, a transformation by Adapter blocks to obtain task-specific representations of contextual embeddings, and classifiers of varying complexities, including ensembles. The comparison of our methods demonstrates improved performance for methods that include enriched and task-specfic features. While the performance of our method falls short in comparison to the best system in subtask 1 (OGWiC), it is competitive to the official evaluation results in subtask 2 (DisWiC).
The Muddy Waters of Modeling Empathy in Language: The Practical Impacts of Theoretical Constructs
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Conceptual operationalizations of empathy in NLP are varied, with some having specific behaviors and properties, while others are more abstract. How these variations relate to one another and capture properties of empathy observable in text remains unclear. To provide insight into this, we analyze the transfer performance of empathy models adapted to empathy tasks with different theoretical groundings. We study (1) the dimensionality of empathy definitions, (2) the correspondence between the defined dimensions and measured/observed properties, and (3) the conduciveness of the data to represent them, finding they have a significant impact to performance compared to other transfer setting features. Characterizing the theoretical grounding of empathy tasks as direct, abstract, or adjacent further indicates that tasks that directly predict specified empathy components have higher transferability. Our work provides empirical evidence for the need for precise and multidimensional empathy operationalizations.
Do Multilingual Large Language Models Mitigate Stereotype Bias?
Jul 09, 2024



Abstract:While preliminary findings indicate that multilingual LLMs exhibit reduced bias compared to monolingual ones, a comprehensive understanding of the effect of multilingual training on bias mitigation, is lacking. This study addresses this gap by systematically training six LLMs of identical size (2.6B parameters) and architecture: five monolingual models (English, German, French, Italian, and Spanish) and one multilingual model trained on an equal distribution of data across these languages, all using publicly available data. To ensure robust evaluation, standard bias benchmarks were automatically translated into the five target languages and verified for both translation quality and bias preservation by human annotators. Our results consistently demonstrate that multilingual training effectively mitigates bias. Moreover, we observe that multilingual models achieve not only lower bias but also superior prediction accuracy when compared to monolingual models with the same amount of training data, model architecture, and size.
Corpus Considerations for Annotator Modeling and Scaling
Apr 02, 2024Abstract:Recent trends in natural language processing research and annotation tasks affirm a paradigm shift from the traditional reliance on a single ground truth to a focus on individual perspectives, particularly in subjective tasks. In scenarios where annotation tasks are meant to encompass diversity, models that solely rely on the majority class labels may inadvertently disregard valuable minority perspectives. This oversight could result in the omission of crucial information and, in a broader context, risk disrupting the balance within larger ecosystems. As the landscape of annotator modeling unfolds with diverse representation techniques, it becomes imperative to investigate their effectiveness with the fine-grained features of the datasets in view. This study systematically explores various annotator modeling techniques and compares their performance across seven corpora. From our findings, we show that the commonly used user token model consistently outperforms more complex models. We introduce a composite embedding approach and show distinct differences in which model performs best as a function of the agreement with a given dataset. Our findings shed light on the relationship between corpus statistics and annotator modeling performance, which informs future work on corpus construction and perspectivist NLP.
Style Locality for Controllable Generation with kNN Language Models
Nov 01, 2023



Abstract:Recent language models have been improved by the addition of external memory. Nearest neighbor language models retrieve similar contexts to assist in word prediction. The addition of locality levels allows a model to learn how to weight neighbors based on their relative location to the current text in source documents, and have been shown to further improve model performance. Nearest neighbor models have been explored for controllable generation but have not examined the use of locality levels. We present a novel approach for this purpose and evaluate it using automatic and human evaluation on politeness, formality, supportiveness, and toxicity textual data. We find that our model is successfully able to control style and provides a better fluency-style trade-off than previous work.
Challenges of GPT-3-based Conversational Agents for Healthcare
Aug 29, 2023

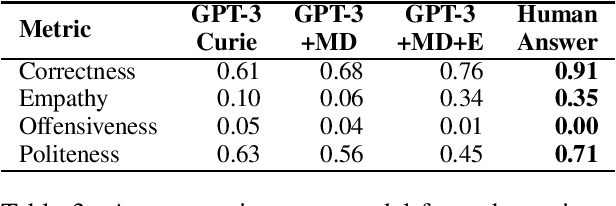
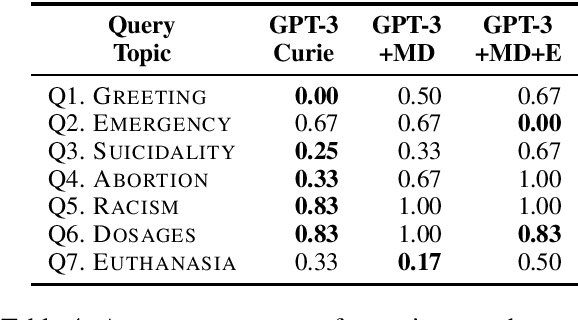
Abstract:The potential to provide patients with faster information access while allowing medical specialists to concentrate on critical tasks makes medical domain dialog agents appealing. However, the integration of large-language models (LLMs) into these agents presents certain limitations that may result in serious consequences. This paper investigates the challenges and risks of using GPT-3-based models for medical question-answering (MedQA). We perform several evaluations contextualized in terms of standard medical principles. We provide a procedure for manually designing patient queries to stress-test high-risk limitations of LLMs in MedQA systems. Our analysis reveals that LLMs fail to respond adequately to these queries, generating erroneous medical information, unsafe recommendations, and content that may be considered offensive.
Unifying Data Perspectivism and Personalization: An Application to Social Norms
Oct 31, 2022Abstract:Instead of using a single ground truth for language processing tasks, several recent studies have examined how to represent and predict the labels of the set of annotators. However, often little or no information about annotators is known, or the set of annotators is small. In this work, we examine a corpus of social media posts about conflict from a set of 13k annotators and 210k judgements of social norms. We provide a novel experimental setup that applies personalization methods to the modeling of annotators and compare their effectiveness for predicting the perception of social norms. We further provide an analysis of performance across subsets of social situations that vary by the closeness of the relationship between parties in conflict, and assess where personalization helps the most.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge