Héctor Allende-Cid
Textual Data Bias Detection and Mitigation -- An Extensible Pipeline with Experimental Evaluation
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Textual data used to train large language models (LLMs) exhibits multifaceted bias manifestations encompassing harmful language and skewed demographic distributions. Regulations such as the European AI Act require identifying and mitigating biases against protected groups in data, with the ultimate goal of preventing unfair model outputs. However, practical guidance and operationalization are lacking. We propose a comprehensive data bias detection and mitigation pipeline comprising four components that address two data bias types, namely representation bias and (explicit) stereotypes for a configurable sensitive attribute. First, we leverage LLM-generated word lists created based on quality criteria to detect relevant group labels. Second, representation bias is quantified using the Demographic Representation Score. Third, we detect and mitigate stereotypes using sociolinguistically informed filtering. Finally, we compensate representation bias through Grammar- and Context-Aware Counterfactual Data Augmentation. We conduct a two-fold evaluation using the examples of gender, religion and age. First, the effectiveness of each individual component on data debiasing is evaluated through human validation and baseline comparison. The findings demonstrate that we successfully reduce representation bias and (explicit) stereotypes in a text dataset. Second, the effect of data debiasing on model bias reduction is evaluated by bias benchmarking of several models (0.6B-8B parameters), fine-tuned on the debiased text dataset. This evaluation reveals that LLMs fine-tuned on debiased data do not consistently show improved performance on bias benchmarks, exposing critical gaps in current evaluation methodologies and highlighting the need for targeted data manipulation to address manifested model bias.
GG-BBQ: German Gender Bias Benchmark for Question Answering
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Within the context of Natural Language Processing (NLP), fairness evaluation is often associated with the assessment of bias and reduction of associated harm. In this regard, the evaluation is usually carried out by using a benchmark dataset, for a task such as Question Answering, created for the measurement of bias in the model's predictions along various dimensions, including gender identity. In our work, we evaluate gender bias in German Large Language Models (LLMs) using the Bias Benchmark for Question Answering by Parrish et al. (2022) as a reference. Specifically, the templates in the gender identity subset of this English dataset were machine translated into German. The errors in the machine translated templates were then manually reviewed and corrected with the help of a language expert. We find that manual revision of the translation is crucial when creating datasets for gender bias evaluation because of the limitations of machine translation from English to a language such as German with grammatical gender. Our final dataset is comprised of two subsets: Subset-I, which consists of group terms related to gender identity, and Subset-II, where group terms are replaced with proper names. We evaluate several LLMs used for German NLP on this newly created dataset and report the accuracy and bias scores. The results show that all models exhibit bias, both along and against existing social stereotypes.
Detecting Linguistic Indicators for Stereotype Assessment with Large Language Models
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Social categories and stereotypes are embedded in language and can introduce data bias into Large Language Models (LLMs). Despite safeguards, these biases often persist in model behavior, potentially leading to representational harm in outputs. While sociolinguistic research provides valuable insights into the formation of stereotypes, NLP approaches for stereotype detection rarely draw on this foundation and often lack objectivity, precision, and interpretability. To fill this gap, in this work we propose a new approach that detects and quantifies the linguistic indicators of stereotypes in a sentence. We derive linguistic indicators from the Social Category and Stereotype Communication (SCSC) framework which indicate strong social category formulation and stereotyping in language, and use them to build a categorization scheme. To automate this approach, we instruct different LLMs using in-context learning to apply the approach to a sentence, where the LLM examines the linguistic properties and provides a basis for a fine-grained assessment. Based on an empirical evaluation of the importance of different linguistic indicators, we learn a scoring function that measures the linguistic indicators of a stereotype. Our annotations of stereotyped sentences show that these indicators are present in these sentences and explain the strength of a stereotype. In terms of model performance, our results show that the models generally perform well in detecting and classifying linguistic indicators of category labels used to denote a category, but sometimes struggle to correctly evaluate the associated behaviors and characteristics. Using more few-shot examples within the prompts, significantly improves performance. Model performance increases with size, as Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct and GPT-4 achieve comparable results that surpass those of Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct, GPT-4-mini and Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct.
Predicting Brazilian court decisions
Apr 20, 2019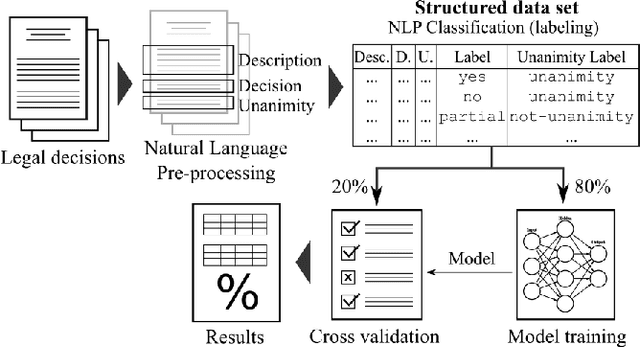

Abstract:Predicting case outcomes is useful but still an extremely hard task for attorneys and other Law professionals. It is not easy to search case information to extract valuable information as this requires dealing with huge data sets and their complexity. For instance, the complexity of Brazil legal system along with the high litigation rates makes this problem even harder. This paper introduces an approach for predicting Brazilian court decisions which is also able to predict whether the decision will be unanimous. We developed a working prototype which performs 79% of accuracy (F1-score) on a data set composed of 4,043 cases from a Brazilian court. To our knowledge, this is the first study to forecast judge decisions in Brazil.
Working Memory Networks: Augmenting Memory Networks with a Relational Reasoning Module
May 23, 2018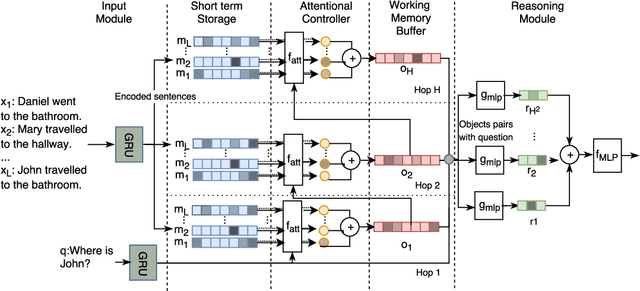
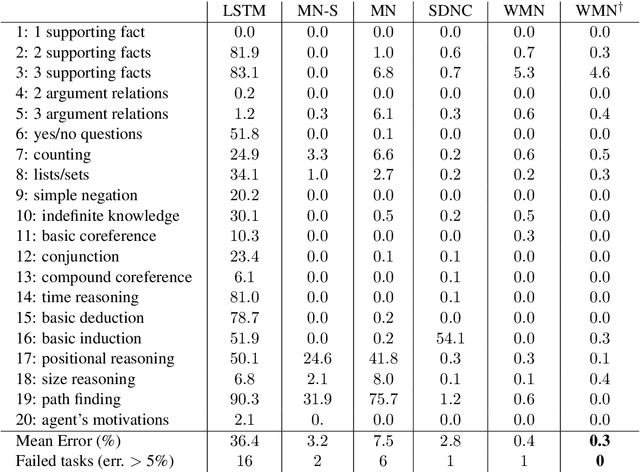
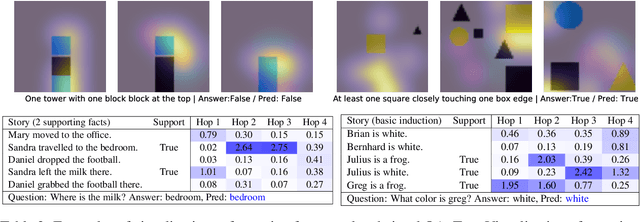
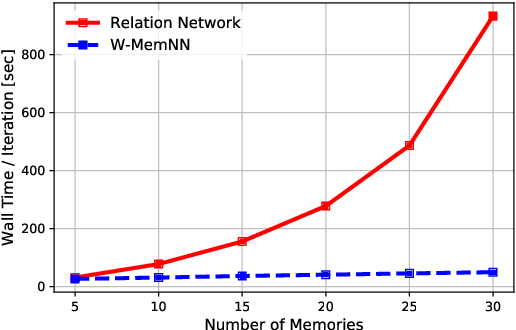
Abstract:During the last years, there has been a lot of interest in achieving some kind of complex reasoning using deep neural networks. To do that, models like Memory Networks (MemNNs) have combined external memory storages and attention mechanisms. These architectures, however, lack of more complex reasoning mechanisms that could allow, for instance, relational reasoning. Relation Networks (RNs), on the other hand, have shown outstanding results in relational reasoning tasks. Unfortunately, their computational cost grows quadratically with the number of memories, something prohibitive for larger problems. To solve these issues, we introduce the Working Memory Network, a MemNN architecture with a novel working memory storage and reasoning module. Our model retains the relational reasoning abilities of the RN while reducing its computational complexity from quadratic to linear. We tested our model on the text QA dataset bAbI and the visual QA dataset NLVR. In the jointly trained bAbI-10k, we set a new state-of-the-art, achieving a mean error of less than 0.5%. Moreover, a simple ensemble of two of our models solves all 20 tasks in the joint version of the benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge