Marco Pistoia
MetaTT: A Global Tensor-Train Adapter for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Jun 10, 2025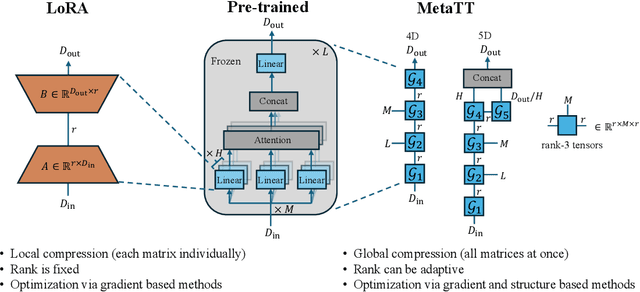
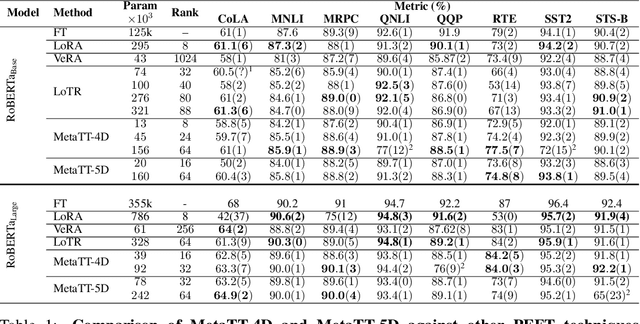
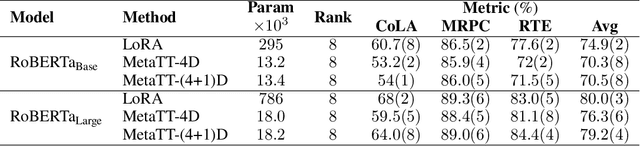
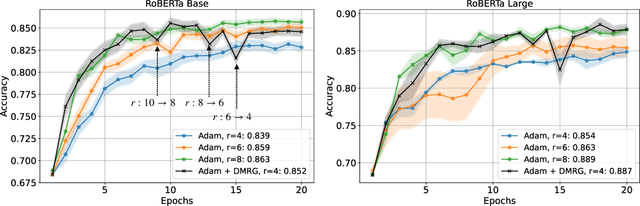
Abstract:We present MetaTT, a unified Tensor Train (TT) adapter framework for global low-rank fine-tuning of pre-trained transformers. Unlike LoRA, which fine-tunes each weight matrix independently, MetaTT uses a single shared TT to factorize all transformer sub-modules -- query, key, value, projection, and feed-forward layers -- by indexing the structural axes like layer and matrix type, and optionally heads and tasks. For a given rank, while LoRA adds parameters proportional to the product across modes, MetaTT only adds parameters proportional to the sum across modes leading to a significantly compressed final adapter. Our benchmarks compare MetaTT with LoRA along with recent state-of-the-art matrix and tensor decomposition based fine-tuning schemes. We observe that when tested on standard language modeling benchmarks, MetaTT leads to the most reduction in the parameters while maintaining similar accuracy to LoRA and even outperforming other tensor-based methods. Unlike CP or other rank-factorizations, the TT ansatz benefits from mature optimization routines -- e.g., DMRG-style rank adaptive minimization in addition to Adam, which we find simplifies training. Because new modes can be appended cheaply, MetaTT naturally extends to shared adapters across many tasks without redesigning the core tensor.
A Unified Framework for Provably Efficient Algorithms to Estimate Shapley Values
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Shapley values have emerged as a critical tool for explaining which features impact the decisions made by machine learning models. However, computing exact Shapley values is difficult, generally requiring an exponential (in the feature dimension) number of model evaluations. To address this, many model-agnostic randomized estimators have been developed, the most influential and widely used being the KernelSHAP method (Lundberg & Lee, 2017). While related estimators such as unbiased KernelSHAP (Covert & Lee, 2021) and LeverageSHAP (Musco & Witter, 2025) are known to satisfy theoretical guarantees, bounds for KernelSHAP have remained elusive. We describe a broad and unified framework that encompasses KernelSHAP and related estimators constructed using both with and without replacement sampling strategies. We then prove strong non-asymptotic theoretical guarantees that apply to all estimators from our framework. This provides, to the best of our knowledge, the first theoretical guarantees for KernelSHAP and sheds further light on tradeoffs between existing estimators. Through comprehensive benchmarking on small and medium dimensional datasets for Decision-Tree models, we validate our approach against exact Shapley values, consistently achieving low mean squared error with modest sample sizes. Furthermore, we make specific implementation improvements to enable scalability of our methods to high-dimensional datasets. Our methods, tested on datasets such MNIST and CIFAR10, provide consistently better results compared to the KernelSHAP library.
Provably faster randomized and quantum algorithms for k-means clustering via uniform sampling
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:The $k$-means algorithm (Lloyd's algorithm) is a widely used method for clustering unlabeled data. A key bottleneck of the $k$-means algorithm is that each iteration requires time linear in the number of data points, which can be expensive in big data applications. This was improved in recent works proposing quantum and quantum-inspired classical algorithms to approximate the $k$-means algorithm locally, in time depending only logarithmically on the number of data points (along with data dependent parameters) [$q$-means: A quantum algorithm for unsupervised machine learning; Kerenidis, Landman, Luongo, and Prakash, NeurIPS 2019; Do you know what $q$-means?, Doriguello, Luongo, Tang]. In this work, we describe a simple randomized mini-batch $k$-means algorithm and a quantum algorithm inspired by the classical algorithm. We prove worse-case guarantees that significantly improve upon the bounds for previous algorithms. Our improvements are due to a careful use of uniform sampling, which preserves certain symmetries of the $k$-means problem that are not preserved in previous algorithms that use data norm-based sampling.
A Numerical Gradient Inversion Attack in Variational Quantum Neural-Networks
Apr 17, 2025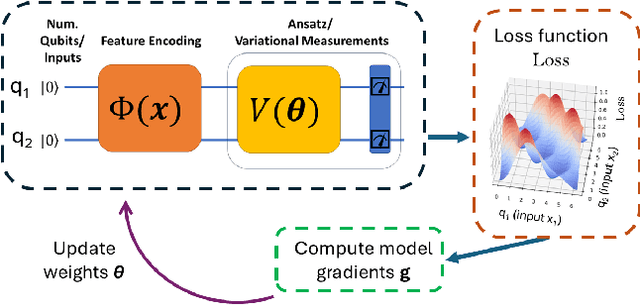
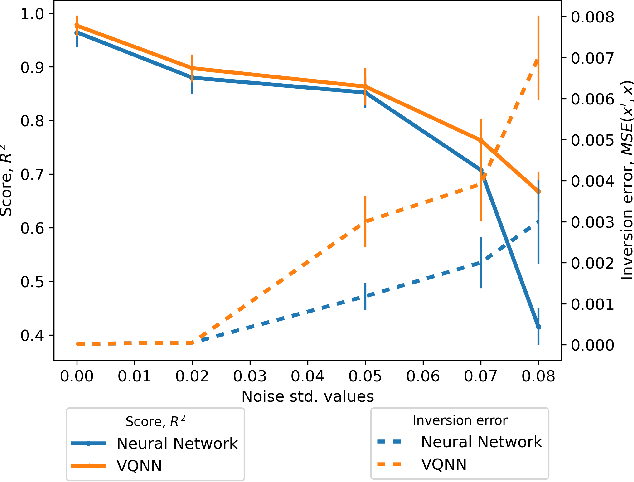
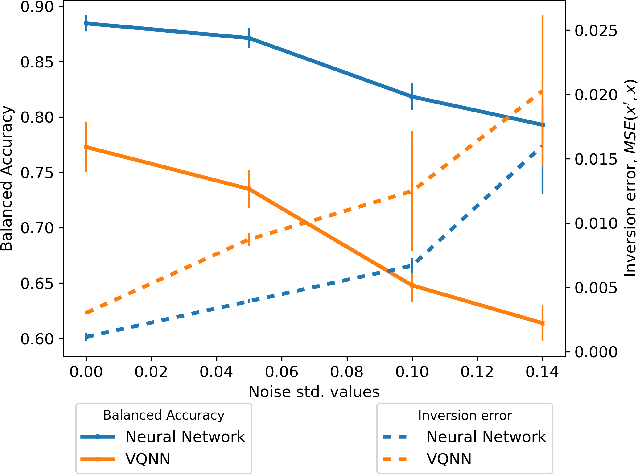
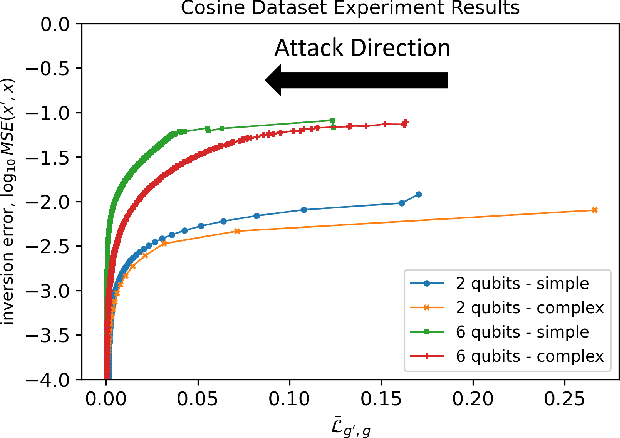
Abstract:The loss landscape of Variational Quantum Neural Networks (VQNNs) is characterized by local minima that grow exponentially with increasing qubits. Because of this, it is more challenging to recover information from model gradients during training compared to classical Neural Networks (NNs). In this paper we present a numerical scheme that successfully reconstructs input training, real-world, practical data from trainable VQNNs' gradients. Our scheme is based on gradient inversion that works by combining gradients estimation with the finite difference method and adaptive low-pass filtering. The scheme is further optimized with Kalman filter to obtain efficient convergence. Our experiments show that our algorithm can invert even batch-trained data, given the VQNN model is sufficiently over-parameterized.
QC-Forest: a Classical-Quantum Algorithm to Provably Speedup Retraining of Random Forest
Jun 17, 2024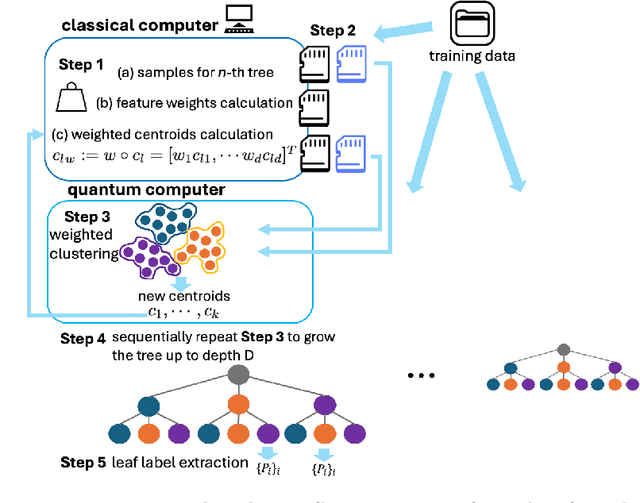
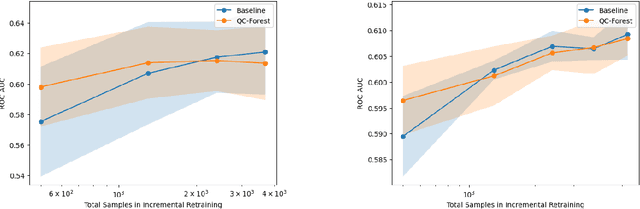
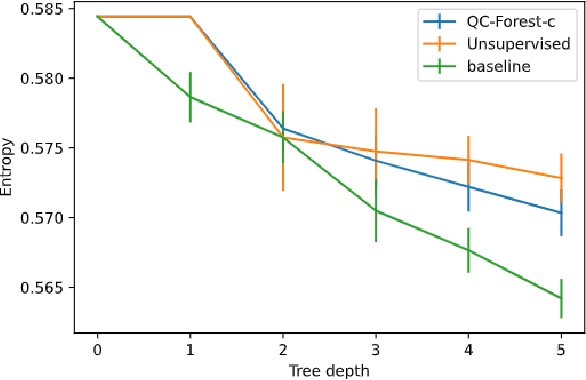
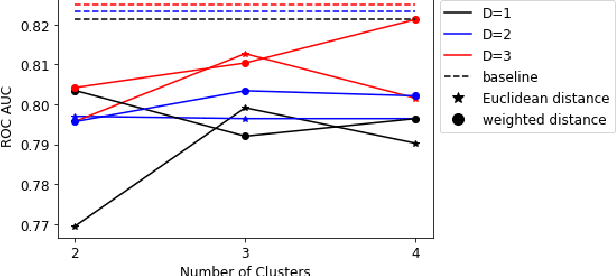
Abstract:Random Forest (RF) is a popular tree-ensemble method for supervised learning, prized for its ease of use and flexibility. Online RF models require to account for new training data to maintain model accuracy. This is particularly important in applications were data is periodically and sequentially generated over time in data streams, such as auto-driving systems, and credit card payments. In this setting, performing periodic model retraining with the old and new data accumulated is beneficial as it fully captures possible drifts in the data distribution over time. However, this is unpractical with state-of-the-art classical algorithms for RF as they scale linearly with the accumulated number of samples. We propose QC-Forest, a classical-quantum algorithm designed to time-efficiently retrain RF models in the streaming setting for multi-class classification and regression, achieving a runtime poly-logarithmic in the total number of accumulated samples. QC-Forest leverages Des-q, a quantum algorithm for single tree construction and retraining proposed by Kumar et al. by expanding to multi-class classification, as the original proposal was limited to binary classes, and introducing an exact classical method to replace an underlying quantum subroutine incurring a finite error, while maintaining the same poly-logarithmic dependence. Finally, we showcase that QC-Forest achieves competitive accuracy in comparison to state-of-the-art RF methods on widely used benchmark datasets with up to 80,000 samples, while significantly speeding up the model retrain.
Model-Agnostic Utility-Preserving Biometric Information Anonymization
May 23, 2024Abstract:The recent rapid advancements in both sensing and machine learning technologies have given rise to the universal collection and utilization of people's biometrics, such as fingerprints, voices, retina/facial scans, or gait/motion/gestures data, enabling a wide range of applications including authentication, health monitoring, or much more sophisticated analytics. While providing better user experiences and deeper business insights, the use of biometrics has raised serious privacy concerns due to their intrinsic sensitive nature and the accompanying high risk of leaking sensitive information such as identity or medical conditions. In this paper, we propose a novel modality-agnostic data transformation framework that is capable of anonymizing biometric data by suppressing its sensitive attributes and retaining features relevant to downstream machine learning-based analyses that are of research and business values. We carried out a thorough experimental evaluation using publicly available facial, voice, and motion datasets. Results show that our proposed framework can achieve a \highlight{high suppression level for sensitive information}, while at the same time retain underlying data utility such that subsequent analyses on the anonymized biometric data could still be carried out to yield satisfactory accuracy.
Prospects of Privacy Advantage in Quantum Machine Learning
May 15, 2024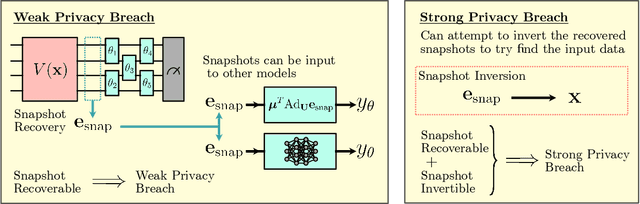
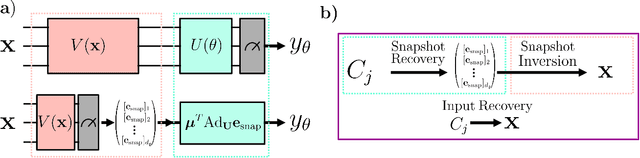
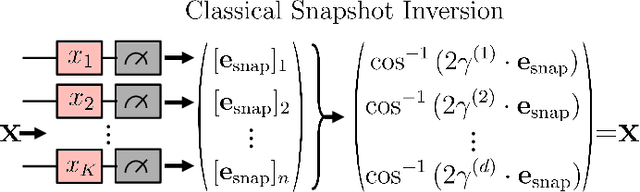
Abstract:Ensuring data privacy in machine learning models is critical, particularly in distributed settings where model gradients are typically shared among multiple parties to allow collaborative learning. Motivated by the increasing success of recovering input data from the gradients of classical models, this study addresses a central question: How hard is it to recover the input data from the gradients of quantum machine learning models? Focusing on variational quantum circuits (VQC) as learning models, we uncover the crucial role played by the dynamical Lie algebra (DLA) of the VQC ansatz in determining privacy vulnerabilities. While the DLA has previously been linked to the classical simulatability and trainability of VQC models, this work, for the first time, establishes its connection to the privacy of VQC models. In particular, we show that properties conducive to the trainability of VQCs, such as a polynomial-sized DLA, also facilitate the extraction of detailed snapshots of the input. We term this a weak privacy breach, as the snapshots enable training VQC models for distinct learning tasks without direct access to the original input. Further, we investigate the conditions for a strong privacy breach where the original input data can be recovered from these snapshots by classical or quantum-assisted polynomial time methods. We establish conditions on the encoding map such as classical simulatability, overlap with DLA basis, and its Fourier frequency characteristics that enable such a privacy breach of VQC models. Our findings thus play a crucial role in detailing the prospects of quantum privacy advantage by guiding the requirements for designing quantum machine learning models that balance trainability with robust privacy protection.
Privacy-preserving quantum federated learning via gradient hiding
Dec 07, 2023Abstract:Distributed quantum computing, particularly distributed quantum machine learning, has gained substantial prominence for its capacity to harness the collective power of distributed quantum resources, transcending the limitations of individual quantum nodes. Meanwhile, the critical concern of privacy within distributed computing protocols remains a significant challenge, particularly in standard classical federated learning (FL) scenarios where data of participating clients is susceptible to leakage via gradient inversion attacks by the server. This paper presents innovative quantum protocols with quantum communication designed to address the FL problem, strengthen privacy measures, and optimize communication efficiency. In contrast to previous works that leverage expressive variational quantum circuits or differential privacy techniques, we consider gradient information concealment using quantum states and propose two distinct FL protocols, one based on private inner-product estimation and the other on incremental learning. These protocols offer substantial advancements in privacy preservation with low communication resources, forging a path toward efficient quantum communication-assisted FL protocols and contributing to the development of secure distributed quantum machine learning, thus addressing critical privacy concerns in the quantum computing era.
Blind quantum machine learning with quantum bipartite correlator
Oct 19, 2023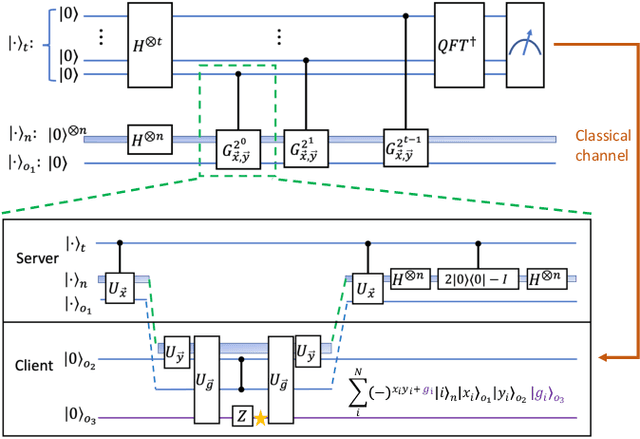
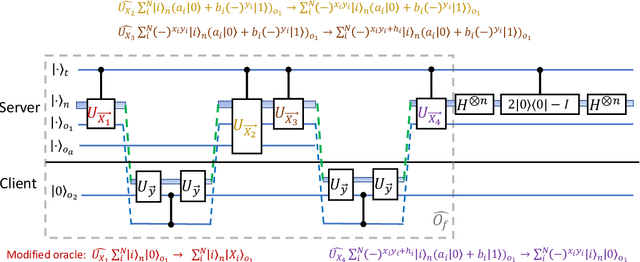
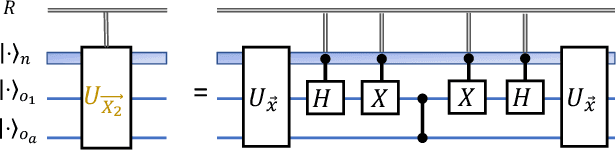
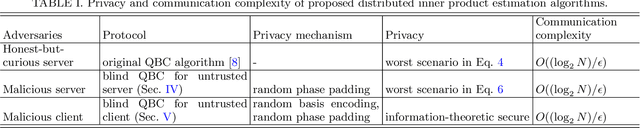
Abstract:Distributed quantum computing is a promising computational paradigm for performing computations that are beyond the reach of individual quantum devices. Privacy in distributed quantum computing is critical for maintaining confidentiality and protecting the data in the presence of untrusted computing nodes. In this work, we introduce novel blind quantum machine learning protocols based on the quantum bipartite correlator algorithm. Our protocols have reduced communication overhead while preserving the privacy of data from untrusted parties. We introduce robust algorithm-specific privacy-preserving mechanisms with low computational overhead that do not require complex cryptographic techniques. We then validate the effectiveness of the proposed protocols through complexity and privacy analysis. Our findings pave the way for advancements in distributed quantum computing, opening up new possibilities for privacy-aware machine learning applications in the era of quantum technologies.
Expressive variational quantum circuits provide inherent privacy in federated learning
Sep 25, 2023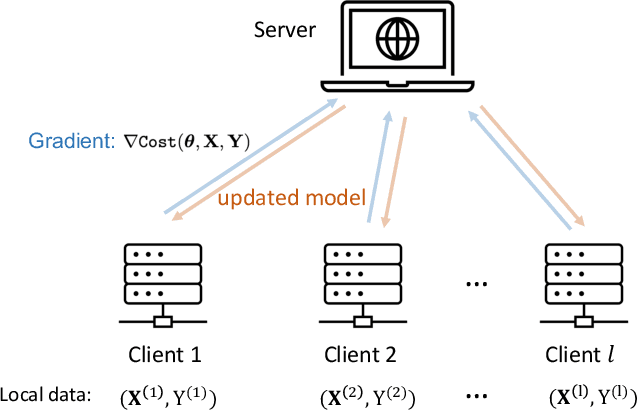
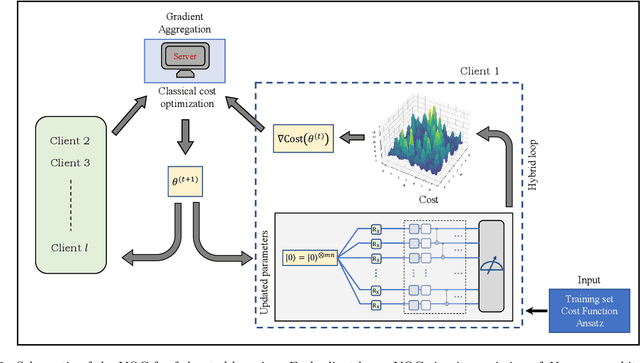
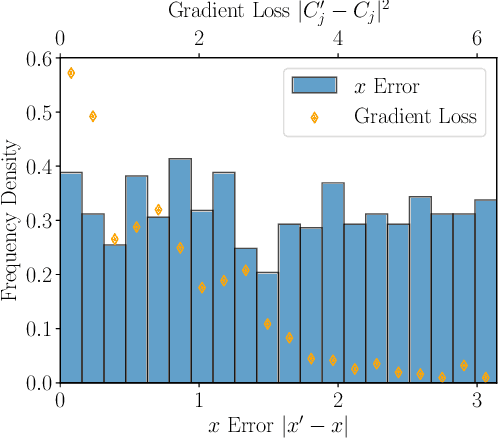
Abstract:Federated learning has emerged as a viable distributed solution to train machine learning models without the actual need to share data with the central aggregator. However, standard neural network-based federated learning models have been shown to be susceptible to data leakage from the gradients shared with the server. In this work, we introduce federated learning with variational quantum circuit model built using expressive encoding maps coupled with overparameterized ans\"atze. We show that expressive maps lead to inherent privacy against gradient inversion attacks, while overparameterization ensures model trainability. Our privacy framework centers on the complexity of solving the system of high-degree multivariate Chebyshev polynomials generated by the gradients of quantum circuit. We present compelling arguments highlighting the inherent difficulty in solving these equations, both in exact and approximate scenarios. Additionally, we delve into machine learning-based attack strategies and establish a direct connection between overparameterization in the original federated learning model and underparameterization in the attack model. Furthermore, we provide numerical scaling arguments showcasing that underparameterization of the expressive map in the attack model leads to the loss landscape being swamped with exponentially many spurious local minima points, thus making it extremely hard to realize a successful attack. This provides a strong claim, for the first time, that the nature of quantum machine learning models inherently helps prevent data leakage in federated learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge