Dylan Herman
Provably faster randomized and quantum algorithms for k-means clustering via uniform sampling
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:The $k$-means algorithm (Lloyd's algorithm) is a widely used method for clustering unlabeled data. A key bottleneck of the $k$-means algorithm is that each iteration requires time linear in the number of data points, which can be expensive in big data applications. This was improved in recent works proposing quantum and quantum-inspired classical algorithms to approximate the $k$-means algorithm locally, in time depending only logarithmically on the number of data points (along with data dependent parameters) [$q$-means: A quantum algorithm for unsupervised machine learning; Kerenidis, Landman, Luongo, and Prakash, NeurIPS 2019; Do you know what $q$-means?, Doriguello, Luongo, Tang]. In this work, we describe a simple randomized mini-batch $k$-means algorithm and a quantum algorithm inspired by the classical algorithm. We prove worse-case guarantees that significantly improve upon the bounds for previous algorithms. Our improvements are due to a careful use of uniform sampling, which preserves certain symmetries of the $k$-means problem that are not preserved in previous algorithms that use data norm-based sampling.
Prospects of Privacy Advantage in Quantum Machine Learning
May 15, 2024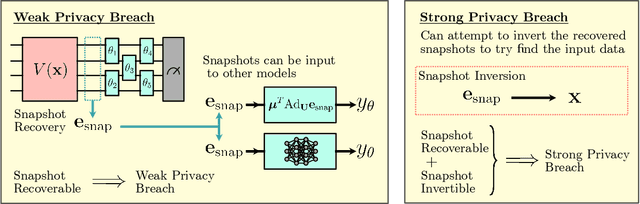
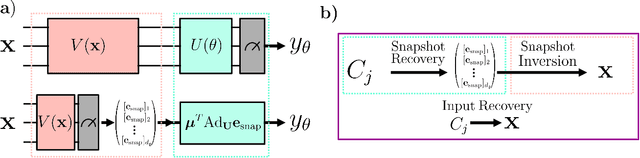
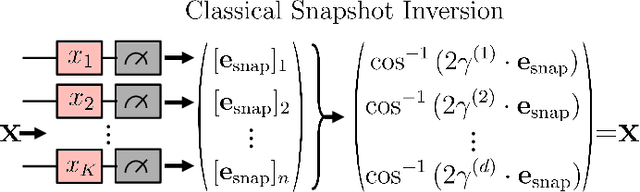
Abstract:Ensuring data privacy in machine learning models is critical, particularly in distributed settings where model gradients are typically shared among multiple parties to allow collaborative learning. Motivated by the increasing success of recovering input data from the gradients of classical models, this study addresses a central question: How hard is it to recover the input data from the gradients of quantum machine learning models? Focusing on variational quantum circuits (VQC) as learning models, we uncover the crucial role played by the dynamical Lie algebra (DLA) of the VQC ansatz in determining privacy vulnerabilities. While the DLA has previously been linked to the classical simulatability and trainability of VQC models, this work, for the first time, establishes its connection to the privacy of VQC models. In particular, we show that properties conducive to the trainability of VQCs, such as a polynomial-sized DLA, also facilitate the extraction of detailed snapshots of the input. We term this a weak privacy breach, as the snapshots enable training VQC models for distinct learning tasks without direct access to the original input. Further, we investigate the conditions for a strong privacy breach where the original input data can be recovered from these snapshots by classical or quantum-assisted polynomial time methods. We establish conditions on the encoding map such as classical simulatability, overlap with DLA basis, and its Fourier frequency characteristics that enable such a privacy breach of VQC models. Our findings thus play a crucial role in detailing the prospects of quantum privacy advantage by guiding the requirements for designing quantum machine learning models that balance trainability with robust privacy protection.
Quantum Deep Hedging
Mar 29, 2023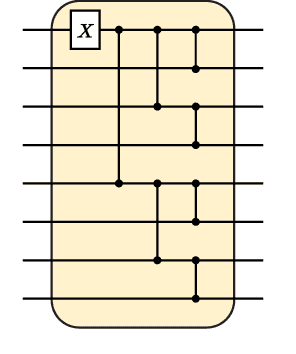
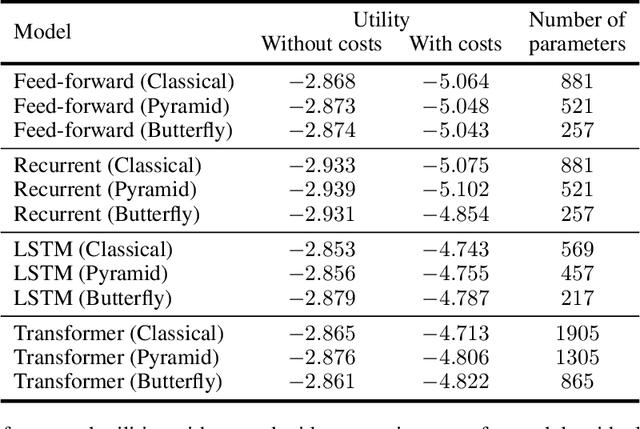
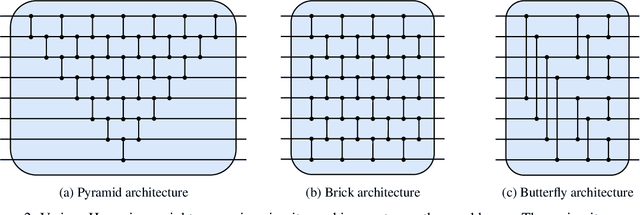
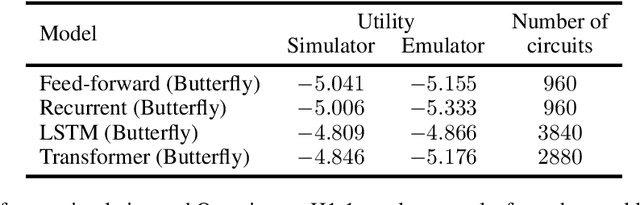
Abstract:Quantum machine learning has the potential for a transformative impact across industry sectors and in particular in finance. In our work we look at the problem of hedging where deep reinforcement learning offers a powerful framework for real markets. We develop quantum reinforcement learning methods based on policy-search and distributional actor-critic algorithms that use quantum neural network architectures with orthogonal and compound layers for the policy and value functions. We prove that the quantum neural networks we use are trainable, and we perform extensive simulations that show that quantum models can reduce the number of trainable parameters while achieving comparable performance and that the distributional approach obtains better performance than other standard approaches, both classical and quantum. We successfully implement the proposed models on a trapped-ion quantum processor, utilizing circuits with up to $16$ qubits, and observe performance that agrees well with noiseless simulation. Our quantum techniques are general and can be applied to other reinforcement learning problems beyond hedging.
Quantum Machine Learning for Finance
Sep 09, 2021Abstract:Quantum computers are expected to surpass the computational capabilities of classical computers during this decade, and achieve disruptive impact on numerous industry sectors, particularly finance. In fact, finance is estimated to be the first industry sector to benefit from Quantum Computing not only in the medium and long terms, but even in the short term. This review paper presents the state of the art of quantum algorithms for financial applications, with particular focus to those use cases that can be solved via Machine Learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge