Luis Espinosa Anke
Automatic Extraction of Metaphoric Analogies from Literary Texts: Task Formulation, Dataset Construction, and Evaluation
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Extracting metaphors and analogies from free text requires high-level reasoning abilities such as abstraction and language understanding. Our study focuses on the extraction of the concepts that form metaphoric analogies in literary texts. To this end, we construct a novel dataset in this domain with the help of domain experts. We compare the out-of-the-box ability of recent large language models (LLMs) to structure metaphoric mappings from fragments of texts containing proportional analogies. The models are further evaluated on the generation of implicit elements of the analogy, which are indirectly suggested in the texts and inferred by human readers. The competitive results obtained by LLMs in our experiments are encouraging and open up new avenues such as automatically extracting analogies and metaphors from text instead of investing resources in domain experts to manually label data.
What do Deck Chairs and Sun Hats Have in Common? Uncovering Shared Properties in Large Concept Vocabularies
Oct 23, 2023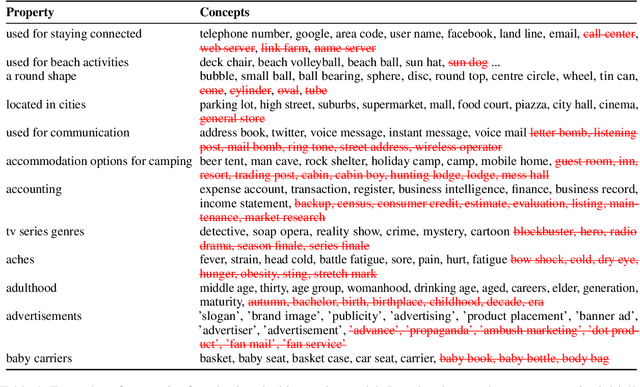
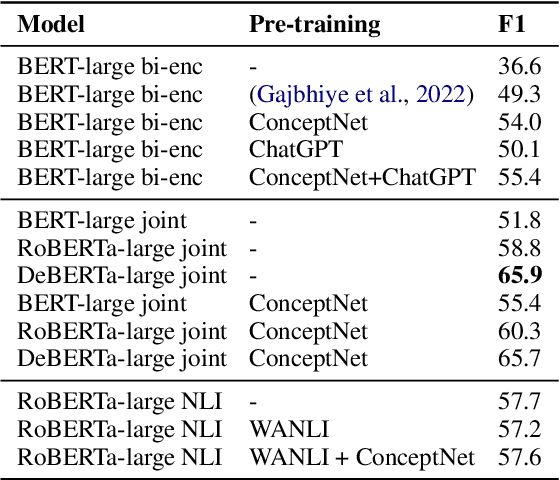
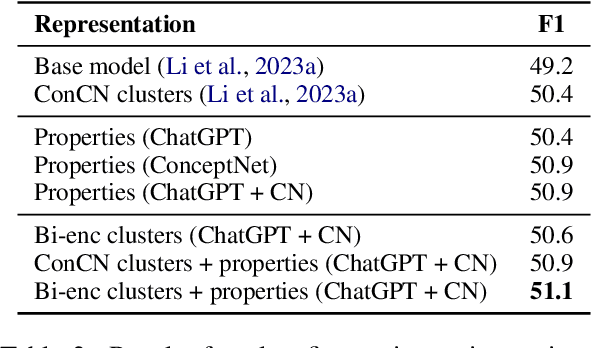
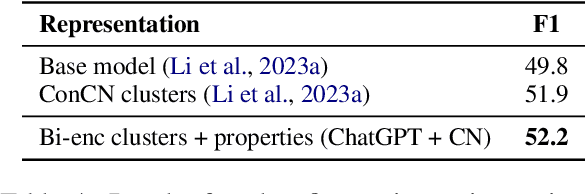
Abstract:Concepts play a central role in many applications. This includes settings where concepts have to be modelled in the absence of sentence context. Previous work has therefore focused on distilling decontextualised concept embeddings from language models. But concepts can be modelled from different perspectives, whereas concept embeddings typically mostly capture taxonomic structure. To address this issue, we propose a strategy for identifying what different concepts, from a potentially large concept vocabulary, have in common with others. We then represent concepts in terms of the properties they share with the other concepts. To demonstrate the practical usefulness of this way of modelling concepts, we consider the task of ultra-fine entity typing, which is a challenging multi-label classification problem. We show that by augmenting the label set with shared properties, we can improve the performance of the state-of-the-art models for this task.
Tweet Insights: A Visualization Platform to Extract Temporal Insights from Twitter
Aug 04, 2023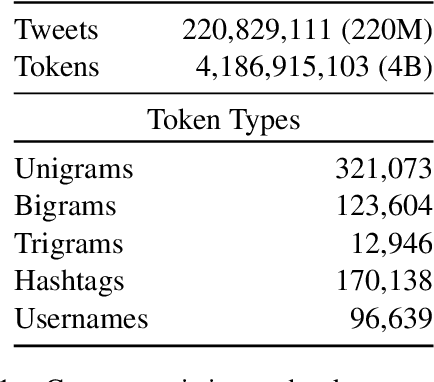
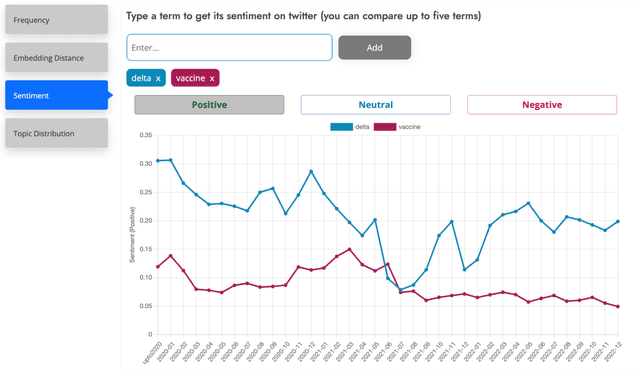
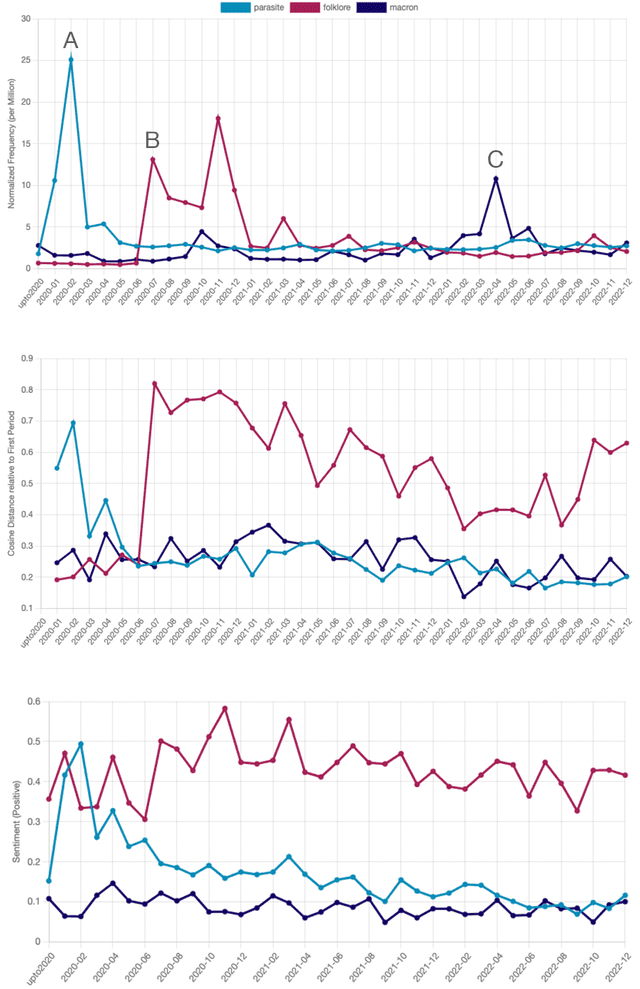
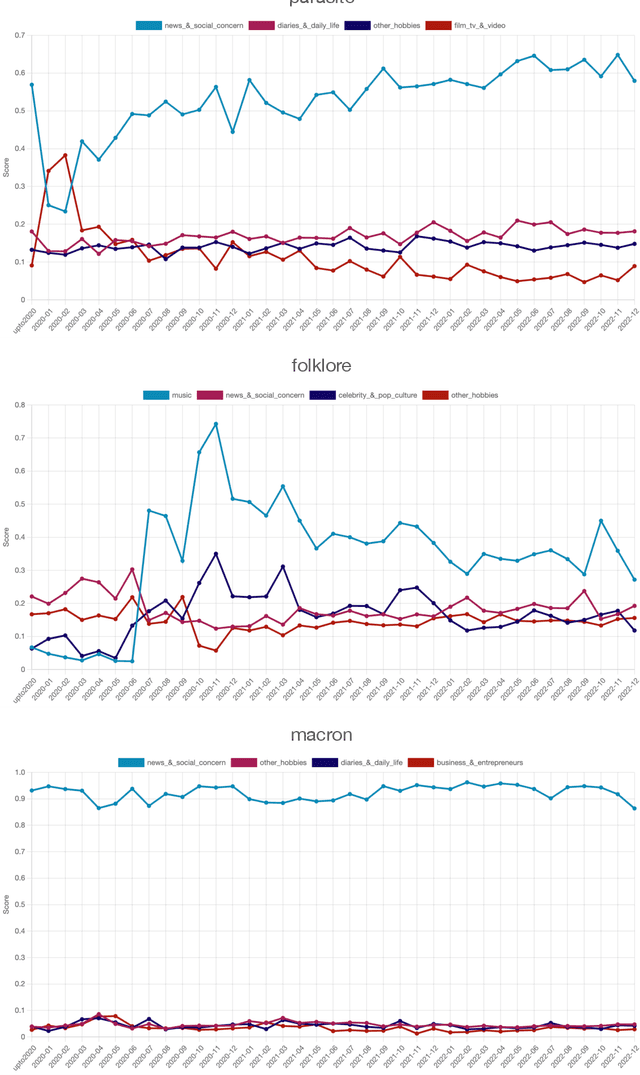
Abstract:This paper introduces a large collection of time series data derived from Twitter, postprocessed using word embedding techniques, as well as specialized fine-tuned language models. This data comprises the past five years and captures changes in n-gram frequency, similarity, sentiment and topic distribution. The interface built on top of this data enables temporal analysis for detecting and characterizing shifts in meaning, including complementary information to trending metrics, such as sentiment and topic association over time. We release an online demo for easy experimentation, and we share code and the underlying aggregated data for future work. In this paper, we also discuss three case studies unlocked thanks to our platform, showcasing its potential for temporal linguistic analysis.
TempoWiC: An Evaluation Benchmark for Detecting Meaning Shift in Social Media
Sep 16, 2022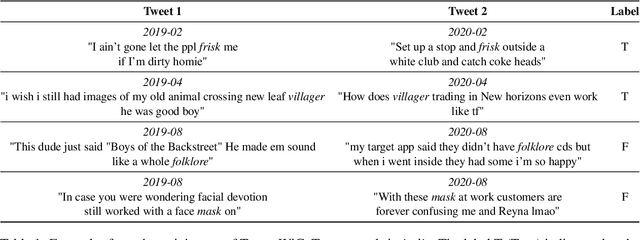
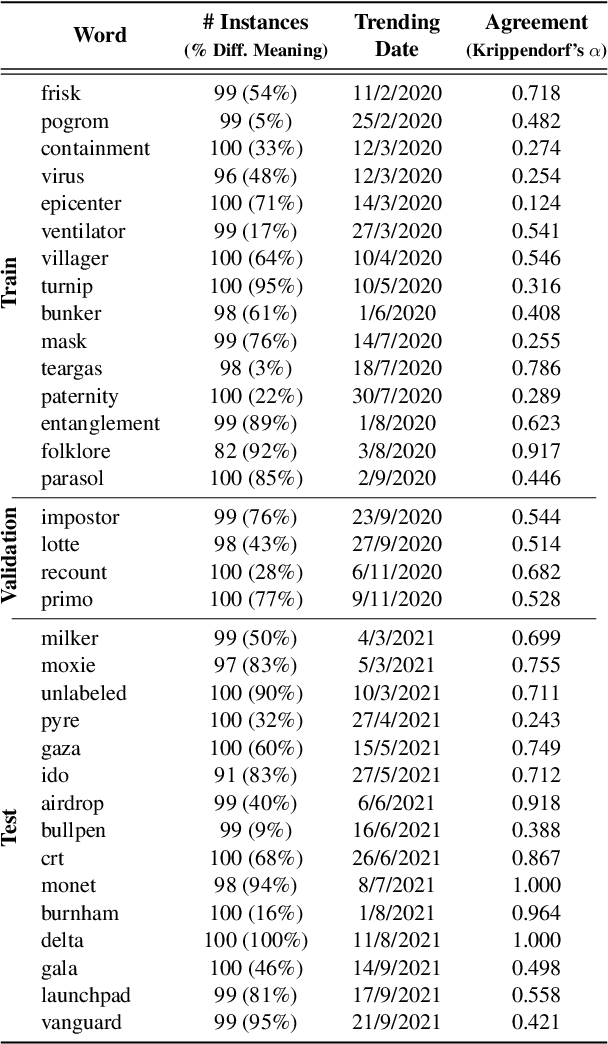
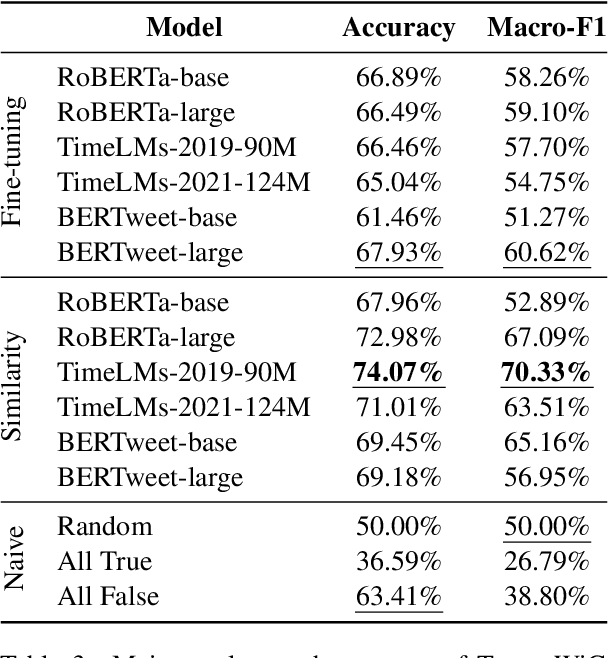
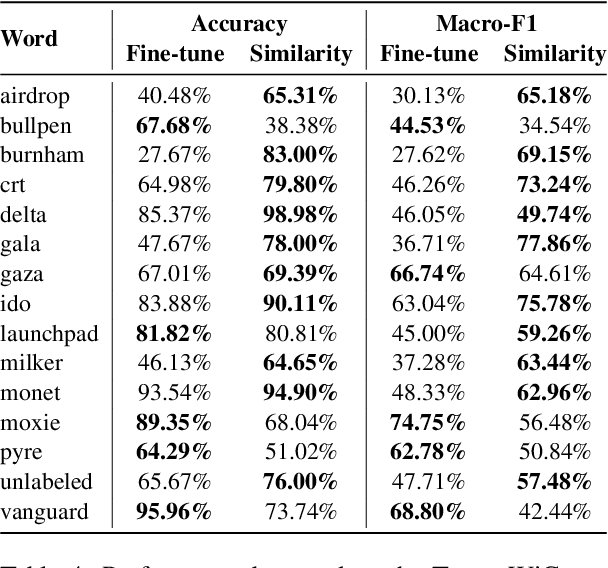
Abstract:Language evolves over time, and word meaning changes accordingly. This is especially true in social media, since its dynamic nature leads to faster semantic shifts, making it challenging for NLP models to deal with new content and trends. However, the number of datasets and models that specifically address the dynamic nature of these social platforms is scarce. To bridge this gap, we present TempoWiC, a new benchmark especially aimed at accelerating research in social media-based meaning shift. Our results show that TempoWiC is a challenging benchmark, even for recently-released language models specialized in social media.
Distilling Hypernymy Relations from Language Models: On the Effectiveness of Zero-Shot Taxonomy Induction
Feb 10, 2022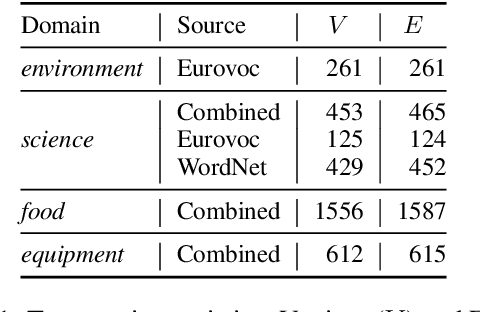
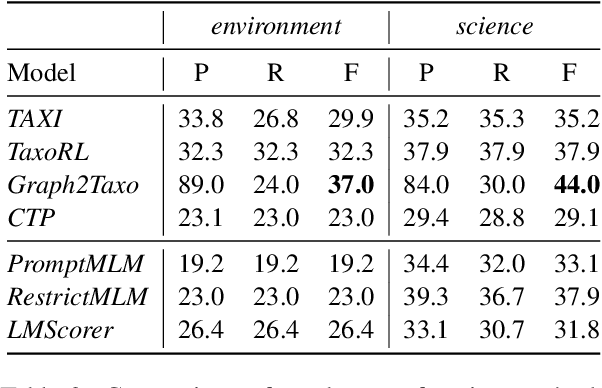
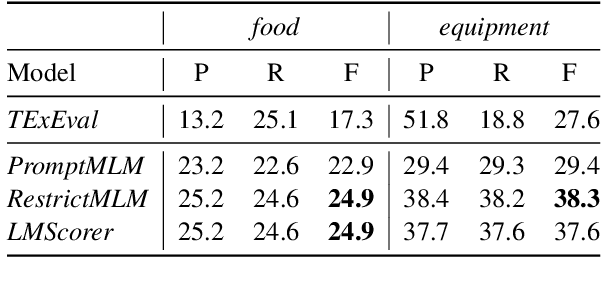
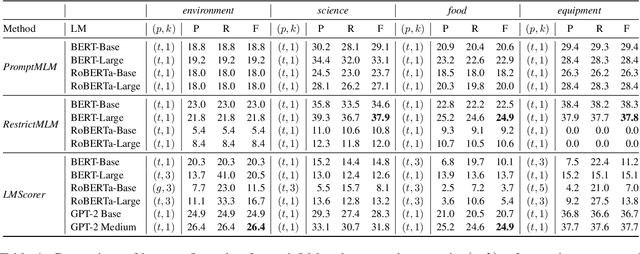
Abstract:In this paper, we analyze zero-shot taxonomy learning methods which are based on distilling knowledge from language models via prompting and sentence scoring. We show that, despite their simplicity, these methods outperform some supervised strategies and are competitive with the current state-of-the-art under adequate conditions. We also show that statistical and linguistic properties of prompts dictate downstream performance.
TimeLMs: Diachronic Language Models from Twitter
Feb 08, 2022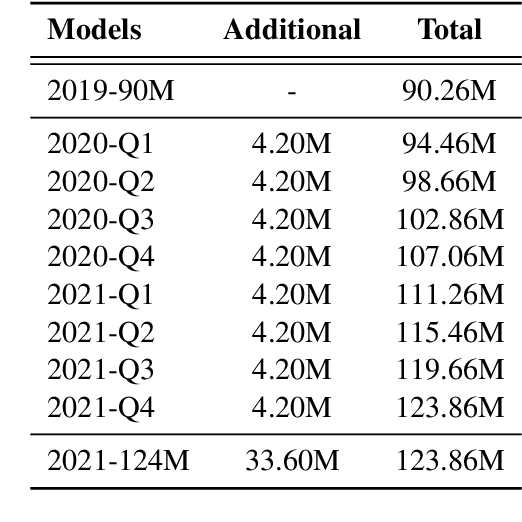
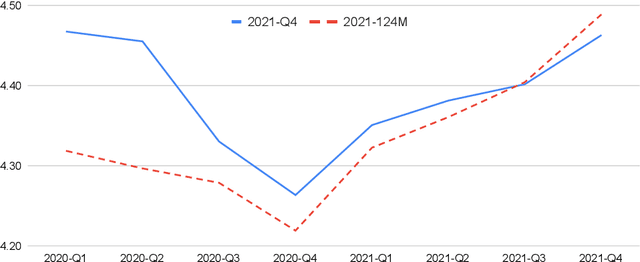
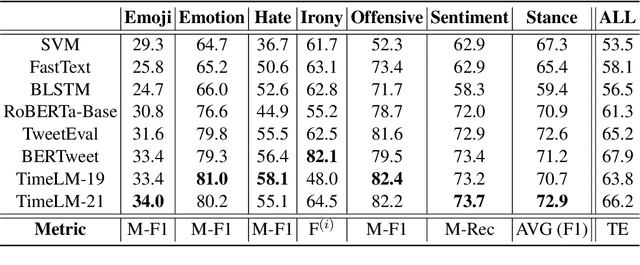
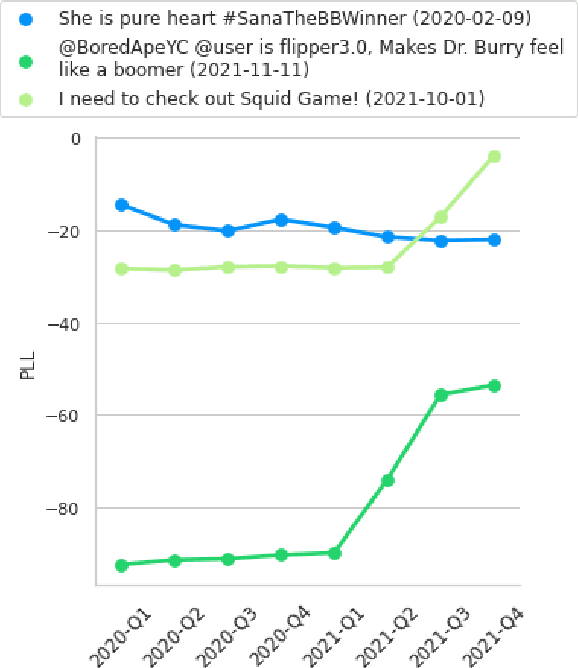
Abstract:Despite its importance, the time variable has been largely neglected in the NLP and language model literature. In this paper, we present TimeLMs, a set of language models specialized on diachronic Twitter data. We show that a continual learning strategy contributes to enhancing Twitter-based language models' capacity to deal with future and out-of-distribution tweets, while making them competitive with standardized and more monolithic benchmarks. We also perform a number of qualitative analyses showing how they cope with trends and peaks in activity involving specific named entities or concept drift.
Overview of ADoBo 2021: Automatic Detection of Unassimilated Borrowings in the Spanish Press
Oct 29, 2021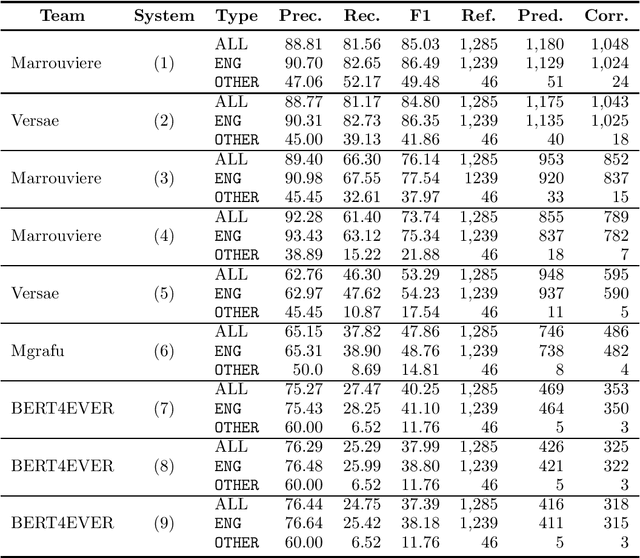
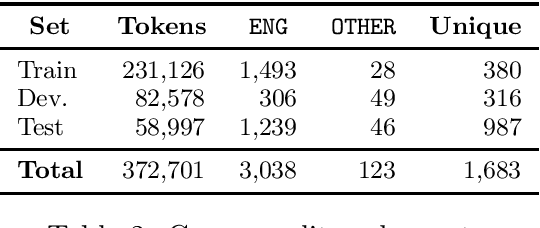
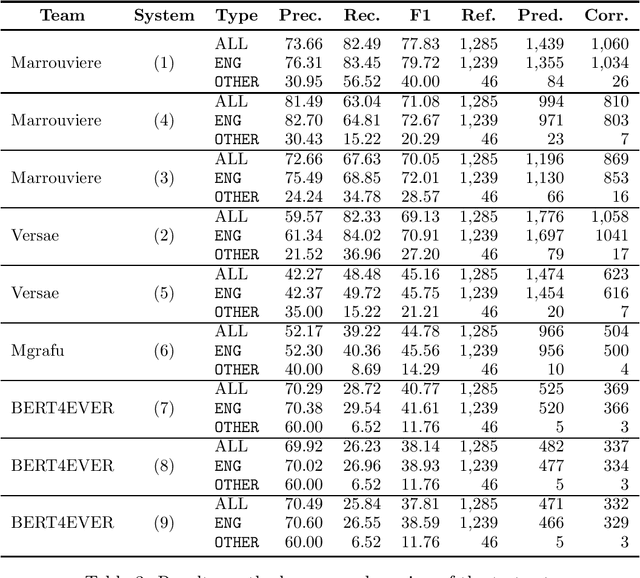
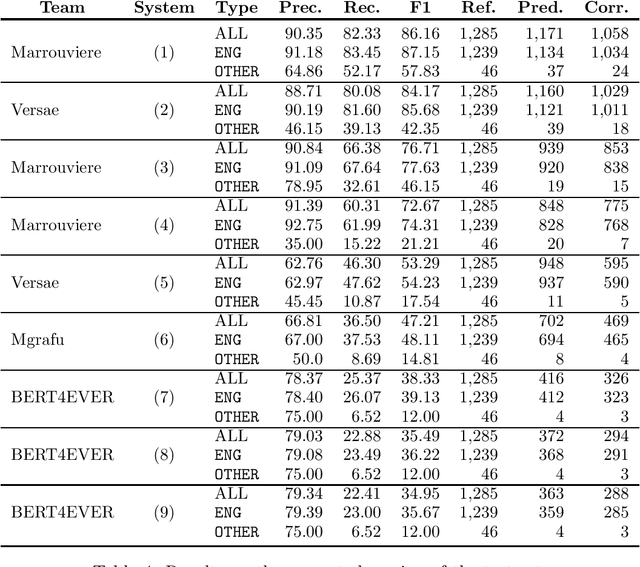
Abstract:This paper summarizes the main findings of the ADoBo 2021 shared task, proposed in the context of IberLef 2021. In this task, we invited participants to detect lexical borrowings (coming mostly from English) in Spanish newswire texts. This task was framed as a sequence classification problem using BIO encoding. We provided participants with an annotated corpus of lexical borrowings which we split into training, development and test splits. We received submissions from 4 teams with 9 different system runs overall. The results, which range from F1 scores of 37 to 85, suggest that this is a challenging task, especially when out-of-domain or OOV words are considered, and that traditional methods informed with lexicographic information would benefit from taking advantage of current NLP trends.
* Post-print. Original version at Procesamiento del Lenguaje Natural 67 (2021), p. 277-285
Deriving Word Vectors from Contextualized Language Models using Topic-Aware Mention Selection
Jun 15, 2021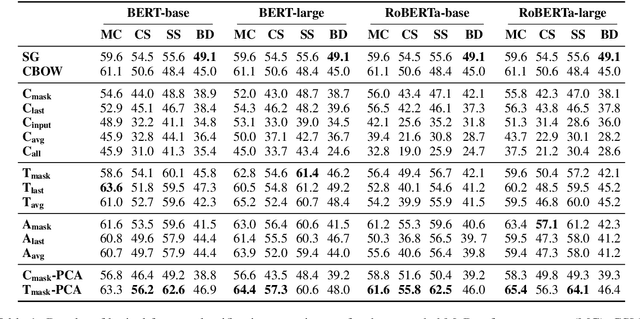
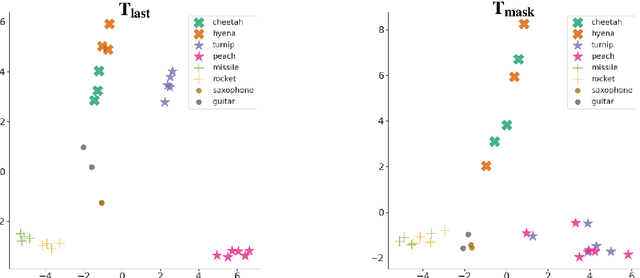
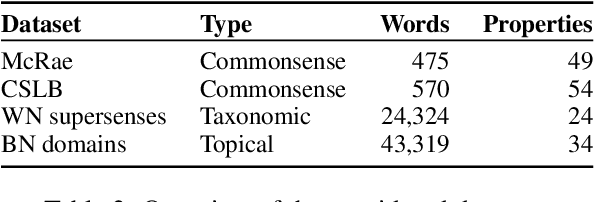
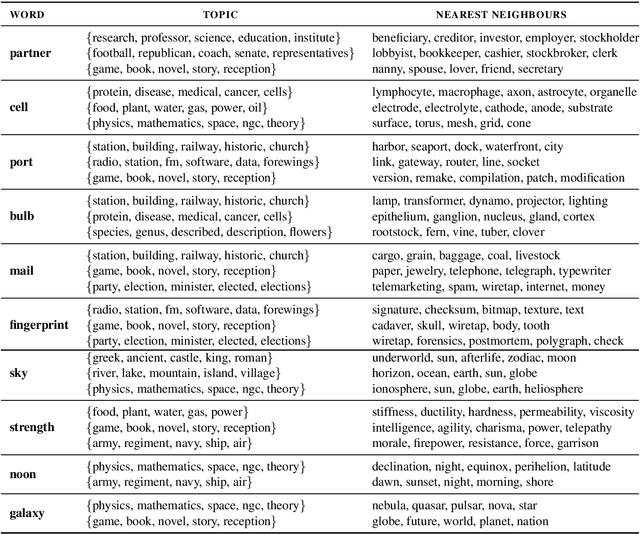
Abstract:One of the long-standing challenges in lexical semantics consists in learning representations of words which reflect their semantic properties. The remarkable success of word embeddings for this purpose suggests that high-quality representations can be obtained by summarizing the sentence contexts of word mentions. In this paper, we propose a method for learning word representations that follows this basic strategy, but differs from standard word embeddings in two important ways. First, we take advantage of contextualized language models (CLMs) rather than bags of word vectors to encode contexts. Second, rather than learning a word vector directly, we use a topic model to partition the contexts in which words appear, and then learn different topic-specific vectors for each word. Finally, we use a task-specific supervision signal to make a soft selection of the resulting vectors. We show that this simple strategy leads to high-quality word vectors, which are more predictive of semantic properties than word embeddings and existing CLM-based strategies.
XLM-T: A Multilingual Language Model Toolkit for Twitter
Apr 25, 2021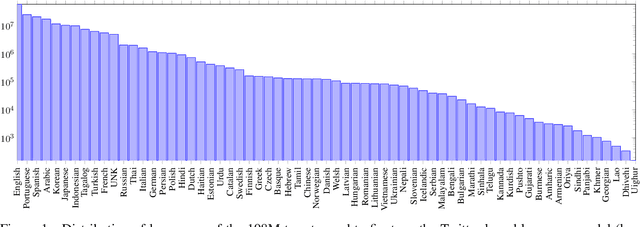
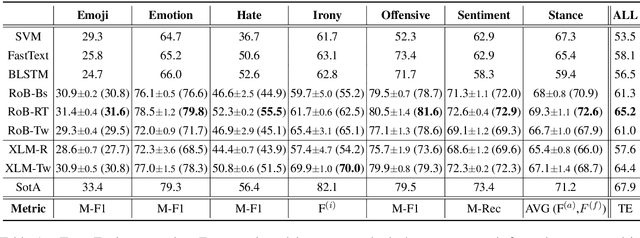
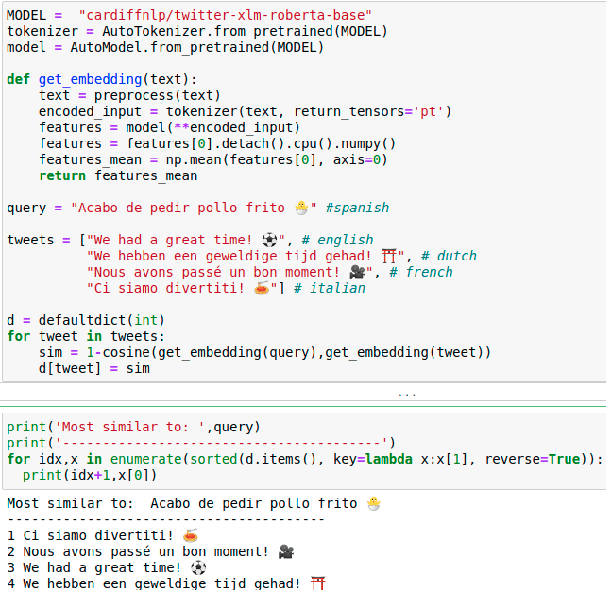
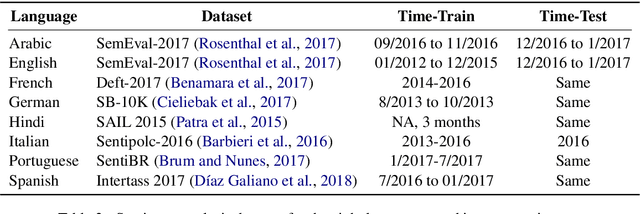
Abstract:Language models are ubiquitous in current NLP, and their multilingual capacity has recently attracted considerable attention. However, current analyses have almost exclusively focused on (multilingual variants of) standard benchmarks, and have relied on clean pre-training and task-specific corpora as multilingual signals. In this paper, we introduce XLM-T, a framework for using and evaluating multilingual language models in Twitter. This framework features two main assets: (1) a strong multilingual baseline consisting of an XLM-R (Conneau et al. 2020) model pre-trained on millions of tweets in over thirty languages, alongside starter code to subsequently fine-tune on a target task; and (2) a set of unified sentiment analysis Twitter datasets in eight different languages. This is a modular framework that can easily be extended to additional tasks, as well as integrated with recent efforts also aimed at the homogenization of Twitter-specific datasets (Barbieri et al. 2020).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge