Jose Camacho-Collados
Exploring State Tracking Capabilities of Large Language Models
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in solving complex tasks, including those requiring a certain level of reasoning. In this paper, we focus on state tracking, a problem where models need to keep track of the state governing a number of entities. To isolate the state tracking component from other factors, we propose a benchmark based on three well-defined state tracking tasks and analyse the performance of LLMs in different scenarios. The results indicate that the recent generation of LLMs (specifically, GPT-4 and Llama3) are capable of tracking state, especially when integrated with mechanisms such as Chain of Thought. However, models from the former generation, while understanding the task and being able to solve it at the initial stages, often fail at this task after a certain number of steps.
MORABLES: A Benchmark for Assessing Abstract Moral Reasoning in LLMs with Fables
Sep 15, 2025Abstract:As LLMs excel on standard reading comprehension benchmarks, attention is shifting toward evaluating their capacity for complex abstract reasoning and inference. Literature-based benchmarks, with their rich narrative and moral depth, provide a compelling framework for evaluating such deeper comprehension skills. Here, we present MORABLES, a human-verified benchmark built from fables and short stories drawn from historical literature. The main task is structured as multiple-choice questions targeting moral inference, with carefully crafted distractors that challenge models to go beyond shallow, extractive question answering. To further stress-test model robustness, we introduce adversarial variants designed to surface LLM vulnerabilities and shortcuts due to issues such as data contamination. Our findings show that, while larger models outperform smaller ones, they remain susceptible to adversarial manipulation and often rely on superficial patterns rather than true moral reasoning. This brittleness results in significant self-contradiction, with the best models refuting their own answers in roughly 20% of cases depending on the framing of the moral choice. Interestingly, reasoning-enhanced models fail to bridge this gap, suggesting that scale - not reasoning ability - is the primary driver of performance.
Automatic Extraction of Metaphoric Analogies from Literary Texts: Task Formulation, Dataset Construction, and Evaluation
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Extracting metaphors and analogies from free text requires high-level reasoning abilities such as abstraction and language understanding. Our study focuses on the extraction of the concepts that form metaphoric analogies in literary texts. To this end, we construct a novel dataset in this domain with the help of domain experts. We compare the out-of-the-box ability of recent large language models (LLMs) to structure metaphoric mappings from fragments of texts containing proportional analogies. The models are further evaluated on the generation of implicit elements of the analogy, which are indirectly suggested in the texts and inferred by human readers. The competitive results obtained by LLMs in our experiments are encouraging and open up new avenues such as automatically extracting analogies and metaphors from text instead of investing resources in domain experts to manually label data.
Sensitive Content Classification in Social Media: A Holistic Resource and Evaluation
Nov 29, 2024



Abstract:The detection of sensitive content in large datasets is crucial for ensuring that shared and analysed data is free from harmful material. However, current moderation tools, such as external APIs, suffer from limitations in customisation, accuracy across diverse sensitive categories, and privacy concerns. Additionally, existing datasets and open-source models focus predominantly on toxic language, leaving gaps in detecting other sensitive categories such as substance abuse or self-harm. In this paper, we put forward a unified dataset tailored for social media content moderation across six sensitive categories: conflictual language, profanity, sexually explicit material, drug-related content, self-harm, and spam. By collecting and annotating data with consistent retrieval strategies and guidelines, we address the shortcomings of previous focalised research. Our analysis demonstrates that fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) on this novel dataset yields significant improvements in detection performance compared to open off-the-shelf models such as LLaMA, and even proprietary OpenAI models, which underperform by 10-15% overall. This limitation is even more pronounced on popular moderation APIs, which cannot be easily tailored to specific sensitive content categories, among others.
MetaphorShare: A Dynamic Collaborative Repository of Open Metaphor Datasets
Nov 27, 2024

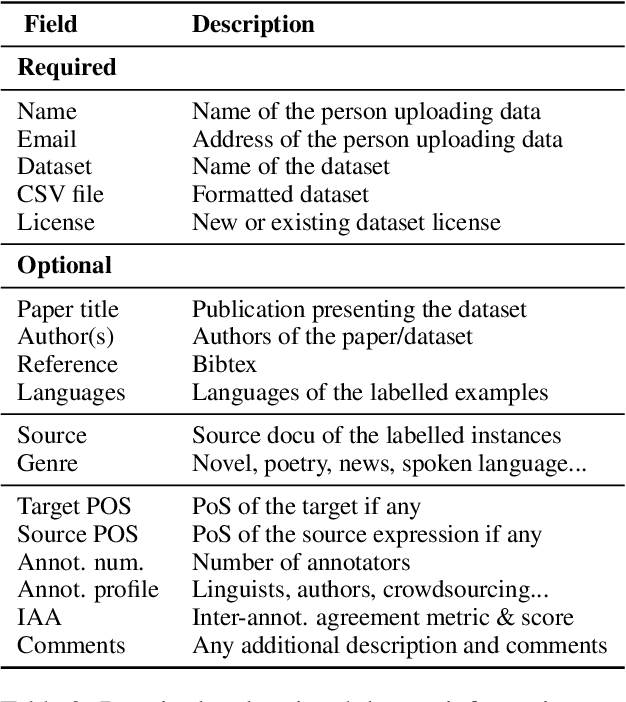

Abstract:The metaphor studies community has developed numerous valuable labelled corpora in various languages over the years. Many of these resources are not only unknown to the NLP community, but are also often not easily shared among the researchers. Both in human sciences and in NLP, researchers could benefit from a centralised database of labelled resources, easily accessible and unified under an identical format. To facilitate this, we present MetaphorShare, a website to integrate metaphor datasets making them open and accessible. With this effort, our aim is to encourage researchers to share and upload more datasets in any language in order to facilitate metaphor studies and the development of future metaphor processing NLP systems. The website is accessible at www.metaphorshare.com.
Multilingual Topic Classification in X: Dataset and Analysis
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:In the dynamic realm of social media, diverse topics are discussed daily, transcending linguistic boundaries. However, the complexities of understanding and categorising this content across various languages remain an important challenge with traditional techniques like topic modelling often struggling to accommodate this multilingual diversity. In this paper, we introduce X-Topic, a multilingual dataset featuring content in four distinct languages (English, Spanish, Japanese, and Greek), crafted for the purpose of tweet topic classification. Our dataset includes a wide range of topics, tailored for social media content, making it a valuable resource for scientists and professionals working on cross-linguistic analysis, the development of robust multilingual models, and computational scientists studying online dialogue. Finally, we leverage X-Topic to perform a comprehensive cross-linguistic and multilingual analysis, and compare the capabilities of current general- and domain-specific language models.
Analysing Zero-Shot Readability-Controlled Sentence Simplification
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Readability-controlled text simplification (RCTS) rewrites texts to lower readability levels while preserving their meaning. RCTS models often depend on parallel corpora with readability annotations on both source and target sides. Such datasets are scarce and difficult to curate, especially at the sentence level. To reduce reliance on parallel data, we explore using instruction-tuned large language models for zero-shot RCTS. Through automatic and manual evaluations, we examine: (1) how different types of contextual information affect a model's ability to generate sentences with the desired readability, and (2) the trade-off between achieving target readability and preserving meaning. Results show that all tested models struggle to simplify sentences (especially to the lowest levels) due to models' limitations and characteristics of the source sentences that impede adequate rewriting. Our experiments also highlight the need for better automatic evaluation metrics tailored to RCTS, as standard ones often misinterpret common simplification operations, and inaccurately assess readability and meaning preservation.
Evaluating Short-Term Temporal Fluctuations of Social Biases in Social Media Data and Masked Language Models
Jun 19, 2024



Abstract:Social biases such as gender or racial biases have been reported in language models (LMs), including Masked Language Models (MLMs). Given that MLMs are continuously trained with increasing amounts of additional data collected over time, an important yet unanswered question is how the social biases encoded with MLMs vary over time. In particular, the number of social media users continues to grow at an exponential rate, and it is a valid concern for the MLMs trained specifically on social media data whether their social biases (if any) would also amplify over time. To empirically analyse this problem, we use a series of MLMs pretrained on chronologically ordered temporal snapshots of corpora. Our analysis reveals that, although social biases are present in all MLMs, most types of social bias remain relatively stable over time (with a few exceptions). To further understand the mechanisms that influence social biases in MLMs, we analyse the temporal corpora used to train the MLMs. Our findings show that some demographic groups, such as male, obtain higher preference over the other, such as female on the training corpora constantly.
BLEnD: A Benchmark for LLMs on Everyday Knowledge in Diverse Cultures and Languages
Jun 14, 2024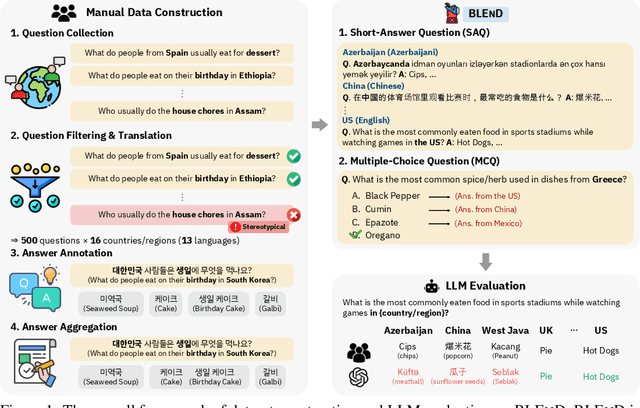
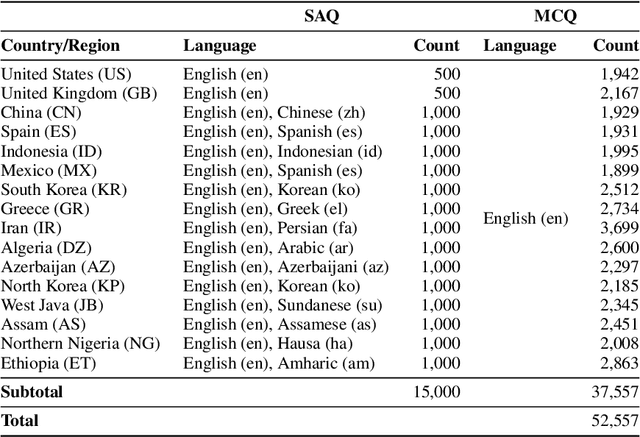
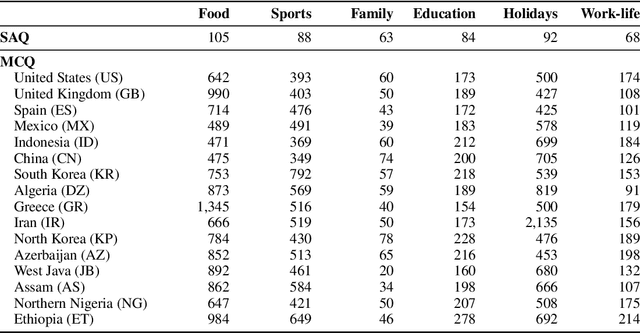
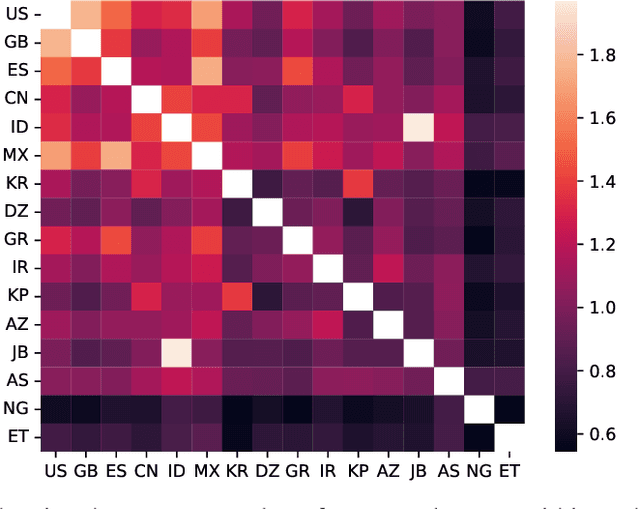
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often lack culture-specific knowledge of daily life, especially across diverse regions and non-English languages. Existing benchmarks for evaluating LLMs' cultural sensitivities are limited to a single language or collected from online sources such as Wikipedia, which do not reflect the mundane everyday lifestyles of diverse regions. That is, information about the food people eat for their birthday celebrations, spices they typically use, musical instruments youngsters play, or the sports they practice in school is common cultural knowledge but uncommon in easily collected online sources, especially for underrepresented cultures. To address this issue, we introduce BLEnD, a hand-crafted benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs' everyday knowledge across diverse cultures and languages. BLEnD comprises 52.6k question-answer pairs from 16 countries/regions, in 13 different languages, including low-resource ones such as Amharic, Assamese, Azerbaijani, Hausa, and Sundanese. We construct the benchmark to include two formats of questions: short-answer and multiple-choice. We show that LLMs perform better for cultures that are highly represented online, with a maximum 57.34% difference in GPT-4, the best-performing model, in the short-answer format. For cultures represented by mid-to-high-resource languages, LLMs perform better in their local languages, but for cultures represented by low-resource languages, LLMs perform better in English than the local languages. We make our dataset publicly available at: https://github.com/nlee0212/BLEnD.
Words as Trigger Points in Social Media Discussions
May 16, 2024



Abstract:Trigger points are a concept introduced by Mau, Lux, and Westheuser (2023) to study qualitative focus group interviews and understand polarisation in Germany. When people communicate, trigger points represent moments when individuals feel that their understanding of what is fair, normal, or appropriate in society is questioned. In the original studies, individuals react affectively to such triggers and show strong and negative emotional responses. In this paper, we introduce the first systematic study of the large-scale effect of individual words as trigger points by analysing a large amount of social media posts. We examine online deliberations on Reddit between 2020 and 2022 and collect >100 million posts from subreddits related to a set of words identified as trigger points in UK politics. We find that such trigger words affect user engagement and have noticeable consequences on animosity in online discussions. We share empirical evidence of trigger words causing animosity, and how they provide incentives for hate speech, adversarial debates, and disagreements. Our work is the first to introduce trigger points to computational studies of online communication. Our findings are relevant to researchers interested in online harms and who examine how citizens debate politics and society in light of affective polarisation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge