Joanne Boisson
Automatic Extraction of Metaphoric Analogies from Literary Texts: Task Formulation, Dataset Construction, and Evaluation
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Extracting metaphors and analogies from free text requires high-level reasoning abilities such as abstraction and language understanding. Our study focuses on the extraction of the concepts that form metaphoric analogies in literary texts. To this end, we construct a novel dataset in this domain with the help of domain experts. We compare the out-of-the-box ability of recent large language models (LLMs) to structure metaphoric mappings from fragments of texts containing proportional analogies. The models are further evaluated on the generation of implicit elements of the analogy, which are indirectly suggested in the texts and inferred by human readers. The competitive results obtained by LLMs in our experiments are encouraging and open up new avenues such as automatically extracting analogies and metaphors from text instead of investing resources in domain experts to manually label data.
MetaphorShare: A Dynamic Collaborative Repository of Open Metaphor Datasets
Nov 27, 2024

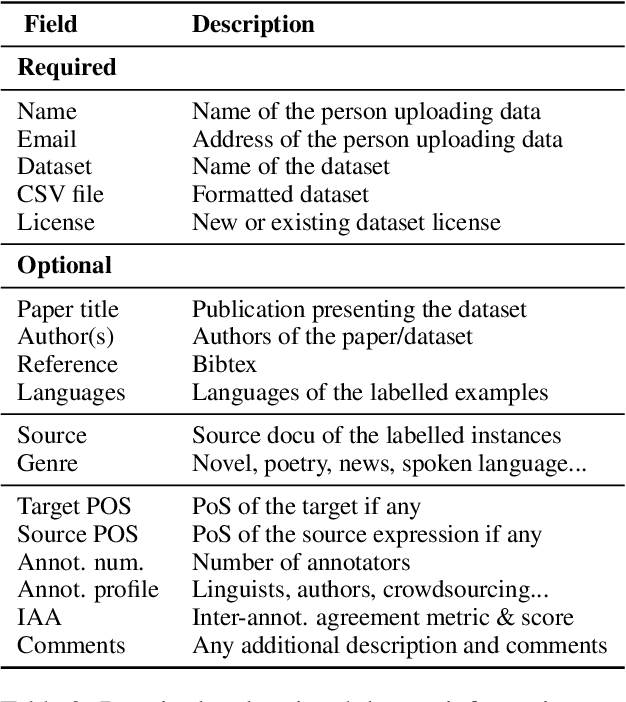

Abstract:The metaphor studies community has developed numerous valuable labelled corpora in various languages over the years. Many of these resources are not only unknown to the NLP community, but are also often not easily shared among the researchers. Both in human sciences and in NLP, researchers could benefit from a centralised database of labelled resources, easily accessible and unified under an identical format. To facilitate this, we present MetaphorShare, a website to integrate metaphor datasets making them open and accessible. With this effort, our aim is to encourage researchers to share and upload more datasets in any language in order to facilitate metaphor studies and the development of future metaphor processing NLP systems. The website is accessible at www.metaphorshare.com.
Construction Artifacts in Metaphor Identification Datasets
Nov 15, 2023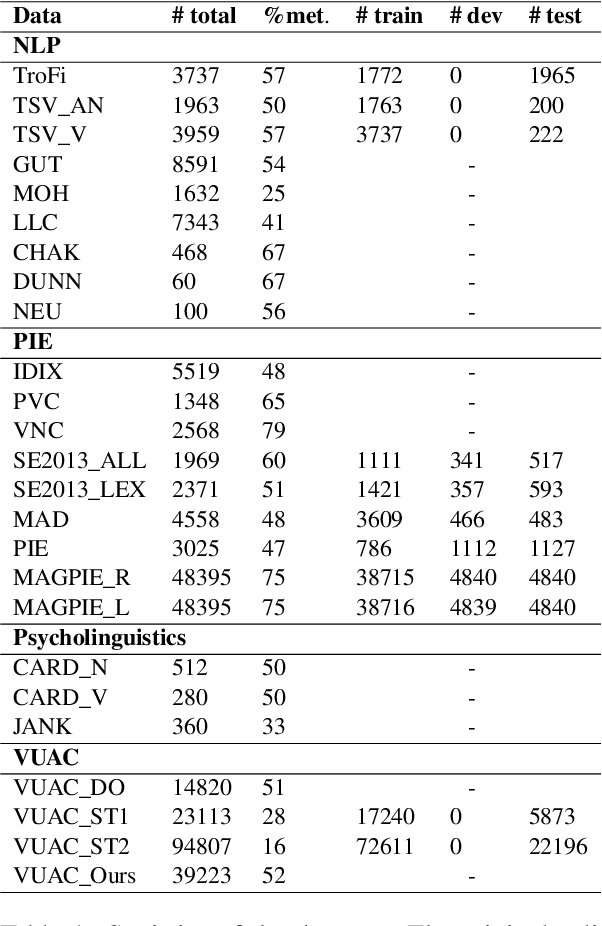
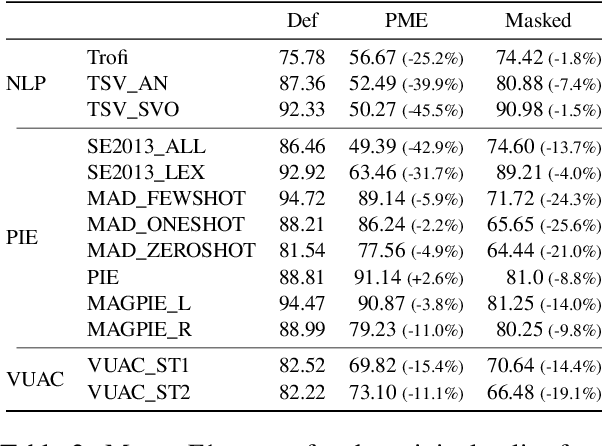
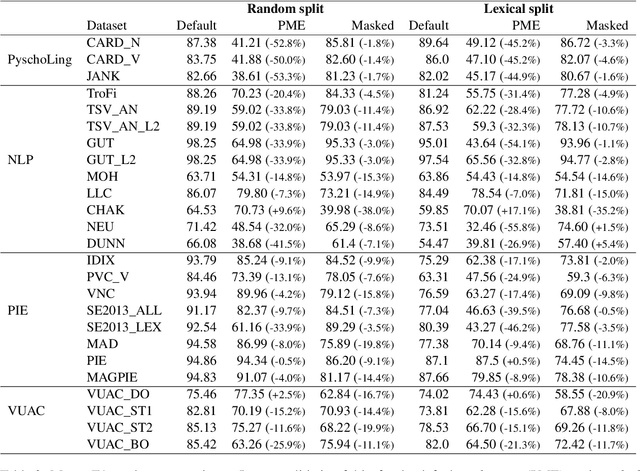
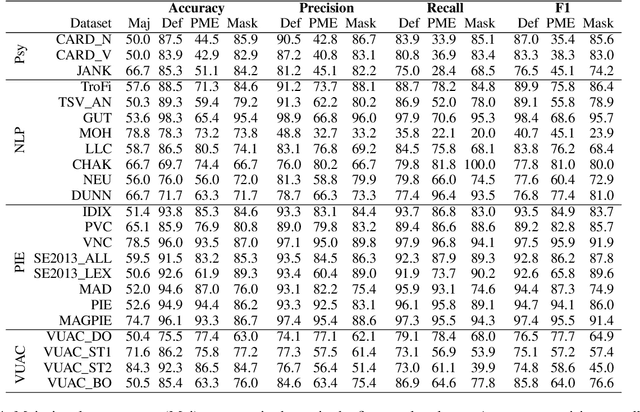
Abstract:Metaphor identification aims at understanding whether a given expression is used figuratively in context. However, in this paper we show how existing metaphor identification datasets can be gamed by fully ignoring the potential metaphorical expression or the context in which it occurs. We test this hypothesis in a variety of datasets and settings, and show that metaphor identification systems based on language models without complete information can be competitive with those using the full context. This is due to the construction procedures to build such datasets, which introduce unwanted biases for positive and negative classes. Finally, we test the same hypothesis on datasets that are carefully sampled from natural corpora and where this bias is not present, making these datasets more challenging and reliable.
TweetNLP: Cutting-Edge Natural Language Processing for Social Media
Jun 29, 2022
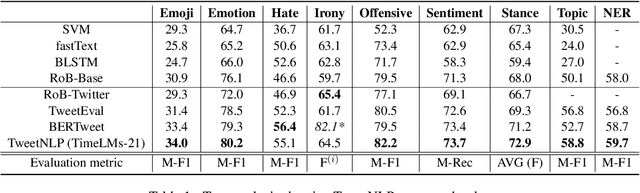
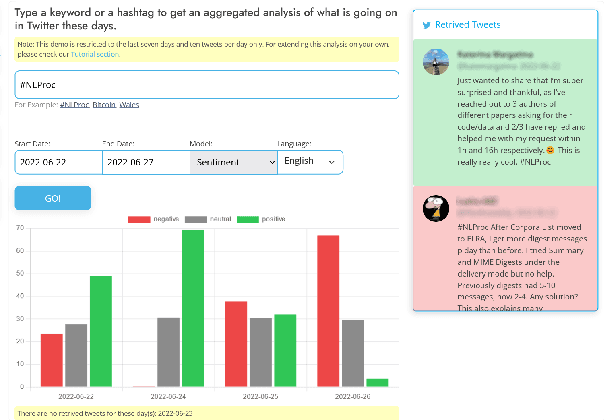
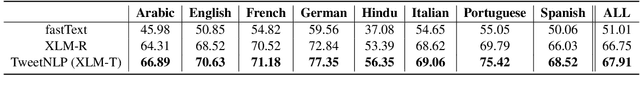
Abstract:In this paper we present TweetNLP, an integrated platform for Natural Language Processing (NLP) in social media. TweetNLP supports a diverse set of NLP tasks, including generic focus areas such as sentiment analysis and named entity recognition, as well as social media-specific tasks such as emoji prediction and offensive language identification. Task-specific systems are powered by reasonably-sized Transformer-based language models specialized on social media text (in particular, Twitter) which can be run without the need for dedicated hardware or cloud services. The main contributions of TweetNLP are: (1) an integrated Python library for a modern toolkit supporting social media analysis using our various task-specific models adapted to the social domain; (2) an interactive online demo for codeless experimentation using our models; and (3) a tutorial covering a wide variety of typical social media applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge