Talayeh Riahi
Tweet Insights: A Visualization Platform to Extract Temporal Insights from Twitter
Aug 04, 2023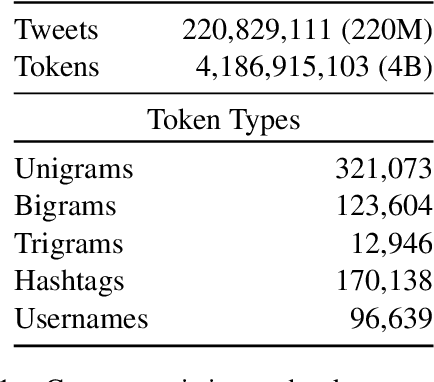
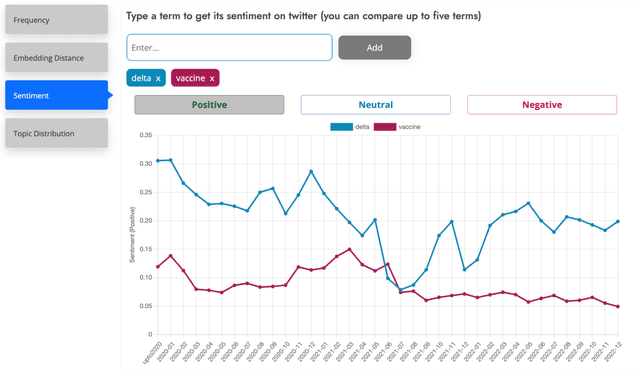
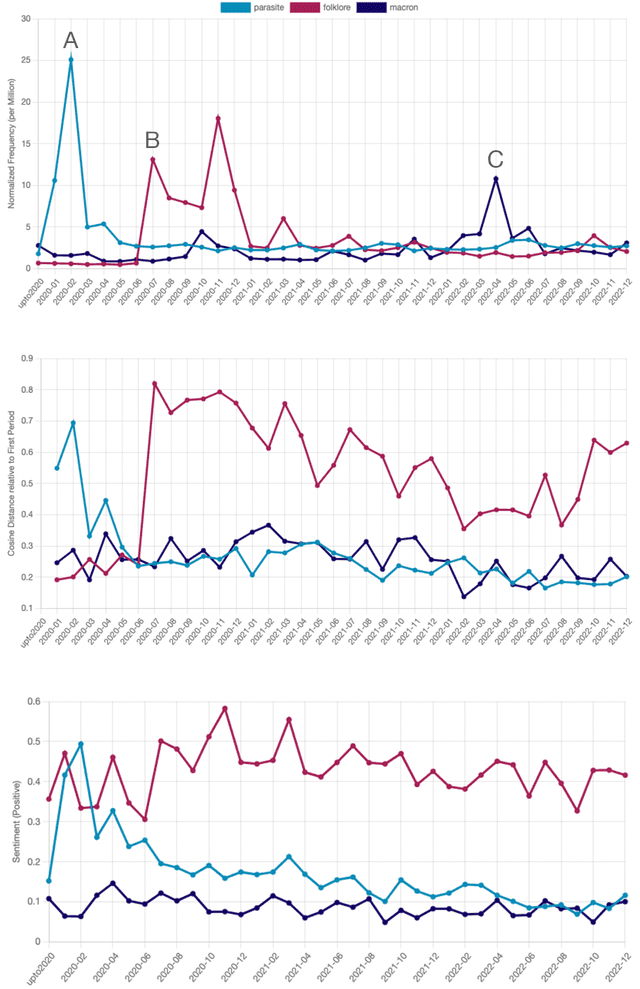
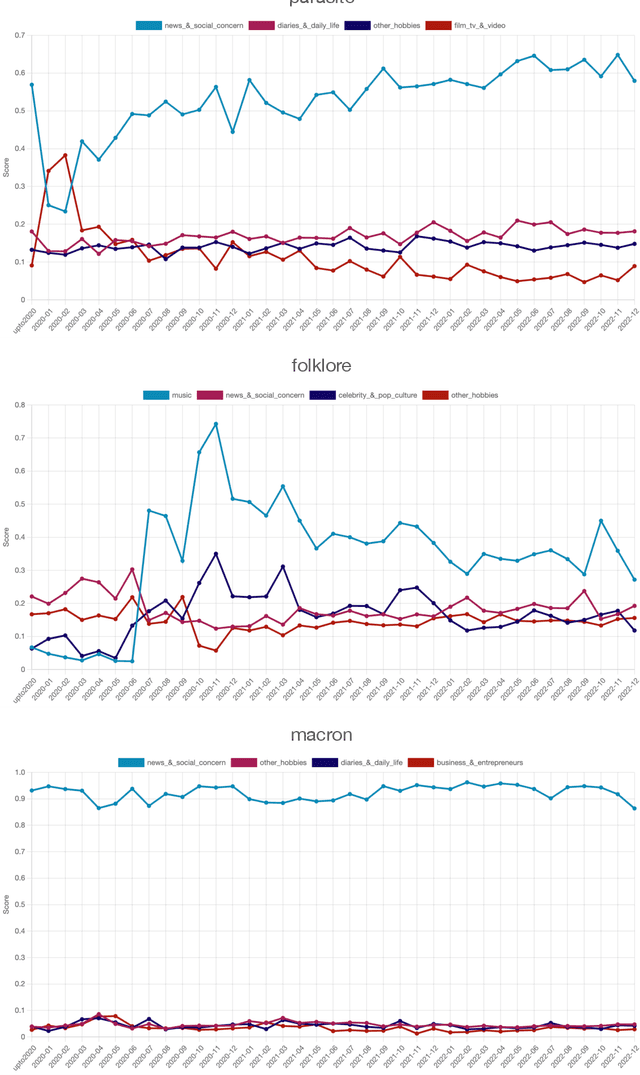
Abstract:This paper introduces a large collection of time series data derived from Twitter, postprocessed using word embedding techniques, as well as specialized fine-tuned language models. This data comprises the past five years and captures changes in n-gram frequency, similarity, sentiment and topic distribution. The interface built on top of this data enables temporal analysis for detecting and characterizing shifts in meaning, including complementary information to trending metrics, such as sentiment and topic association over time. We release an online demo for easy experimentation, and we share code and the underlying aggregated data for future work. In this paper, we also discuss three case studies unlocked thanks to our platform, showcasing its potential for temporal linguistic analysis.
TweetNLP: Cutting-Edge Natural Language Processing for Social Media
Jun 29, 2022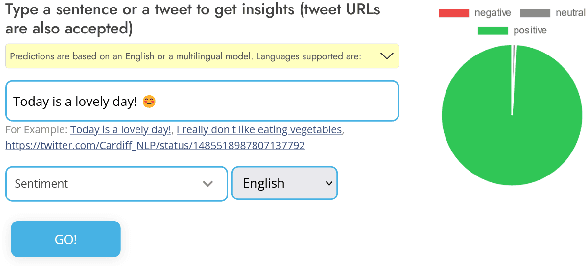
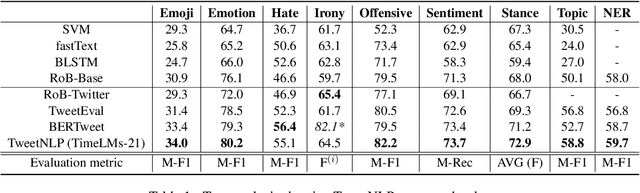
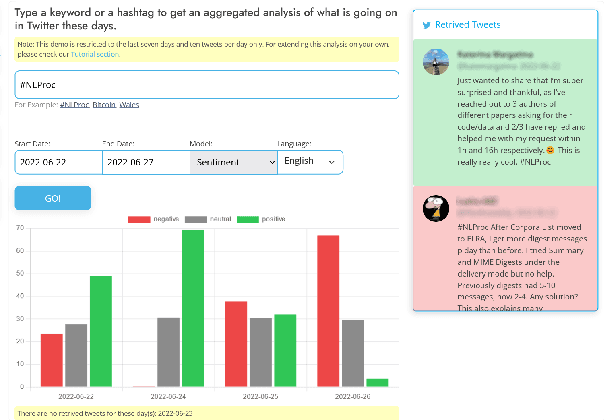
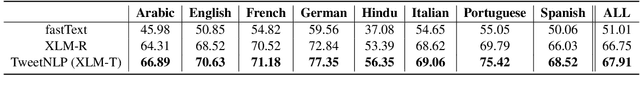
Abstract:In this paper we present TweetNLP, an integrated platform for Natural Language Processing (NLP) in social media. TweetNLP supports a diverse set of NLP tasks, including generic focus areas such as sentiment analysis and named entity recognition, as well as social media-specific tasks such as emoji prediction and offensive language identification. Task-specific systems are powered by reasonably-sized Transformer-based language models specialized on social media text (in particular, Twitter) which can be run without the need for dedicated hardware or cloud services. The main contributions of TweetNLP are: (1) an integrated Python library for a modern toolkit supporting social media analysis using our various task-specific models adapted to the social domain; (2) an interactive online demo for codeless experimentation using our models; and (3) a tutorial covering a wide variety of typical social media applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge