Lijiang Chen
Dynamic Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Graphs for Long-term Language-Guided Mobile Manipulation
Oct 17, 2024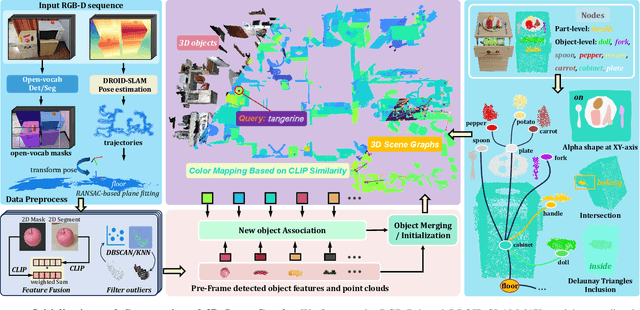
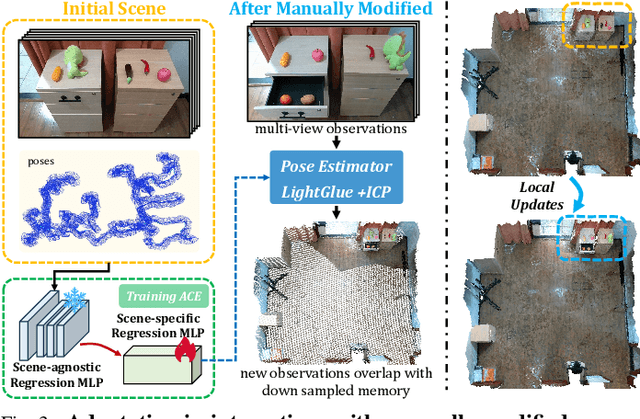
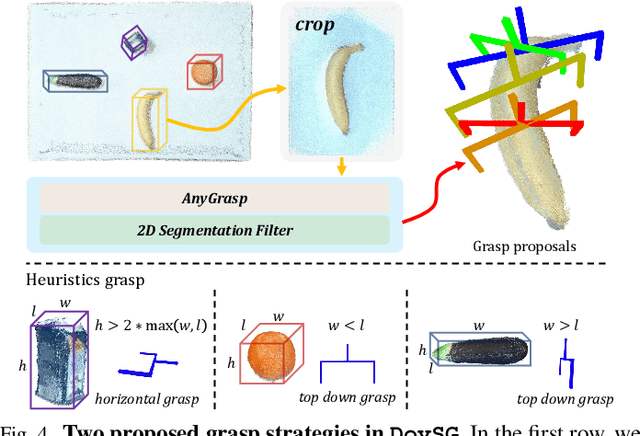
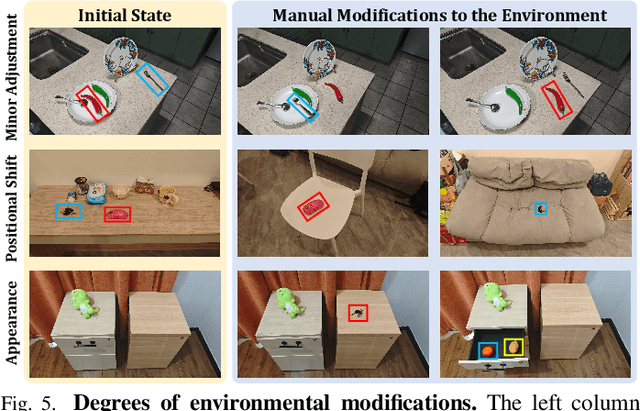
Abstract:Enabling mobile robots to perform long-term tasks in dynamic real-world environments is a formidable challenge, especially when the environment changes frequently due to human-robot interactions or the robot's own actions. Traditional methods typically assume static scenes, which limits their applicability in the continuously changing real world. To overcome these limitations, we present DovSG, a novel mobile manipulation framework that leverages dynamic open-vocabulary 3D scene graphs and a language-guided task planning module for long-term task execution. DovSG takes RGB-D sequences as input and utilizes vision-language models (VLMs) for object detection to obtain high-level object semantic features. Based on the segmented objects, a structured 3D scene graph is generated for low-level spatial relationships. Furthermore, an efficient mechanism for locally updating the scene graph, allows the robot to adjust parts of the graph dynamically during interactions without the need for full scene reconstruction. This mechanism is particularly valuable in dynamic environments, enabling the robot to continually adapt to scene changes and effectively support the execution of long-term tasks. We validated our system in real-world environments with varying degrees of manual modifications, demonstrating its effectiveness and superior performance in long-term tasks. Our project page is available at: https://BJHYZJ.github.io/DoviSG.
OV-VG: A Benchmark for Open-Vocabulary Visual Grounding
Oct 22, 2023



Abstract:Open-vocabulary learning has emerged as a cutting-edge research area, particularly in light of the widespread adoption of vision-based foundational models. Its primary objective is to comprehend novel concepts that are not encompassed within a predefined vocabulary. One key facet of this endeavor is Visual Grounding, which entails locating a specific region within an image based on a corresponding language description. While current foundational models excel at various visual language tasks, there's a noticeable absence of models specifically tailored for open-vocabulary visual grounding. This research endeavor introduces novel and challenging OV tasks, namely Open-Vocabulary Visual Grounding and Open-Vocabulary Phrase Localization. The overarching aim is to establish connections between language descriptions and the localization of novel objects. To facilitate this, we have curated a comprehensive annotated benchmark, encompassing 7,272 OV-VG images and 1,000 OV-PL images. In our pursuit of addressing these challenges, we delved into various baseline methodologies rooted in existing open-vocabulary object detection, VG, and phrase localization frameworks. Surprisingly, we discovered that state-of-the-art methods often falter in diverse scenarios. Consequently, we developed a novel framework that integrates two critical components: Text-Image Query Selection and Language-Guided Feature Attention. These modules are designed to bolster the recognition of novel categories and enhance the alignment between visual and linguistic information. Extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed framework, which consistently attains SOTA performance across the OV-VG task. Additionally, ablation studies provide further evidence of the effectiveness of our innovative models. Codes and datasets will be made publicly available at https://github.com/cv516Buaa/OV-VG.
Self-Training Guided Disentangled Adaptation for Cross-Domain Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation
Jan 13, 2023Abstract:Deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) based remote sensing (RS) image semantic segmentation technology has achieved great success used in many real-world applications such as geographic element analysis. However, strong dependency on annotated data of specific scene makes it hard for DCNNs to fit different RS scenes. To solve this problem, recent works gradually focus on cross-domain RS image semantic segmentation task. In this task, different ground sampling distance, remote sensing sensor variation and different geographical landscapes are three main factors causing dramatic domain shift between source and target images. To decrease the negative influence of domain shift, we propose a self-training guided disentangled adaptation network (ST-DASegNet). We first propose source student backbone and target student backbone to respectively extract the source-style and target-style feature for both source and target images. Towards the intermediate output feature maps of each backbone, we adopt adversarial learning for alignment. Then, we propose a domain disentangled module to extract the universal feature and purify the distinct feature of source-style and target-style features. Finally, these two features are fused and served as input of source student decoder and target student decoder to generate final predictions. Based on our proposed domain disentangled module, we further propose exponential moving average (EMA) based cross-domain separated self-training mechanism to ease the instability and disadvantageous effect during adversarial optimization. Extensive experiments and analysis on benchmark RS datasets show that ST-DASegNet outperforms previous methods on cross-domain RS image semantic segmentation task and achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results. Our code is available at https://github.com/cv516Buaa/ST-DASegNet.
Look in Different Views: Multi-Scheme Regression Guided Cell Instance Segmentation
Aug 17, 2022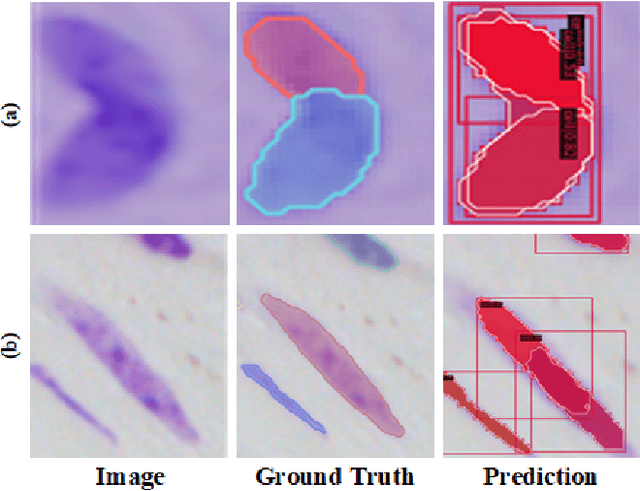
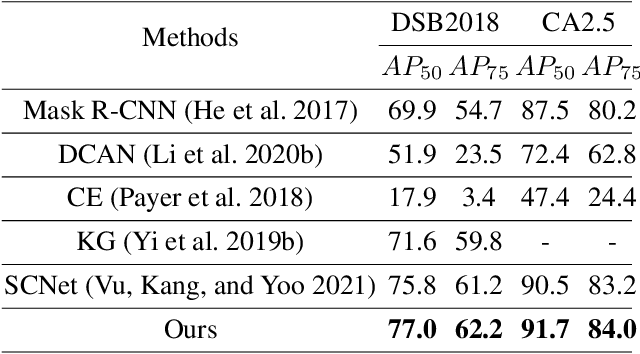
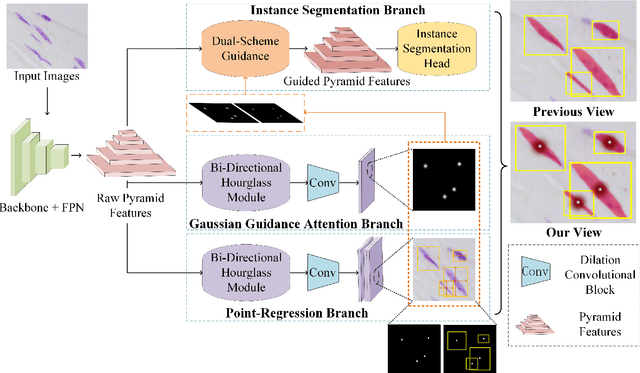
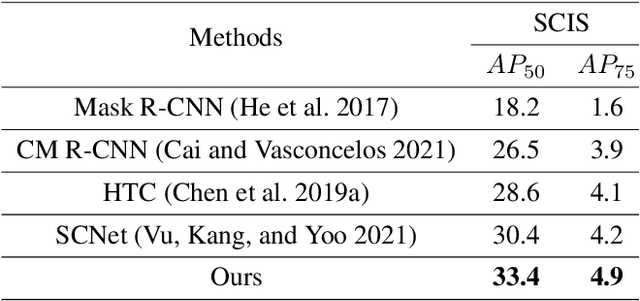
Abstract:Cell instance segmentation is a new and challenging task aiming at joint detection and segmentation of every cell in an image. Recently, many instance segmentation methods have applied in this task. Despite their great success, there still exists two main weaknesses caused by uncertainty of localizing cell center points. First, densely packed cells can easily be recognized into one cell. Second, elongated cell can easily be recognized into two cells. To overcome these two weaknesses, we propose a novel cell instance segmentation network based on multi-scheme regression guidance. With multi-scheme regression guidance, the network has the ability to look each cell in different views. Specifically, we first propose a gaussian guidance attention mechanism to use gaussian labels for guiding the network's attention. We then propose a point-regression module for assisting the regression of cell center. Finally, we utilize the output of the above two modules to further guide the instance segmentation. With multi-scheme regression guidance, we can take full advantage of the characteristics of different regions, especially the central region of the cell. We conduct extensive experiments on benchmark datasets, DSB2018, CA2.5 and SCIS. The encouraging results show that our network achieves SOTA (state-of-the-art) performance. On the DSB2018 and CA2.5, our network surpasses previous methods by 1.2% (AP50). Particularly on SCIS dataset, our network performs stronger by large margin (3.0% higher AP50). Visualization and analysis further prove that our proposed method is interpretable.
A Multi-Modality Ovarian Tumor Ultrasound Image Dataset for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation
Jul 14, 2022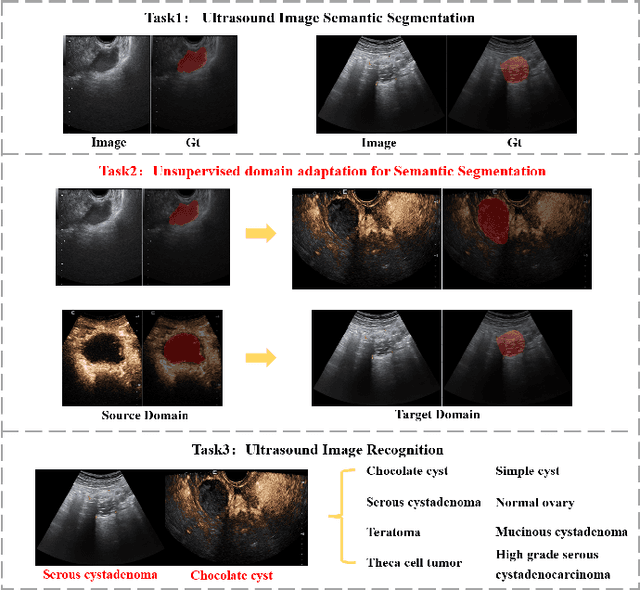
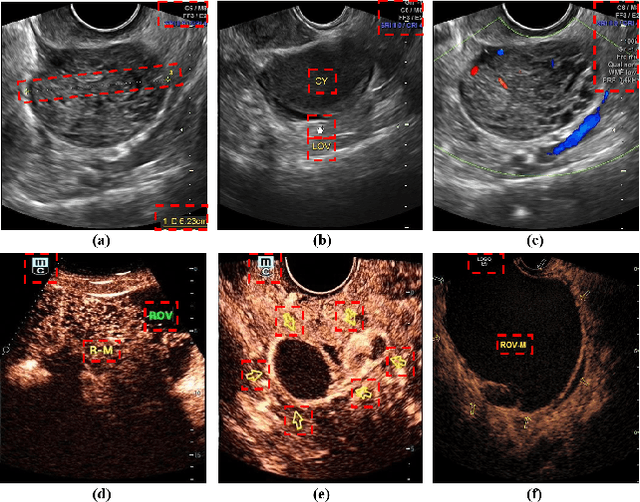
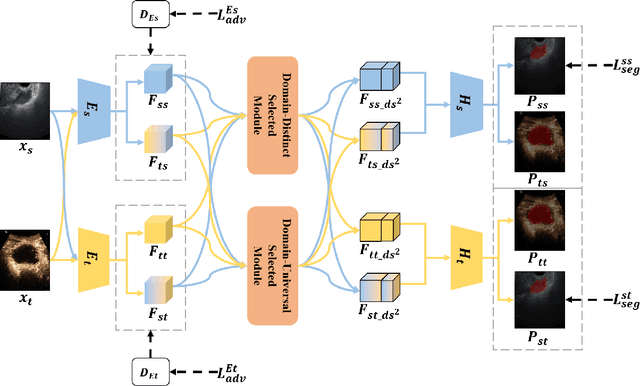
Abstract:Ovarian cancer is one of the most harmful gynecological diseases. Detecting ovarian tumors in early stage with computer-aided techniques can efficiently decrease the mortality rate. With the improvement of medical treatment standard, ultrasound images are widely applied in clinical treatment. However, recent notable methods mainly focus on single-modality ultrasound ovarian tumor segmentation or recognition, which means there still lacks of researches on exploring the representation capability of multi-modality ultrasound ovarian tumor images. To solve this problem, we propose a Multi-Modality Ovarian Tumor Ultrasound (MMOTU) image dataset containing 1469 2d ultrasound images and 170 contrast enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) images with pixel-wise and global-wise annotations. Based on MMOTU, we mainly focus on unsupervised cross-domain semantic segmentation task. To solve the domain shift problem, we propose a feature alignment based architecture named Dual-Scheme Domain-Selected Network (DS$^2$Net). Specifically, we first design source-encoder and target-encoder to extract two-style features of source and target images. Then, we propose Domain-Distinct Selected Module (DDSM) and Domain-Universal Selected Module (DUSM) to extract the distinct and universal features in two styles (source-style or target-style). Finally, we fuse these two kinds of features and feed them into the source-decoder and target-decoder to generate final predictions. Extensive comparison experiments and analysis on MMOTU image dataset show that DS$^2$Net can boost the segmentation performance for bidirectional cross-domain adaptation of 2d ultrasound images and CEUS images.
Attention-based Feature Decomposition-Reconstruction Network for Scene Text Detection
Nov 29, 2021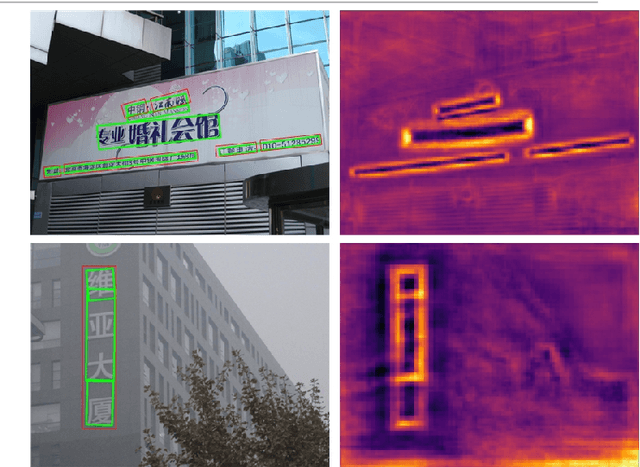
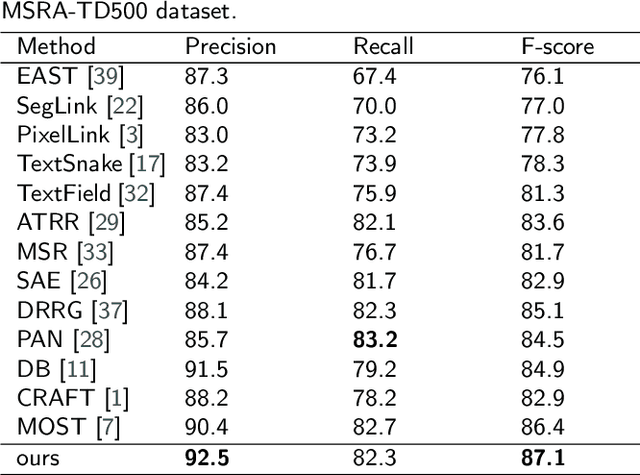
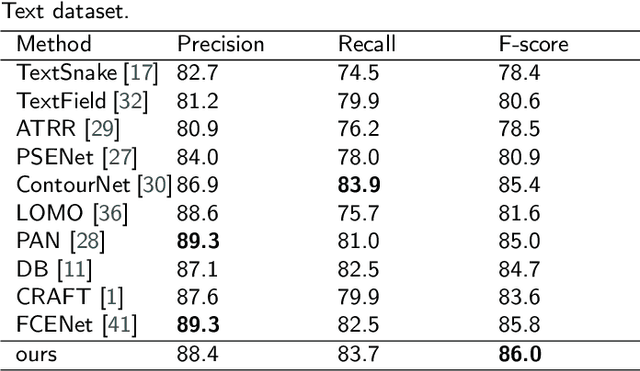
Abstract:Recently, scene text detection has been a challenging task. Texts with arbitrary shape or large aspect ratio are usually hard to detect. Previous segmentation-based methods can describe curve text more accurately but suffer from over segmentation and text adhesion. In this paper, we propose attention-based feature decomposition-reconstruction network for scene text detection, which utilizes contextual information and low-level feature to enhance the performance of segmentation-based text detector. In the phase of feature fusion, we introduce cross level attention module to enrich contextual information of text by adding attention mechanism on fused multi-scaled feature. In the phase of probability map generation, a feature decomposition-reconstruction module is proposed to alleviate the over segmentation problem of large aspect ratio text, which decomposes text feature according to their frequency characteristic and then reconstructs it by adding low-level feature. Experiments have been conducted on two public benchmark datasets and results show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Embedded Self-Distillation in Compact Multi-Branch Ensemble Network for Remote Sensing Scene Classification
Apr 01, 2021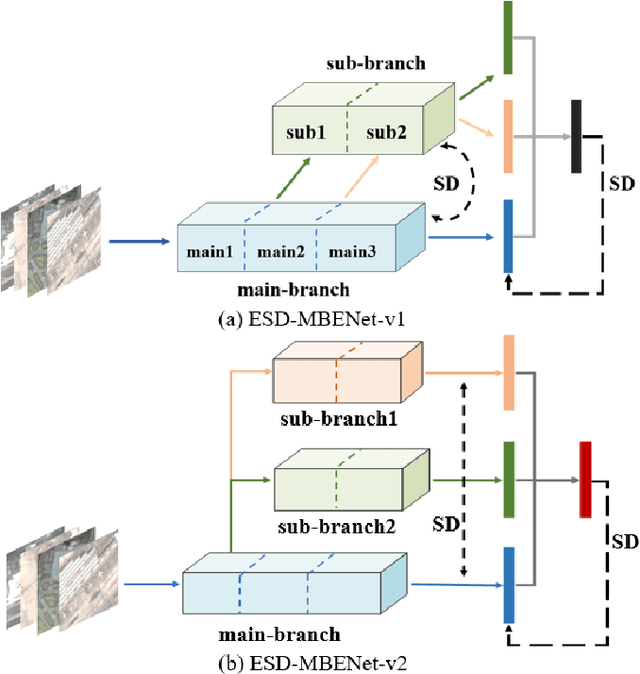
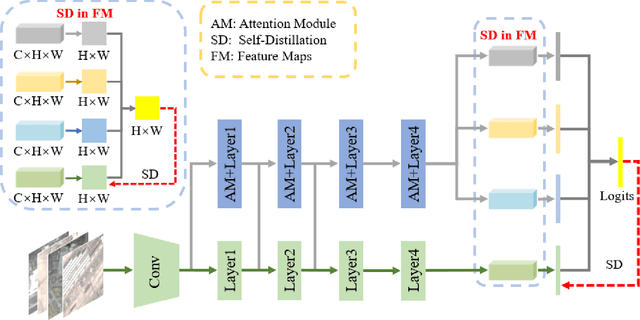
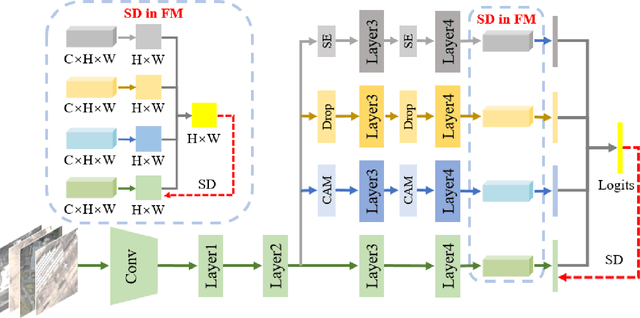
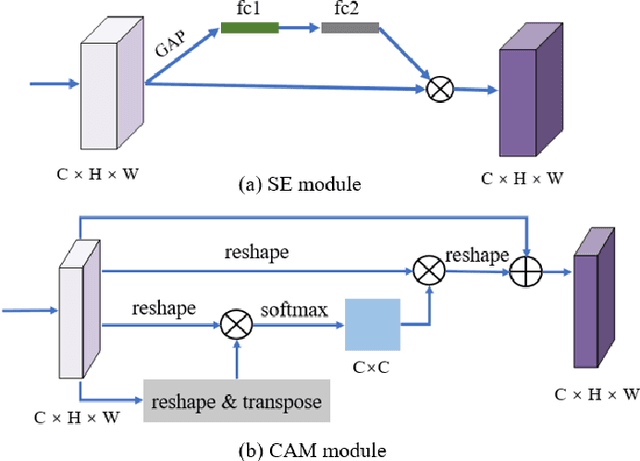
Abstract:Remote sensing (RS) image scene classification task faces many challenges due to the interference from different characteristics of different geographical elements. To solve this problem, we propose a multi-branch ensemble network to enhance the feature representation ability by fusing features in final output logits and intermediate feature maps. However, simply adding branches will increase the complexity of models and decline the inference efficiency. On this issue, we embed self-distillation (SD) method to transfer knowledge from ensemble network to main-branch in it. Through optimizing with SD, main-branch will have close performance as ensemble network. During inference, we can cut other branches to simplify the whole model. In this paper, we first design compact multi-branch ensemble network, which can be trained in an end-to-end manner. Then, we insert SD method on output logits and feature maps. Compared to previous methods, our proposed architecture (ESD-MBENet) performs strongly on classification accuracy with compact design. Extensive experiments are applied on three benchmark RS datasets AID, NWPU-RESISC45 and UC-Merced with three classic baseline models, VGG16, ResNet50 and DenseNet121. Results prove that our proposed ESD-MBENet can achieve better accuracy than previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) complex models. Moreover, abundant visualization analysis make our method more convincing and interpretable.
MGML: Multi-Granularity Multi-Level Feature Ensemble Network for Remote Sensing Scene Classification
Dec 29, 2020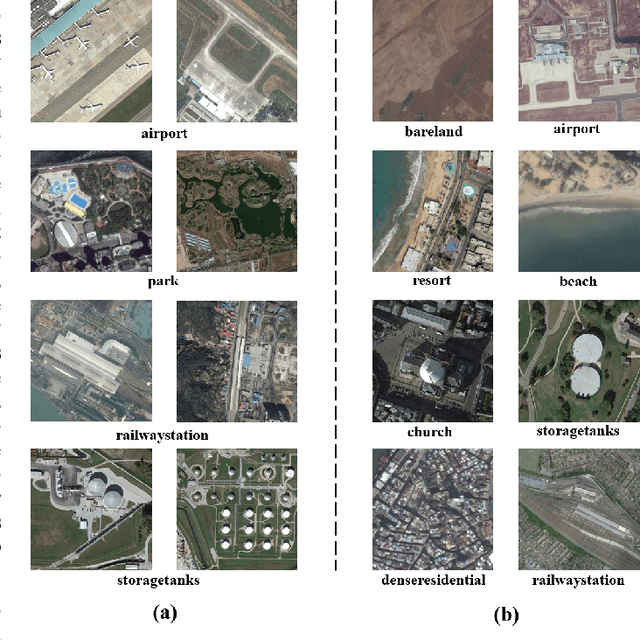
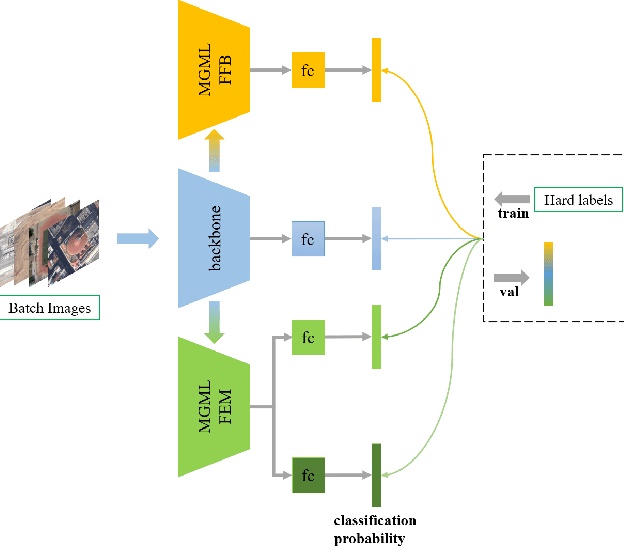
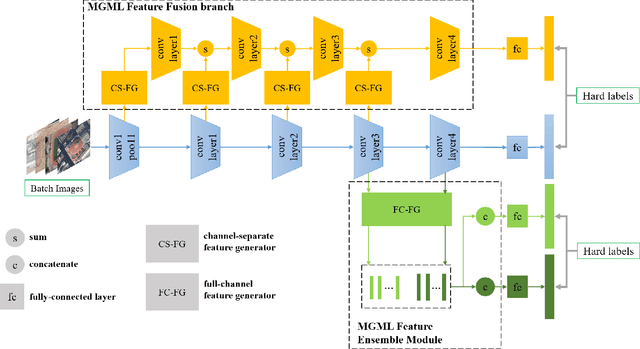
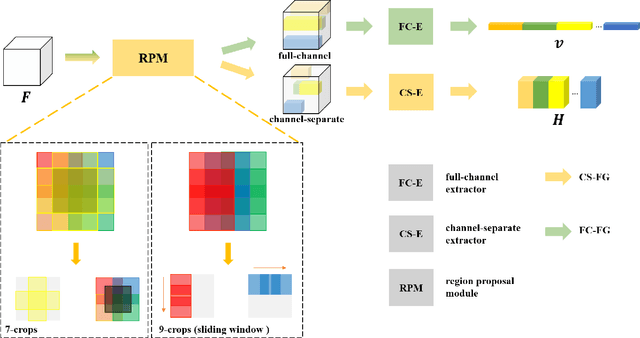
Abstract:Remote sensing (RS) scene classification is a challenging task to predict scene categories of RS images. RS images have two main characters: large intra-class variance caused by large resolution variance and confusing information from large geographic covering area. To ease the negative influence from the above two characters. We propose a Multi-granularity Multi-Level Feature Ensemble Network (MGML-FENet) to efficiently tackle RS scene classification task in this paper. Specifically, we propose Multi-granularity Multi-Level Feature Fusion Branch (MGML-FFB) to extract multi-granularity features in different levels of network by channel-separate feature generator (CS-FG). To avoid the interference from confusing information, we propose Multi-granularity Multi-Level Feature Ensemble Module (MGML-FEM) which can provide diverse predictions by full-channel feature generator (FC-FG). Compared to previous methods, our proposed networks have ability to use structure information and abundant fine-grained features. Furthermore, through ensemble learning method, our proposed MGML-FENets can obtain more convincing final predictions. Extensive classification experiments on multiple RS datasets (AID, NWPU-RESISC45, UC-Merced and VGoogle) demonstrate that our proposed networks achieve better performance than previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) networks. The visualization analysis also shows the good interpretability of MGML-FENet.
Point Context: An Effective Shape Descriptor for RST-invariant Trajectory Recognition
Jan 22, 2015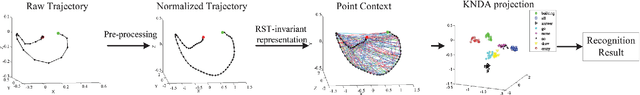

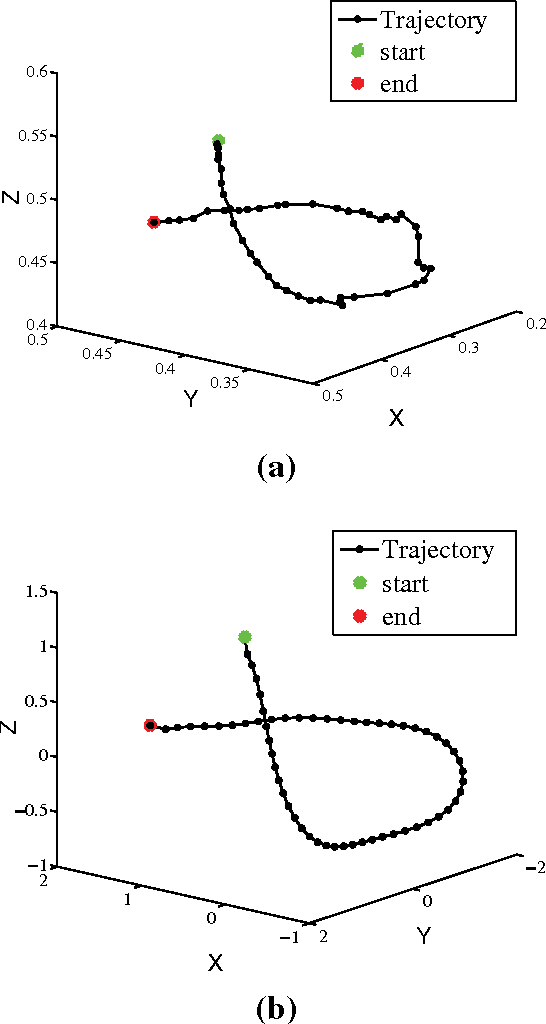
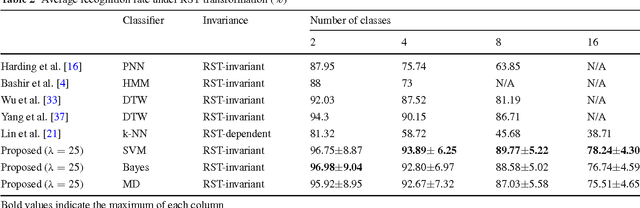
Abstract:Motion trajectory recognition is important for characterizing the moving property of an object. The speed and accuracy of trajectory recognition rely on a compact and discriminative feature representation, and the situations of varying rotation, scaling and translation has to be specially considered. In this paper we propose a novel feature extraction method for trajectories. Firstly a trajectory is represented by a proposed point context, which is a rotation-scale-translation (RST) invariant shape descriptor with a flexible tradeoff between computational complexity and discrimination, yet we prove that it is a complete shape descriptor. Secondly, the shape context is nonlinearly mapped to a subspace by kernel nonparametric discriminant analysis (KNDA) to get a compact feature representation, and thus a trajectory is projected to a single point in a low-dimensional feature space. Experimental results show that, the proposed trajectory feature shows encouraging improvement than state-of-art methods.
* 11 pages, 10 figures
Machine Translation Model based on Non-parallel Corpus and Semi-supervised Transductive Learning
May 22, 2014
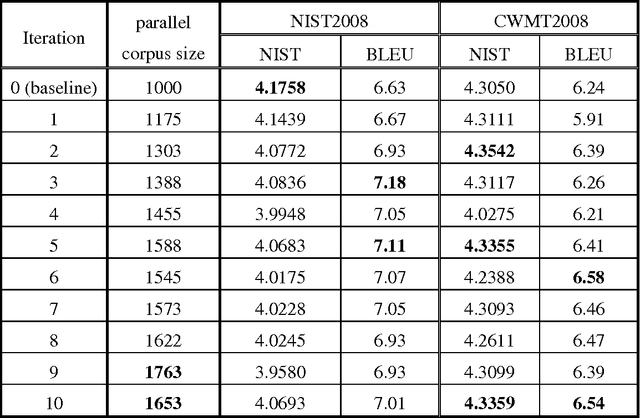
Abstract:Although the parallel corpus has an irreplaceable role in machine translation, its scale and coverage is still beyond the actual needs. Non-parallel corpus resources on the web have an inestimable potential value in machine translation and other natural language processing tasks. This article proposes a semi-supervised transductive learning method for expanding the training corpus in statistical machine translation system by extracting parallel sentences from the non-parallel corpus. This method only requires a small amount of labeled corpus and a large unlabeled corpus to build a high-performance classifier, especially for when there is short of labeled corpus. The experimental results show that by combining the non-parallel corpus alignment and the semi-supervised transductive learning method, we can more effectively use their respective strengths to improve the performance of machine translation system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge