Lihong Gu
Breaking the Barrier: Utilizing Large Language Models for Industrial Recommendation Systems through an Inferential Knowledge Graph
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:Recommendation systems are widely used in e-commerce websites and online platforms to address information overload. However, existing systems primarily rely on historical data and user feedback, making it difficult to capture user intent transitions. Recently, Knowledge Base (KB)-based models are proposed to incorporate expert knowledge, but it struggle to adapt to new items and the evolving e-commerce environment. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Large Language Model based Complementary Knowledge Enhanced Recommendation System (LLM-KERec). It introduces an entity extractor that extracts unified concept terms from item and user information. To provide cost-effective and reliable prior knowledge, entity pairs are generated based on entity popularity and specific strategies. The large language model determines complementary relationships in each entity pair, constructing a complementary knowledge graph. Furthermore, a new complementary recall module and an Entity-Entity-Item (E-E-I) weight decision model refine the scoring of the ranking model using real complementary exposure-click samples. Extensive experiments conducted on three industry datasets demonstrate the significant performance improvement of our model compared to existing approaches. Additionally, detailed analysis shows that LLM-KERec enhances users' enthusiasm for consumption by recommending complementary items. In summary, LLM-KERec addresses the limitations of traditional recommendation systems by incorporating complementary knowledge and utilizing a large language model to capture user intent transitions, adapt to new items, and enhance recommendation efficiency in the evolving e-commerce landscape.
Marketing Budget Allocation with Offline Constrained Deep Reinforcement Learning
Sep 06, 2023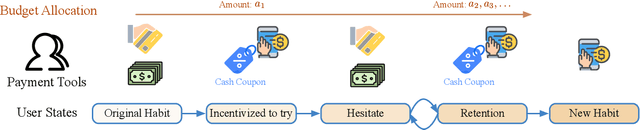
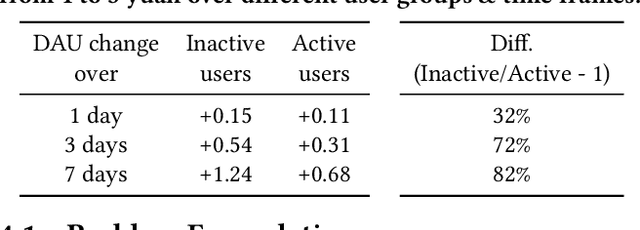
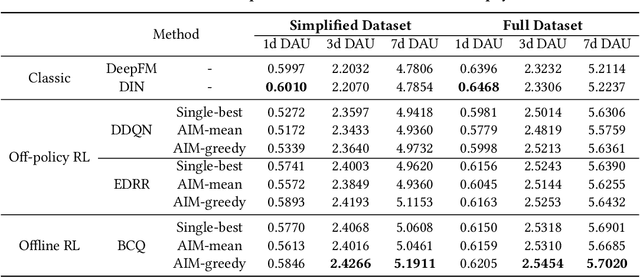
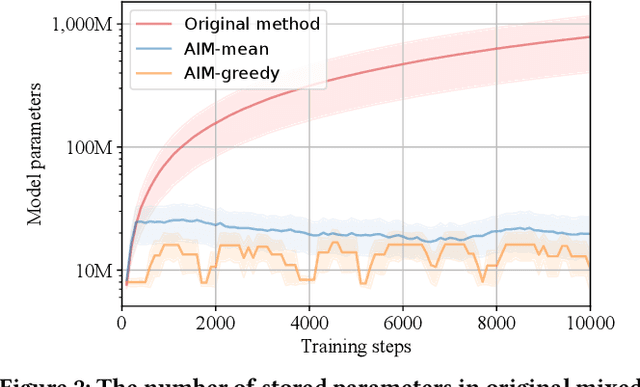
Abstract:We study the budget allocation problem in online marketing campaigns that utilize previously collected offline data. We first discuss the long-term effect of optimizing marketing budget allocation decisions in the offline setting. To overcome the challenge, we propose a novel game-theoretic offline value-based reinforcement learning method using mixed policies. The proposed method reduces the need to store infinitely many policies in previous methods to only constantly many policies, which achieves nearly optimal policy efficiency, making it practical and favorable for industrial usage. We further show that this method is guaranteed to converge to the optimal policy, which cannot be achieved by previous value-based reinforcement learning methods for marketing budget allocation. Our experiments on a large-scale marketing campaign with tens-of-millions users and more than one billion budget verify the theoretical results and show that the proposed method outperforms various baseline methods. The proposed method has been successfully deployed to serve all the traffic of this marketing campaign.
Model-free Reinforcement Learning with Stochastic Reward Stabilization for Recommender Systems
Aug 25, 2023Abstract:Model-free RL-based recommender systems have recently received increasing research attention due to their capability to handle partial feedback and long-term rewards. However, most existing research has ignored a critical feature in recommender systems: one user's feedback on the same item at different times is random. The stochastic rewards property essentially differs from that in classic RL scenarios with deterministic rewards, which makes RL-based recommender systems much more challenging. In this paper, we first demonstrate in a simulator environment where using direct stochastic feedback results in a significant drop in performance. Then to handle the stochastic feedback more efficiently, we design two stochastic reward stabilization frameworks that replace the direct stochastic feedback with that learned by a supervised model. Both frameworks are model-agnostic, i.e., they can effectively utilize various supervised models. We demonstrate the superiority of the proposed frameworks over different RL-based recommendation baselines with extensive experiments on a recommendation simulator as well as an industrial-level recommender system.
Adversarial Learning for Incentive Optimization in Mobile Payment Marketing
Dec 28, 2021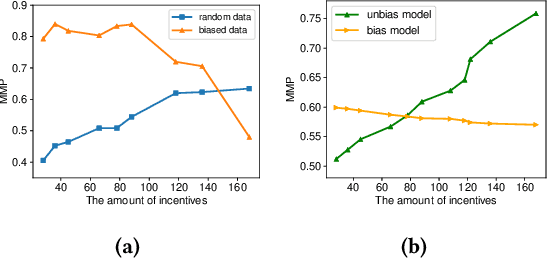
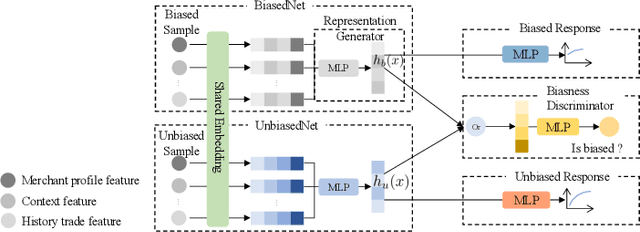
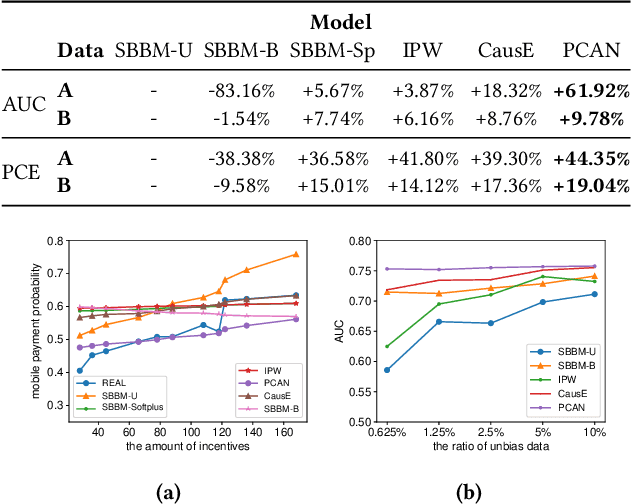
Abstract:Many payment platforms hold large-scale marketing campaigns, which allocate incentives to encourage users to pay through their applications. To maximize the return on investment, incentive allocations are commonly solved in a two-stage procedure. After training a response estimation model to estimate the users' mobile payment probabilities (MPP), a linear programming process is applied to obtain the optimal incentive allocation. However, the large amount of biased data in the training set, generated by the previous biased allocation policy, causes a biased estimation. This bias deteriorates the performance of the response model and misleads the linear programming process, dramatically degrading the performance of the resulting allocation policy. To overcome this obstacle, we propose a bias correction adversarial network. Our method leverages the small set of unbiased data obtained under a full-randomized allocation policy to train an unbiased model and then uses it to reduce the bias with adversarial learning. Offline and online experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches and significantly improves the performance of the resulting allocation policy in a real-world marketing campaign.
A Policy Efficient Reduction Approach to Convex Constrained Deep Reinforcement Learning
Aug 29, 2021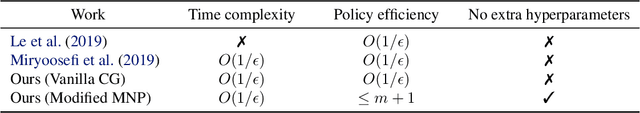
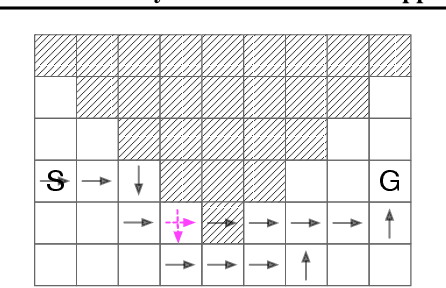
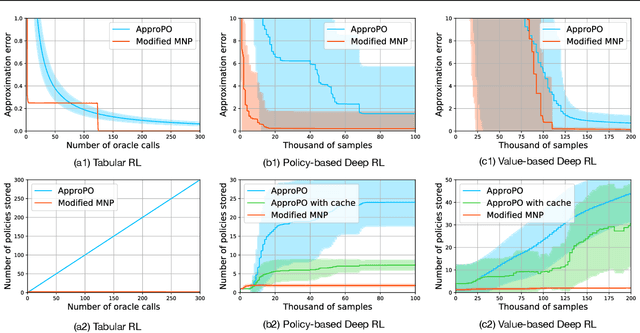

Abstract:Although well-established in general reinforcement learning (RL), value-based methods are rarely explored in constrained RL (CRL) for their incapability of finding policies that can randomize among multiple actions. To apply value-based methods to CRL, a recent groundbreaking line of game-theoretic approaches uses the mixed policy that randomizes among a set of carefully generated policies to converge to the desired constraint-satisfying policy. However, these approaches require storing a large set of policies, which is not policy efficient, and may incur prohibitive memory costs in constrained deep RL. To address this problem, we propose an alternative approach. Our approach first reformulates the CRL to an equivalent distance optimization problem. With a specially designed linear optimization oracle, we derive a meta-algorithm that solves it using any off-the-shelf RL algorithm and any conditional gradient (CG) type algorithm as subroutines. We then propose a new variant of the CG-type algorithm, which generalizes the minimum norm point (MNP) method. The proposed method matches the convergence rate of the existing game-theoretic approaches and achieves the worst-case optimal policy efficiency. The experiments on a navigation task show that our method reduces the memory costs by an order of magnitude, and meanwhile achieves better performance, demonstrating both its effectiveness and efficiency.
Adaptive Optimizers with Sparse Group Lasso for Neural Networks in CTR Prediction
Jul 30, 2021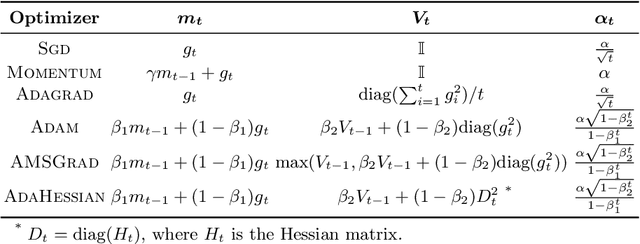
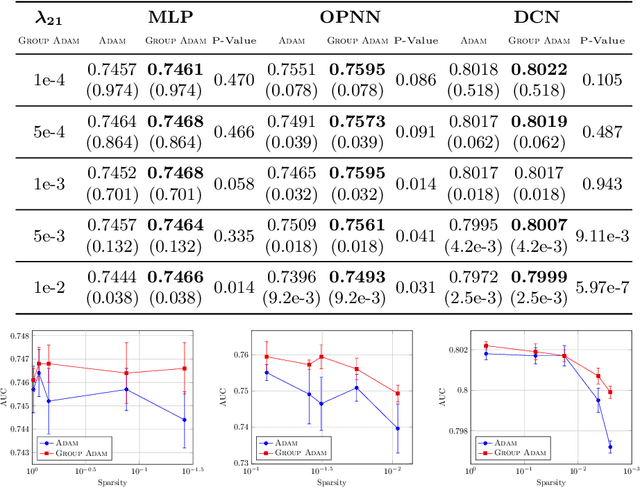
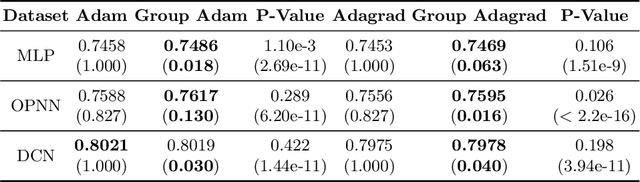
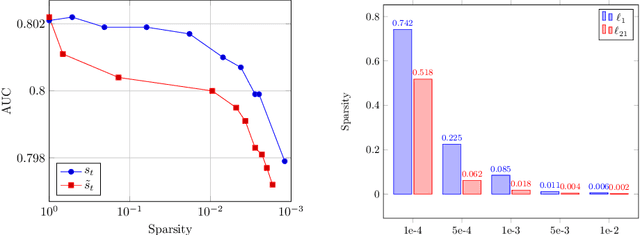
Abstract:We develop a novel framework that adds the regularizers of the sparse group lasso to a family of adaptive optimizers in deep learning, such as Momentum, Adagrad, Adam, AMSGrad, AdaHessian, and create a new class of optimizers, which are named Group Momentum, Group Adagrad, Group Adam, Group AMSGrad and Group AdaHessian, etc., accordingly. We establish theoretically proven convergence guarantees in the stochastic convex settings, based on primal-dual methods. We evaluate the regularized effect of our new optimizers on three large-scale real-world ad click datasets with state-of-the-art deep learning models. The experimental results reveal that compared with the original optimizers with the post-processing procedure which uses the magnitude pruning method, the performance of the models can be significantly improved on the same sparsity level. Furthermore, in comparison to the cases without magnitude pruning, our methods can achieve extremely high sparsity with significantly better or highly competitive performance.
LinkLouvain: Link-Aware A/B Testing and Its Application on Online Marketing Campaign
Feb 03, 2021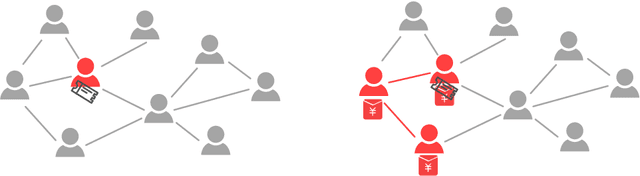
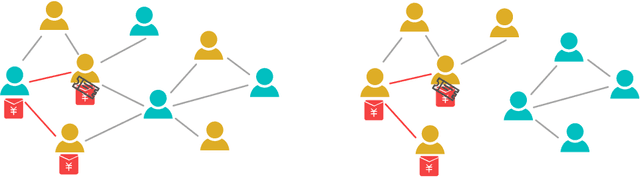
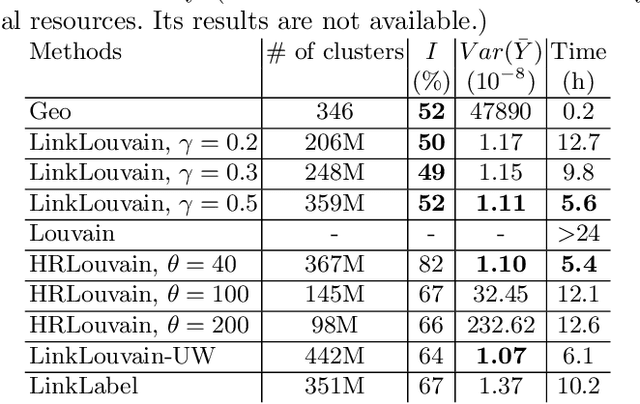
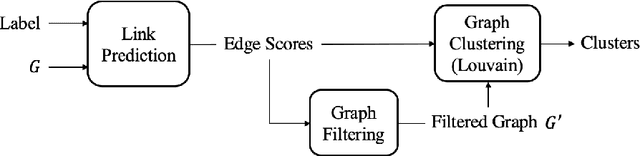
Abstract:A lot of online marketing campaigns aim to promote user interaction. The average treatment effect (ATE) of campaign strategies need to be monitored throughout the campaign. A/B testing is usually conducted for such needs, whereas the existence of user interaction can introduce interference to normal A/B testing. With the help of link prediction, we design a network A/B testing method LinkLouvain to minimize graph interference and it gives an accurate and sound estimate of the campaign's ATE. In this paper, we analyze the network A/B testing problem under a real-world online marketing campaign, describe our proposed LinkLouvain method, and evaluate it on real-world data. Our method achieves significant performance compared with others and is deployed in the online marketing campaign.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge