Shenliao Bao
Model-free Reinforcement Learning with Stochastic Reward Stabilization for Recommender Systems
Aug 25, 2023Abstract:Model-free RL-based recommender systems have recently received increasing research attention due to their capability to handle partial feedback and long-term rewards. However, most existing research has ignored a critical feature in recommender systems: one user's feedback on the same item at different times is random. The stochastic rewards property essentially differs from that in classic RL scenarios with deterministic rewards, which makes RL-based recommender systems much more challenging. In this paper, we first demonstrate in a simulator environment where using direct stochastic feedback results in a significant drop in performance. Then to handle the stochastic feedback more efficiently, we design two stochastic reward stabilization frameworks that replace the direct stochastic feedback with that learned by a supervised model. Both frameworks are model-agnostic, i.e., they can effectively utilize various supervised models. We demonstrate the superiority of the proposed frameworks over different RL-based recommendation baselines with extensive experiments on a recommendation simulator as well as an industrial-level recommender system.
FragmGAN: Generative Adversarial Nets for Fragmentary Data Imputation and Prediction
Mar 09, 2022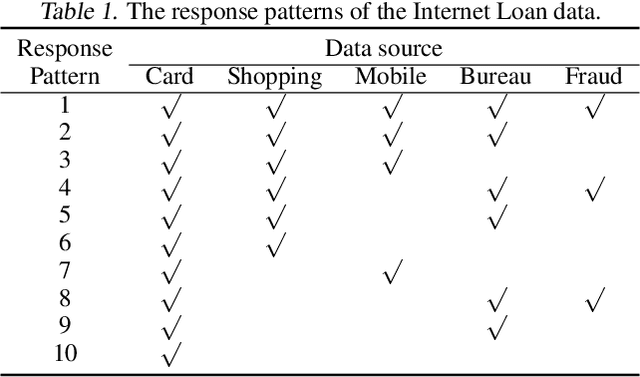
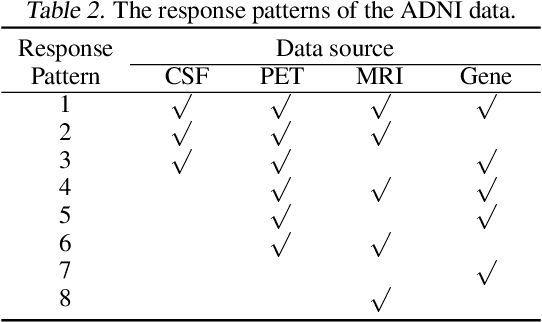
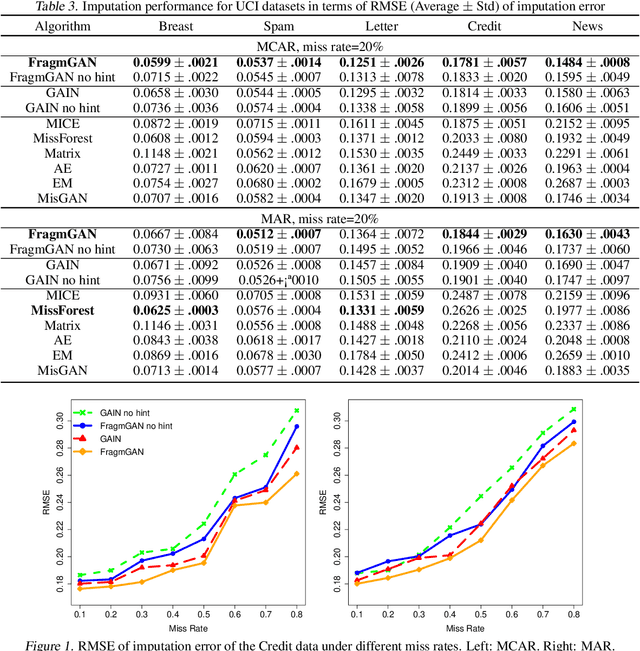
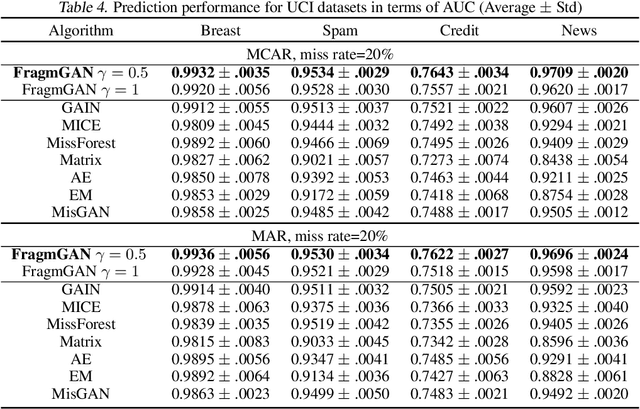
Abstract:Modern scientific research and applications very often encounter "fragmentary data" which brings big challenges to imputation and prediction. By leveraging the structure of response patterns, we propose a unified and flexible framework based on Generative Adversarial Nets (GAN) to deal with fragmentary data imputation and label prediction at the same time. Unlike most of the other generative model based imputation methods that either have no theoretical guarantee or only consider Missing Completed At Random (MCAR), the proposed FragmGAN has theoretical guarantees for imputation with data Missing At Random (MAR) while no hint mechanism is needed. FragmGAN trains a predictor with the generator and discriminator simultaneously. This linkage mechanism shows significant advantages for predictive performances in extensive experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge