Li Pan
MASteer: Multi-Agent Adaptive Steer Strategy for End-to-End LLM Trustworthiness Repair
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) face persistent and evolving trustworthiness issues, motivating developers to seek automated and flexible repair methods that enable convenient deployment across diverse scenarios. Existing repair methods like supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF) are costly and slow, while prompt engineering lacks robustness and scalability. Representation engineering, which steers model behavior by injecting targeted concept vectors during inference, offers a lightweight, training-free alternative. However, current approaches depend on manually crafted samples and fixed steering strategies, limiting automation and adaptability. To overcome these challenges, we propose MASteer, the first end-to-end framework for trustworthiness repair in LLMs based on representation engineering. MASteer integrates two core components: AutoTester, a multi-agent system that generates diverse, high-quality steer samples tailored to developer needs; and AutoRepairer, which constructs adaptive steering strategies with anchor vectors for automated, context-aware strategy selection during inference. Experiments on standard and customized trustworthiness tasks show MASteer consistently outperforms baselines, improving metrics by 15.36% on LLaMA-3.1-8B-Chat and 4.21% on Qwen-3-8B-Chat, while maintaining general model capabilities. MASteer demonstrates strong robustness, generalization, and practical value for scalable, efficient trustworthiness repair.
Beyond Uniform Criteria: Scenario-Adaptive Multi-Dimensional Jailbreak Evaluation
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Precise jailbreak evaluation is vital for LLM red teaming and jailbreak research. Current approaches employ binary classification ( e.g., string matching, toxic text classifiers, LLM-driven methods), yielding only "yes/no" labels without quantifying harm intensity. Existing multi-dimensional frameworks ( e.g., Security Violation, Relative Truthfulness, Informativeness) apply uniform evaluation criteria across scenarios, resulting in scenario-specific mismatches--for instance, "Relative Truthfulness" is irrelevant to "hate speech"--which compromise evaluation precision. To tackle these limitations, we introduce SceneJailEval, with key contributions: (1) A groundbreaking scenario-adaptive multi-dimensional framework for jailbreak evaluation, overcoming the critical "one-size-fits-all" constraint of existing multi-dimensional methods, and featuring strong extensibility to flexibly adapt to customized or emerging scenarios. (2) A comprehensive 14-scenario dataset with diverse jailbreak variants and regional cases, filling the long-standing gap in high-quality, holistic benchmarks for scenario-adaptive evaluation. (3) SceneJailEval achieves state-of-the-art results, with an F1 score of 0.917 on our full-scenario dataset (+6% over prior SOTA) and 0.995 on JBB (+3% over prior SOTA), surpassing accuracy limits of existing evaluation methods in heterogeneous scenarios and confirming its advantage.
CRAVE: A Conflicting Reasoning Approach for Explainable Claim Verification Using LLMs
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:The rapid spread of misinformation, driven by digital media and AI-generated content, has made automatic claim verification essential. Traditional methods, which depend on expert-annotated evidence, are labor-intensive and not scalable. Although recent automated systems have improved, they still struggle with complex claims that require nuanced reasoning. To address this, we propose CRAVE, a Conflicting Reasoning Approach for explainable claim VErification, that verify the complex claims based on the conflicting rationales reasoned by large language models (LLMs). Specifically, CRAVE introduces a three-module framework. Ambiguity Elimination enchanced Evidence Retrieval module performs ambiguity elimination and entity-based search to gather relevant evidence related to claim verification from external sources like Wikipedia. Conflicting Perspective Reasoning and Preliminary Judgment module with LLMs adopts LLMs to reason rationales with conflicting stances about claim verification from retrieved evidence across four dimensions, i.e., direct evidence, semantic relationships, linguistic patterns, and logical reasoning and make a preliminary judgment. Finally, Small Language Model (SLM) based Judge module is fine-tuned to make use of preliminary judgment from LLMs to assess the confidence of the conflicting rationales and make a final authenticity judgment. This methodology allows CRAVE to capture subtle inconsistencies in complex claims, improving both the accuracy and transparency of claim verification. Extensive experiments on two public claim verification datasets demonstrate that our CRAVE model achieves much better performance than state-of-the-art methods and exhibits a superior capacity for finding relevant evidence and explaining the model predictions. The code is provided at https://github.com/8zym/CRAVE.
Long-tailed Medical Diagnosis with Relation-aware Representation Learning and Iterative Classifier Calibration
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Recently computer-aided diagnosis has demonstrated promising performance, effectively alleviating the workload of clinicians. However, the inherent sample imbalance among different diseases leads algorithms biased to the majority categories, leading to poor performance for rare categories. Existing works formulated this challenge as a long-tailed problem and attempted to tackle it by decoupling the feature representation and classification. Yet, due to the imbalanced distribution and limited samples from tail classes, these works are prone to biased representation learning and insufficient classifier calibration. To tackle these problems, we propose a new Long-tailed Medical Diagnosis (LMD) framework for balanced medical image classification on long-tailed datasets. In the initial stage, we develop a Relation-aware Representation Learning (RRL) scheme to boost the representation ability by encouraging the encoder to capture intrinsic semantic features through different data augmentations. In the subsequent stage, we propose an Iterative Classifier Calibration (ICC) scheme to calibrate the classifier iteratively. This is achieved by generating a large number of balanced virtual features and fine-tuning the encoder using an Expectation-Maximization manner. The proposed ICC compensates for minority categories to facilitate unbiased classifier optimization while maintaining the diagnostic knowledge in majority classes. Comprehensive experiments on three public long-tailed medical datasets demonstrate that our LMD framework significantly surpasses state-of-the-art approaches. The source code can be accessed at https://github.com/peterlipan/LMD.
Distinguish Confusion in Legal Judgment Prediction via Revised Relation Knowledge
Aug 18, 2024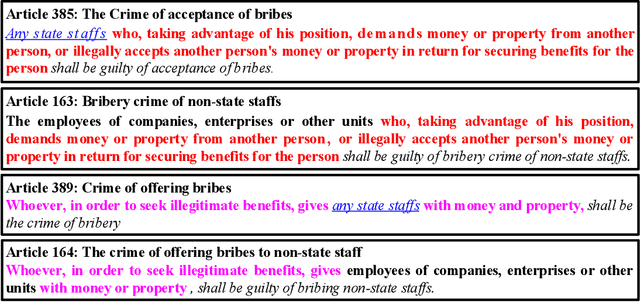
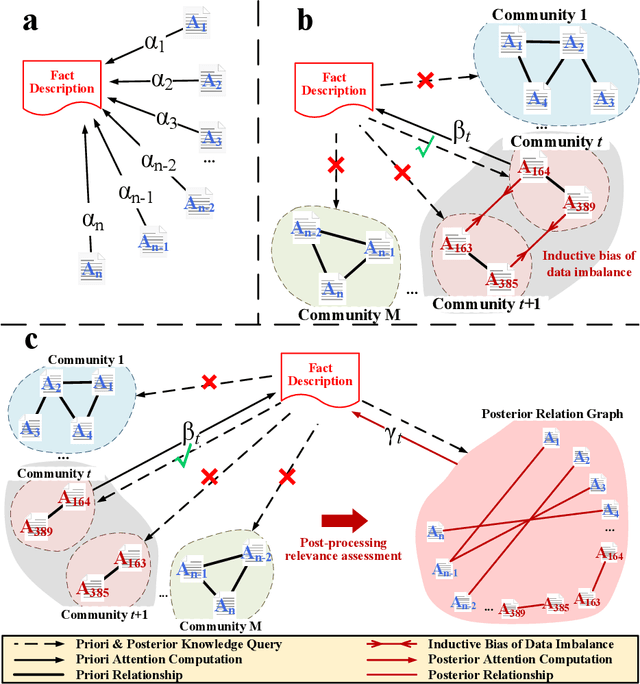
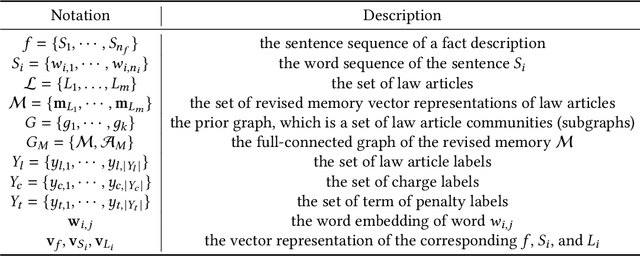
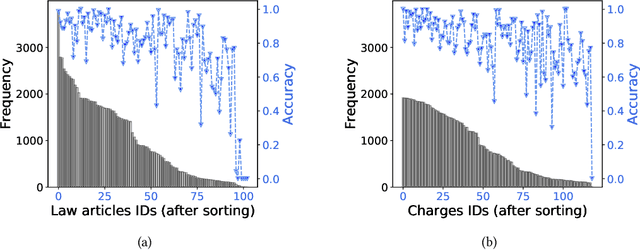
Abstract:Legal Judgment Prediction (LJP) aims to automatically predict a law case's judgment results based on the text description of its facts. In practice, the confusing law articles (or charges) problem frequently occurs, reflecting that the law cases applicable to similar articles (or charges) tend to be misjudged. Although some recent works based on prior knowledge solve this issue well, they ignore that confusion also occurs between law articles with a high posterior semantic similarity due to the data imbalance problem instead of only between the prior highly similar ones, which is this work's further finding. This paper proposes an end-to-end model named \textit{D-LADAN} to solve the above challenges. On the one hand, D-LADAN constructs a graph among law articles based on their text definition and proposes a graph distillation operation (GDO) to distinguish the ones with a high prior semantic similarity. On the other hand, D-LADAN presents a novel momentum-updated memory mechanism to dynamically sense the posterior similarity between law articles (or charges) and a weighted GDO to adaptively capture the distinctions for revising the inductive bias caused by the data imbalance problem. We perform extensive experiments to demonstrate that D-LADAN significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in accuracy and robustness.
Focus on Focus: Focus-oriented Representation Learning and Multi-view Cross-modal Alignment for Glioma Grading
Aug 16, 2024



Abstract:Recently, multimodal deep learning, which integrates histopathology slides and molecular biomarkers, has achieved a promising performance in glioma grading. Despite great progress, due to the intra-modality complexity and inter-modality heterogeneity, existing studies suffer from inadequate histopathology representation learning and inefficient molecular-pathology knowledge alignment. These two issues hinder existing methods to precisely interpret diagnostic molecular-pathology features, thereby limiting their grading performance. Moreover, the real-world applicability of existing multimodal approaches is significantly restricted as molecular biomarkers are not always available during clinical deployment. To address these problems, we introduce a novel Focus on Focus (FoF) framework with paired pathology-genomic training and applicable pathology-only inference, enhancing molecular-pathology representation effectively. Specifically, we propose a Focus-oriented Representation Learning (FRL) module to encourage the model to identify regions positively or negatively related to glioma grading and guide it to focus on the diagnostic areas with a consistency constraint. To effectively link the molecular biomarkers to morphological features, we propose a Multi-view Cross-modal Alignment (MCA) module that projects histopathology representations into molecular subspaces, aligning morphological features with corresponding molecular biomarker status by supervised contrastive learning. Experiments on the TCGA GBM-LGG dataset demonstrate that our FoF framework significantly improves the glioma grading. Remarkably, our FoF achieves superior performance using only histopathology slides compared to existing multimodal methods. The source code is available at https://github.com/peterlipan/FoF.
rLLM: Relational Table Learning with LLMs
Jul 29, 2024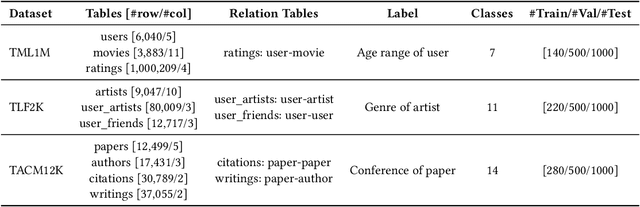
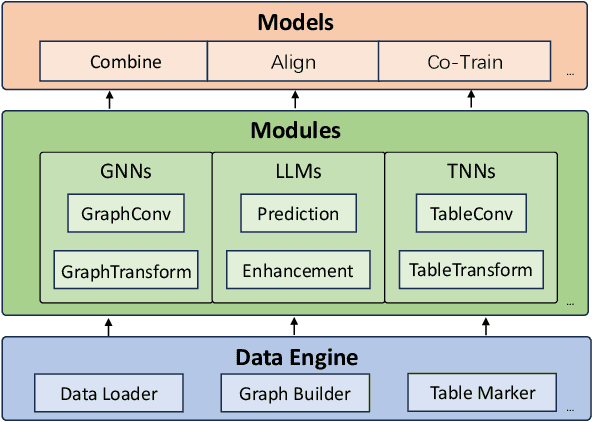
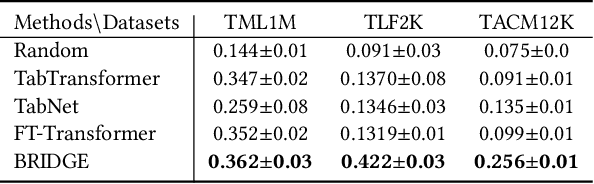
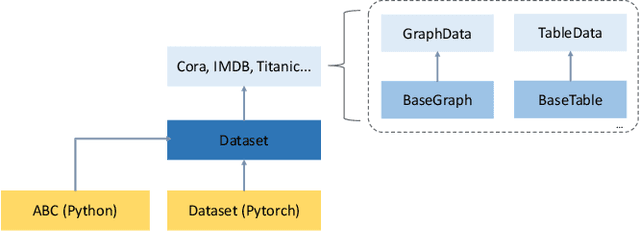
Abstract:We introduce rLLM (relationLLM), a PyTorch library designed for Relational Table Learning (RTL) with Large Language Models (LLMs). The core idea is to decompose state-of-the-art Graph Neural Networks, LLMs, and Table Neural Networks into standardized modules, to enable the fast construction of novel RTL-type models in a simple "combine, align, and co-train" manner. To illustrate the usage of rLLM, we introduce a simple RTL method named \textbf{BRIDGE}. Additionally, we present three novel relational tabular datasets (TML1M, TLF2K, and TACM12K) by enhancing classic datasets. We hope rLLM can serve as a useful and easy-to-use development framework for RTL-related tasks. Our code is available at: https://github.com/rllm-project/rllm.
COOL: Comprehensive Knowledge Enhanced Prompt Learning for Domain Adaptive Few-shot Fake News Detection
Jun 16, 2024Abstract:Most Fake News Detection (FND) methods often struggle with data scarcity for emerging news domain. Recently, prompt learning based on Pre-trained Language Models (PLM) has emerged as a promising approach in domain adaptive few-shot learning, since it greatly reduces the need for labeled data by bridging the gap between pre-training and downstream task. Furthermore, external knowledge is also helpful in verifying emerging news, as emerging news often involves timely knowledge that may not be contained in the PLM's outdated prior knowledge. To this end, we propose COOL, a Comprehensive knOwledge enhanced prOmpt Learning method for domain adaptive few-shot FND. Specifically, we propose a comprehensive knowledge extraction module to extract both structured and unstructured knowledge that are positively or negatively correlated with news from external sources, and adopt an adversarial contrastive enhanced hybrid prompt learning strategy to model the domain-invariant news-knowledge interaction pattern for FND. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of COOL over various state-of-the-arts.
Unified Multi-modal Diagnostic Framework with Reconstruction Pre-training and Heterogeneity-combat Tuning
Apr 09, 2024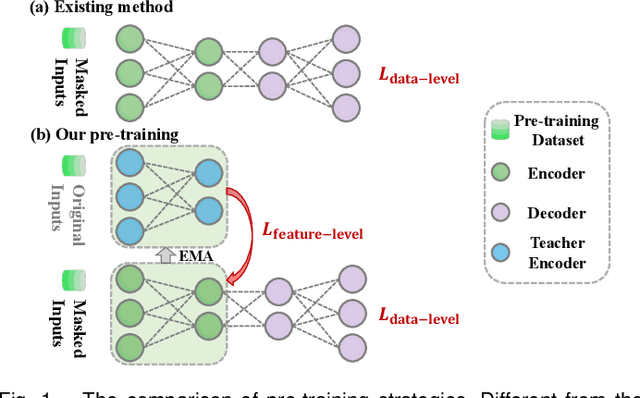
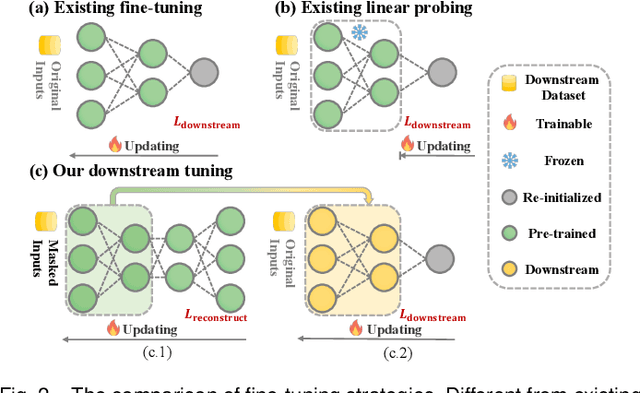
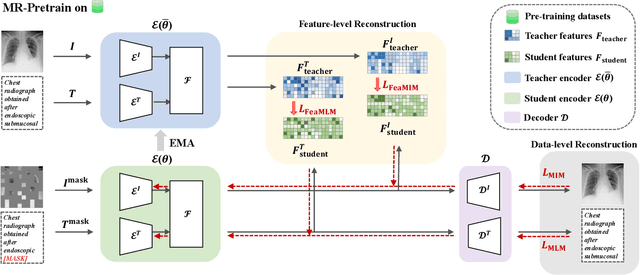
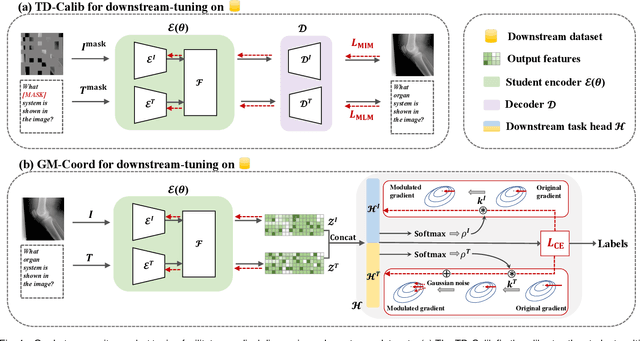
Abstract:Medical multi-modal pre-training has revealed promise in computer-aided diagnosis by leveraging large-scale unlabeled datasets. However, existing methods based on masked autoencoders mainly rely on data-level reconstruction tasks, but lack high-level semantic information. Furthermore, two significant heterogeneity challenges hinder the transfer of pre-trained knowledge to downstream tasks, \textit{i.e.}, the distribution heterogeneity between pre-training data and downstream data, and the modality heterogeneity within downstream data. To address these challenges, we propose a Unified Medical Multi-modal Diagnostic (UMD) framework with tailored pre-training and downstream tuning strategies. Specifically, to enhance the representation abilities of vision and language encoders, we propose the Multi-level Reconstruction Pre-training (MR-Pretrain) strategy, including a feature-level and data-level reconstruction, which guides models to capture the semantic information from masked inputs of different modalities. Moreover, to tackle two kinds of heterogeneities during the downstream tuning, we present the heterogeneity-combat downstream tuning strategy, which consists of a Task-oriented Distribution Calibration (TD-Calib) and a Gradient-guided Modality Coordination (GM-Coord). In particular, TD-Calib fine-tunes the pre-trained model regarding the distribution of downstream datasets, and GM-Coord adjusts the gradient weights according to the dynamic optimization status of different modalities. Extensive experiments on five public medical datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our UMD framework, which remarkably outperforms existing approaches on three kinds of downstream tasks.
Open Knowledge Base Canonicalization with Multi-task Learning
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:The construction of large open knowledge bases (OKBs) is integral to many knowledge-driven applications on the world wide web such as web search. However, noun phrases and relational phrases in OKBs often suffer from redundancy and ambiguity, which calls for the investigation on OKB canonicalization. Current solutions address OKB canonicalization by devising advanced clustering algorithms and using knowledge graph embedding (KGE) to further facilitate the canonicalization process. Nevertheless, these works fail to fully exploit the synergy between clustering and KGE learning, and the methods designed for these subtasks are sub-optimal. To this end, we put forward a multi-task learning framework, namely MulCanon, to tackle OKB canonicalization. In addition, diffusion model is used in the soft clustering process to improve the noun phrase representations with neighboring information, which can lead to more accurate representations. MulCanon unifies the learning objectives of these sub-tasks, and adopts a two-stage multi-task learning paradigm for training. A thorough experimental study on popular OKB canonicalization benchmarks validates that MulCanon can achieve competitive canonicalization results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge