Xifan Zhang
ADMarker: A Multi-Modal Federated Learning System for Monitoring Digital Biomarkers of Alzheimer's Disease
Oct 23, 2023



Abstract:Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and related dementia are a growing global health challenge due to the aging population. In this paper, we present ADMarker, the first end-to-end system that integrates multi-modal sensors and new federated learning algorithms for detecting multidimensional AD digital biomarkers in natural living environments. ADMarker features a novel three-stage multi-modal federated learning architecture that can accurately detect digital biomarkers in a privacy-preserving manner. Our approach collectively addresses several major real-world challenges, such as limited data labels, data heterogeneity, and limited computing resources. We built a compact multi-modality hardware system and deployed it in a four-week clinical trial involving 91 elderly participants. The results indicate that ADMarker can accurately detect a comprehensive set of digital biomarkers with up to 93.8% accuracy and identify early AD with an average of 88.9% accuracy. ADMarker offers a new platform that can allow AD clinicians to characterize and track the complex correlation between multidimensional interpretable digital biomarkers, demographic factors of patients, and AD diagnosis in a longitudinal manner.
Few Shot Learning with Simplex
Oct 30, 2018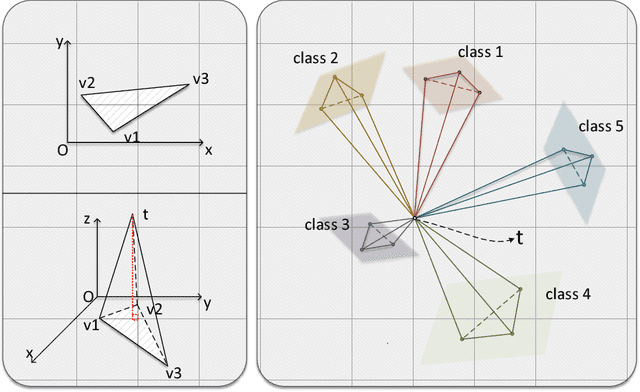

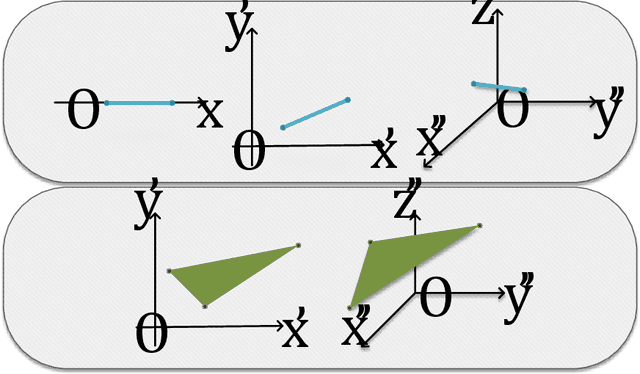
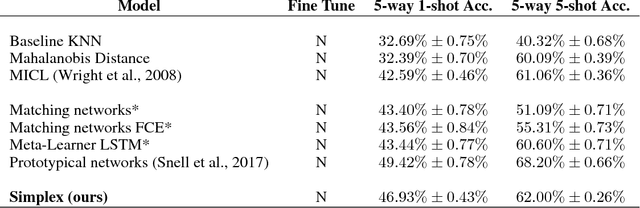
Abstract:Deep learning has made remarkable achievement in many fields. However, learning the parameters of neural networks usually demands a large amount of labeled data. The algorithms of deep learning, therefore, encounter difficulties when applied to supervised learning where only little data are available. This specific task is called few-shot learning. To address it, we propose a novel algorithm for few-shot learning using discrete geometry, in the sense that the samples in a class are modeled as a reduced simplex. The volume of the simplex is used for the measurement of class scatter. During testing, combined with the test sample and the points in the class, a new simplex is formed. Then the similarity between the test sample and the class can be quantized with the ratio of volumes of the new simplex to the original class simplex. Moreover, we present an approach to constructing simplices using local regions of feature maps yielded by convolutional neural networks. Experiments on Omniglot and miniImageNet verify the effectiveness of our simplex algorithm on few-shot learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge