Karl Pazdernik
Uncertainty Quantification for Named Entity Recognition via Full-Sequence and Subsequence Conformal Prediction
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Named Entity Recognition (NER) serves as a foundational component in many natural language processing (NLP) pipelines. However, current NER models typically output a single predicted label sequence without any accompanying measure of uncertainty, leaving downstream applications vulnerable to cascading errors. In this paper, we introduce a general framework for adapting sequence-labeling-based NER models to produce uncertainty-aware prediction sets. These prediction sets are collections of full-sentence labelings that are guaranteed to contain the correct labeling with a user-specified confidence level. This approach serves a role analogous to confidence intervals in classical statistics by providing formal guarantees about the reliability of model predictions. Our method builds on conformal prediction, which offers finite-sample coverage guarantees under minimal assumptions. We design efficient nonconformity scoring functions to construct efficient, well-calibrated prediction sets that support both unconditional and class-conditional coverage. This framework accounts for heterogeneity across sentence length, language, entity type, and number of entities within a sentence. Empirical experiments on four NER models across three benchmark datasets demonstrate the broad applicability, validity, and efficiency of the proposed methods.
Bayesian SegNet for Semantic Segmentation with Improved Interpretation of Microstructural Evolution During Irradiation of Materials
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Understanding the relationship between the evolution of microstructures of irradiated LiAlO2 pellets and tritium diffusion, retention and release could improve predictions of tritium-producing burnable absorber rod performance. Given expert-labeled segmented images of irradiated and unirradiated pellets, we trained Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to segment images into defect, grain, and boundary classes. Qualitative microstructural information was calculated from these segmented images to facilitate the comparison of unirradiated and irradiated pellets. We tested modifications to improve the sensitivity of the model, including incorporating meta-data into the model and utilizing uncertainty quantification. The predicted segmentation was similar to the expert-labeled segmentation for most methods of microstructural qualification, including pixel proportion, defect area, and defect density. Overall, the high performance metrics for the best models for both irradiated and unirradiated images shows that utilizing neural network models is a viable alternative to expert-labeled images.
Surprisingly Fragile: Assessing and Addressing Prompt Instability in Multimodal Foundation Models
Aug 26, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal foundation models (MFMs) such as OFASys show the potential to unlock analysis of complex data such as images, videos, and audio data via text prompts alone. However, their performance may suffer in the face of text input that differs even slightly from their training distribution, which is surprising considering the use of modality-specific data to "ground" the text input. This study demonstrates that prompt instability is a major concern for MFMs, leading to a consistent drop in performance across all modalities, but that instability can be mitigated with additional training with augmented data. We evaluate several methods for grounded prompt perturbation, where we generate perturbations and filter based on similarity to text and/or modality data. After re-training the models on the augmented data, we find improved accuracy and more stable performance on the perturbed test data regardless of perturbation condition, suggesting that the data augmentation strategy helps the models handle domain shifts more effectively. In error analysis, we find consistent patterns of performance improvement across domains, suggesting that retraining on prompt perturbations tends to help general reasoning capabilities in MFMs.
RAG vs. Long Context: Examining Frontier Large Language Models for Environmental Review Document Comprehension
Jul 10, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been applied to many research problems across various domains. One of the applications of LLMs is providing question-answering systems that cater to users from different fields. The effectiveness of LLM-based question-answering systems has already been established at an acceptable level for users posing questions in popular and public domains such as trivia and literature. However, it has not often been established in niche domains that traditionally require specialized expertise. To this end, we construct the NEPAQuAD1.0 benchmark to evaluate the performance of three frontier LLMs -- Claude Sonnet, Gemini, and GPT-4 -- when answering questions originating from Environmental Impact Statements prepared by U.S. federal government agencies in accordance with the National Environmental Environmental Act (NEPA). We specifically measure the ability of LLMs to understand the nuances of legal, technical, and compliance-related information present in NEPA documents in different contextual scenarios. For example, we test the LLMs' internal prior NEPA knowledge by providing questions without any context, as well as assess how LLMs synthesize the contextual information present in long NEPA documents to facilitate the question/answering task. We compare the performance of the long context LLMs and RAG powered models in handling different types of questions (e.g., problem-solving, divergent). Our results suggest that RAG powered models significantly outperform the long context models in the answer accuracy regardless of the choice of the frontier LLM. Our further analysis reveals that many models perform better answering closed questions than divergent and problem-solving questions.
Generalist Multimodal AI: A Review of Architectures, Challenges and Opportunities
Jun 08, 2024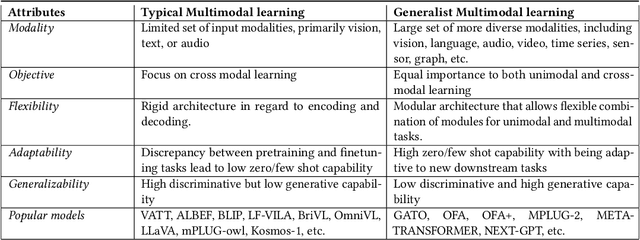
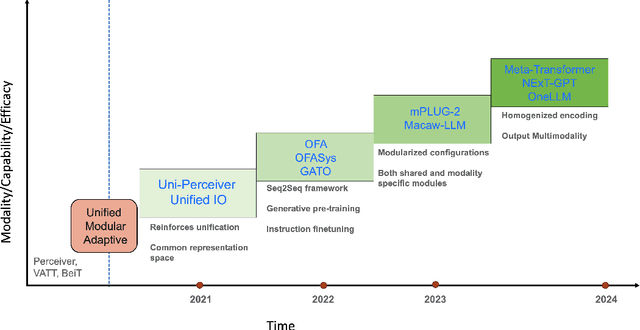
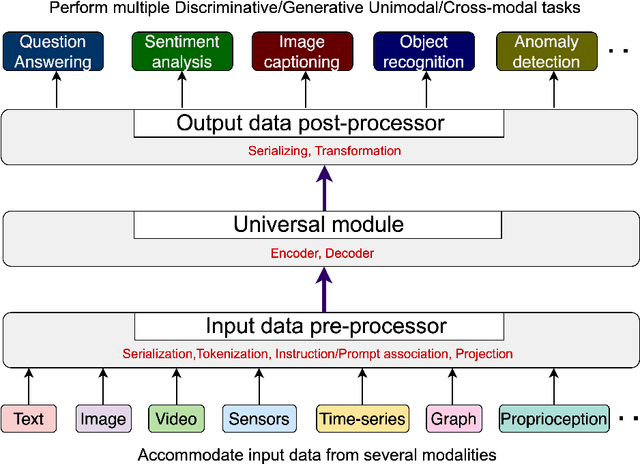
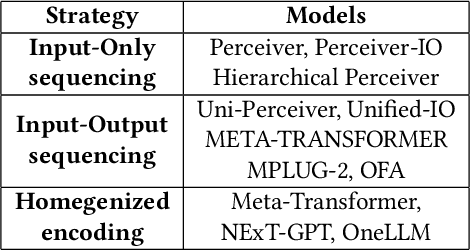
Abstract:Multimodal models are expected to be a critical component to future advances in artificial intelligence. This field is starting to grow rapidly with a surge of new design elements motivated by the success of foundation models in natural language processing (NLP) and vision. It is widely hoped that further extending the foundation models to multiple modalities (e.g., text, image, video, sensor, time series, graph, etc.) will ultimately lead to generalist multimodal models, i.e. one model across different data modalities and tasks. However, there is little research that systematically analyzes recent multimodal models (particularly the ones that work beyond text and vision) with respect to the underling architecture proposed. Therefore, this work provides a fresh perspective on generalist multimodal models (GMMs) via a novel architecture and training configuration specific taxonomy. This includes factors such as Unifiability, Modularity, and Adaptability that are pertinent and essential to the wide adoption and application of GMMs. The review further highlights key challenges and prospects for the field and guide the researchers into the new advancements.
On the Behavior of Audio-Visual Fusion Architectures in Identity Verification Tasks
Nov 09, 2023



Abstract:We train an identity verification architecture and evaluate modifications to the part of the model that combines audio and visual representations, including in scenarios where one input is missing in either of two examples to be compared. We report results on the Voxceleb1-E test set that suggest averaging the output embeddings improves error rate in the full-modality setting and when a single modality is missing, and makes more complete use of the embedding space than systems which use shared layers and discuss possible reasons for this behavior.
DBCal: Density Based Calibration of classifier predictions for uncertainty quantification
Apr 01, 2022



Abstract:Measurement of uncertainty of predictions from machine learning methods is important across scientific domains and applications. We present, to our knowledge, the first such technique that quantifies the uncertainty of predictions from a classifier and accounts for both the classifier's belief and performance. We prove that our method provides an accurate estimate of the probability that the outputs of two neural networks are correct by showing an expected calibration error of less than 0.2% on a binary classifier, and less than 3% on a semantic segmentation network with extreme class imbalance. We empirically show that the uncertainty returned by our method is an accurate measurement of the probability that the classifier's prediction is correct and, therefore has broad utility in uncertainty propagation.
Accelerated Computation of a High Dimensional Kolmogorov-Smirnov Distance
Jun 25, 2021
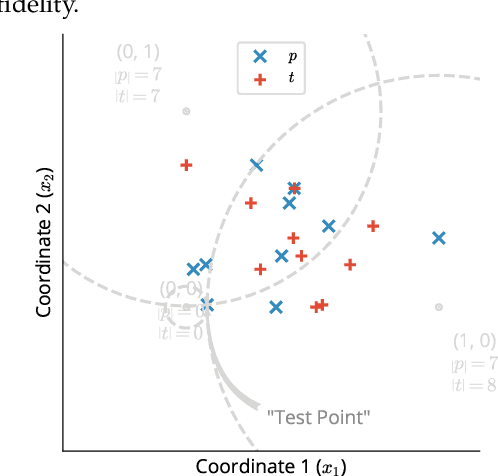


Abstract:Statistical testing is widespread and critical for a variety of scientific disciplines. The advent of machine learning and the increase of computing power has increased the interest in the analysis and statistical testing of multidimensional data. We extend the powerful Kolmogorov-Smirnov two sample test to a high dimensional form in a similar manner to Fasano (Fasano, 1987). We call our result the d-dimensional Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (ddKS) and provide three novel contributions therewith: we develop an analytical equation for the significance of a given ddKS score, we provide an algorithm for computation of ddKS on modern computing hardware that is of constant time complexity for small sample sizes and dimensions, and we provide two approximate calculations of ddKS: one that reduces the time complexity to linear at larger sample sizes, and another that reduces the time complexity to linear with increasing dimension. We perform power analysis of ddKS and its approximations on a corpus of datasets and compare to other common high dimensional two sample tests and distances: Hotelling's T^2 test and Kullback-Leibler divergence. Our ddKS test performs well for all datasets, dimensions, and sizes tested, whereas the other tests and distances fail to reject the null hypothesis on at least one dataset. We therefore conclude that ddKS is a powerful multidimensional two sample test for general use, and can be calculated in a fast and efficient manner using our parallel or approximate methods. Open source implementations of all methods described in this work are located at https://github.com/pnnl/ddks.
NukeLM: Pre-Trained and Fine-Tuned Language Models for the Nuclear and Energy Domains
May 25, 2021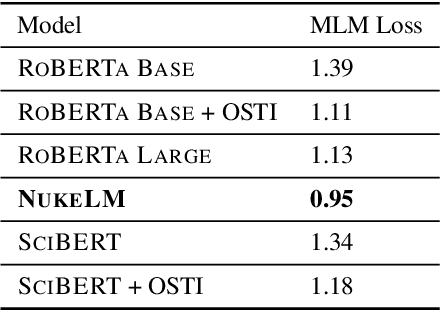
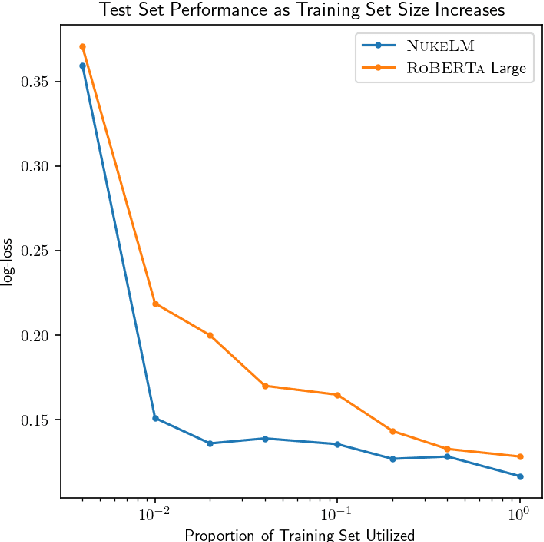
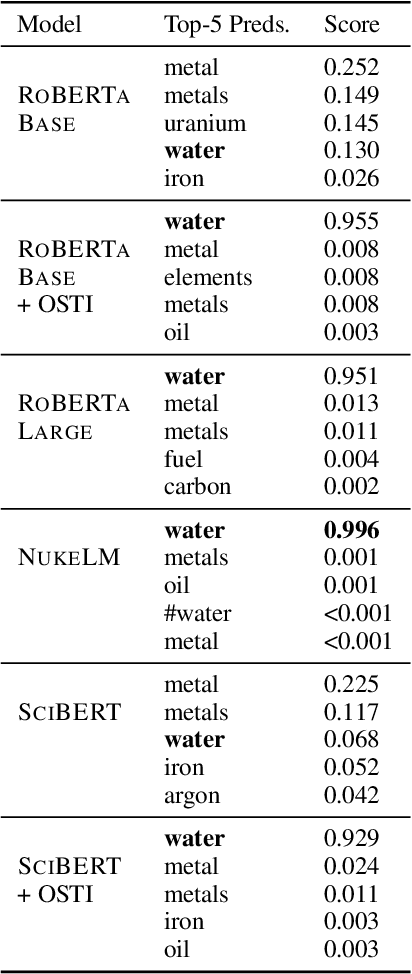
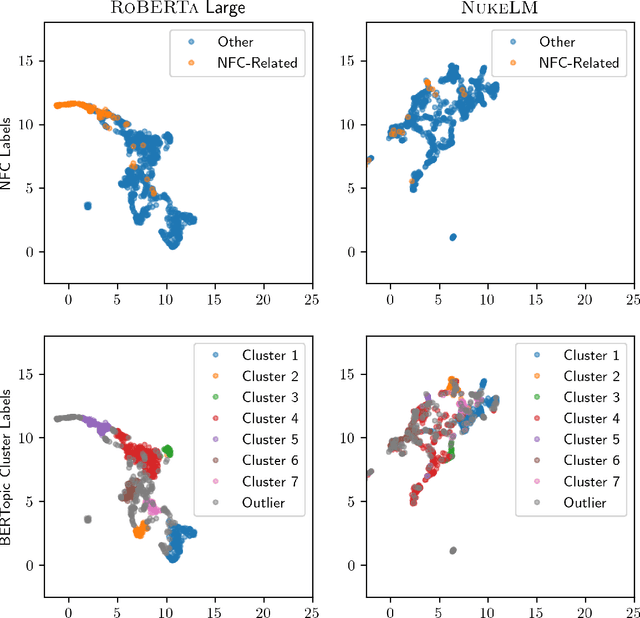
Abstract:Natural language processing (NLP) tasks (text classification, named entity recognition, etc.) have seen revolutionary improvements over the last few years. This is due to language models such as BERT that achieve deep knowledge transfer by using a large pre-trained model, then fine-tuning the model on specific tasks. The BERT architecture has shown even better performance on domain-specific tasks when the model is pre-trained using domain-relevant texts. Inspired by these recent advancements, we have developed NukeLM, a nuclear-domain language model pre-trained on 1.5 million abstracts from the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI) database. This NukeLM model is then fine-tuned for the classification of research articles into either binary classes (related to the nuclear fuel cycle [NFC] or not) or multiple categories related to the subject of the article. We show that continued pre-training of a BERT-style architecture prior to fine-tuning yields greater performance on both article classification tasks. This information is critical for properly triaging manuscripts, a necessary task for better understanding citation networks that publish in the nuclear space, and for uncovering new areas of research in the nuclear (or nuclear-relevant) domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge