Hung Phan
MMP-A*: Multimodal Perception Enhanced Incremental Heuristic Search on Path Planning
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Autonomous path planning requires a synergy between global reasoning and geometric precision, especially in complex or cluttered environments. While classical A* is valued for its optimality, it incurs prohibitive computational and memory costs in large-scale scenarios. Recent attempts to mitigate these limitations by using Large Language Models for waypoint guidance remain insufficient, as they rely only on text-based reasoning without spatial grounding. As a result, such models often produce incorrect waypoints in topologically complex environments with dead ends, and lack the perceptual capacity to interpret ambiguous physical boundaries. These inconsistencies lead to costly corrective expansions and undermine the intended computational efficiency. We introduce MMP-A*, a multimodal framework that integrates the spatial grounding capabilities of vision-language models with a novel adaptive decay mechanism. By anchoring high-level reasoning in physical geometry, the framework produces coherent waypoint guidance that addresses the limitations of text-only planners. The adaptive decay mechanism dynamically regulates the influence of uncertain waypoints within the heuristic, ensuring geometric validity while substantially reducing memory overhead. To evaluate robustness, we test the framework in challenging environments characterized by severe clutter and topological complexity. Experimental results show that MMP-A* achieves near-optimal trajectories with significantly reduced operational costs, demonstrating its potential as a perception-grounded and computationally efficient paradigm for autonomous navigation.
Pareto-Grid-Guided Large Language Models for Fast and High-Quality Heuristics Design in Multi-Objective Combinatorial Optimization
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Multi-objective combinatorial optimization problems (MOCOP) frequently arise in practical applications that require the simultaneous optimization of conflicting objectives. Although traditional evolutionary algorithms can be effective, they typically depend on domain knowledge and repeated parameter tuning, limiting flexibility when applied to unseen MOCOP instances. Recently, integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into evolutionary computation has opened new avenues for automatic heuristic generation, using their advanced language understanding and code synthesis capabilities. Nevertheless, most existing approaches predominantly focus on single-objective tasks, often neglecting key considerations such as runtime efficiency and heuristic diversity in multi-objective settings. To bridge this gap, we introduce Multi-heuristics for MOCOP via Pareto-Grid-guided Evolution of LLMs (MPaGE), a novel enhancement of the Simple Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization (SEMO) framework that leverages LLMs and Pareto Front Grid (PFG) technique. By partitioning the objective space into grids and retaining top-performing candidates to guide heuristic generation, MPaGE utilizes LLMs to prioritize heuristics with semantically distinct logical structures during variation, thus promoting diversity and mitigating redundancy within the population. Through extensive evaluations, MPaGE demonstrates superior performance over existing LLM-based frameworks, and achieves competitive results to traditional Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs), with significantly faster runtime. Our code is available at: https://github.com/langkhachhoha/MPaGE.
PermitQA: A Benchmark for Retrieval Augmented Generation in Wind Siting and Permitting domain
Aug 21, 2024
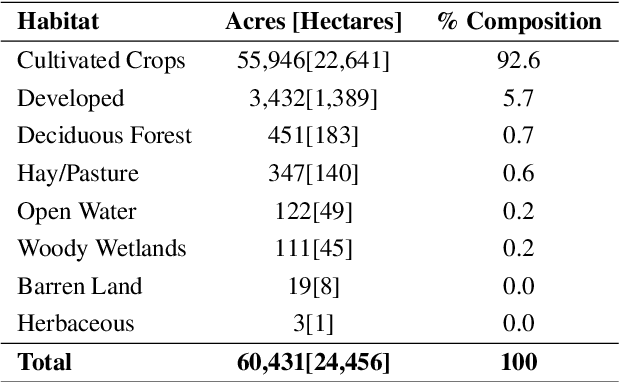

Abstract:In the rapidly evolving landscape of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and text generation, the emergence of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) presents a promising avenue for improving the quality and reliability of generated text by leveraging information retrieved from user specified database. Benchmarking is essential to evaluate and compare the performance of the different RAG configurations in terms of retriever and generator, providing insights into their effectiveness, scalability, and suitability for the specific domain and applications. In this paper, we present a comprehensive framework to generate a domain relevant RAG benchmark. Our framework is based on automatic question-answer generation with Human (domain experts)-AI Large Language Model (LLM) teaming. As a case study, we demonstrate the framework by introducing PermitQA, a first-of-its-kind benchmark on the wind siting and permitting domain which comprises of multiple scientific documents/reports related to environmental impact of wind energy projects. Our framework systematically evaluates RAG performance using diverse metrics and multiple question types with varying complexity level. We also demonstrate the performance of different models on our benchmark.
RAG vs. Long Context: Examining Frontier Large Language Models for Environmental Review Document Comprehension
Jul 10, 2024



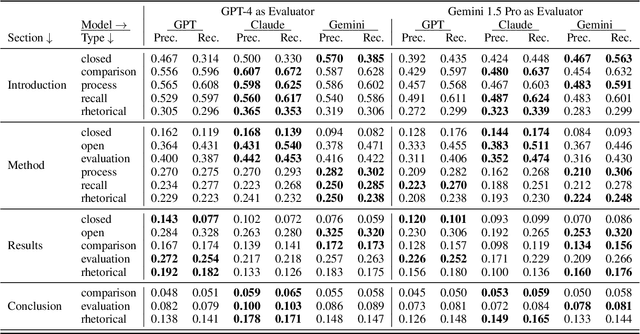
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been applied to many research problems across various domains. One of the applications of LLMs is providing question-answering systems that cater to users from different fields. The effectiveness of LLM-based question-answering systems has already been established at an acceptable level for users posing questions in popular and public domains such as trivia and literature. However, it has not often been established in niche domains that traditionally require specialized expertise. To this end, we construct the NEPAQuAD1.0 benchmark to evaluate the performance of three frontier LLMs -- Claude Sonnet, Gemini, and GPT-4 -- when answering questions originating from Environmental Impact Statements prepared by U.S. federal government agencies in accordance with the National Environmental Environmental Act (NEPA). We specifically measure the ability of LLMs to understand the nuances of legal, technical, and compliance-related information present in NEPA documents in different contextual scenarios. For example, we test the LLMs' internal prior NEPA knowledge by providing questions without any context, as well as assess how LLMs synthesize the contextual information present in long NEPA documents to facilitate the question/answering task. We compare the performance of the long context LLMs and RAG powered models in handling different types of questions (e.g., problem-solving, divergent). Our results suggest that RAG powered models significantly outperform the long context models in the answer accuracy regardless of the choice of the frontier LLM. Our further analysis reveals that many models perform better answering closed questions than divergent and problem-solving questions.
The Landscape and Challenges of HPC Research and LLMs
Feb 07, 2024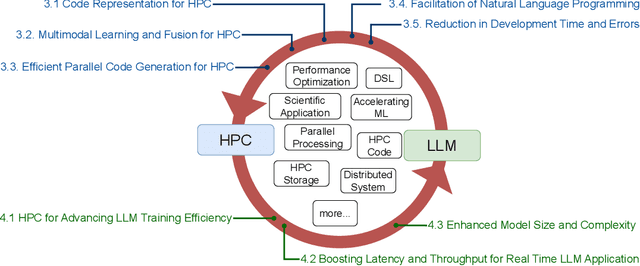

Abstract:Recently, language models (LMs), especially large language models (LLMs), have revolutionized the field of deep learning. Both encoder-decoder models and prompt-based techniques have shown immense potential for natural language processing and code-based tasks. Over the past several years, many research labs and institutions have invested heavily in high-performance computing, approaching or breaching exascale performance levels. In this paper, we posit that adapting and utilizing such language model-based techniques for tasks in high-performance computing (HPC) would be very beneficial. This study presents our reasoning behind the aforementioned position and highlights how existing ideas can be improved and adapted for HPC tasks.
Evaluating and Optimizing the Effectiveness of Neural Machine Translation in Supporting Code Retrieval Models: A Study on the CAT Benchmark
Aug 09, 2023



Abstract:Neural Machine Translation (NMT) is widely applied in software engineering tasks. The effectiveness of NMT for code retrieval relies on the ability to learn from the sequence of tokens in the source language to the sequence of tokens in the target language. While NMT performs well in pseudocode-to-code translation, it might have challenges in learning to translate from natural language query to source code in newly curated real-world code documentation/ implementation datasets. In this work, we analyze the performance of NMT in natural language-to-code translation in the newly curated CAT benchmark that includes the optimized versions of three Java datasets TLCodeSum, CodeSearchNet, Funcom, and a Python dataset PCSD. Our evaluation shows that NMT has low accuracy, measured by CrystalBLEU and Meteor metrics in this task. To alleviate the duty of NMT in learning complex representation of source code, we propose ASTTrans Representation, a tailored representation of an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) using a subset of non-terminal nodes. We show that the classical approach NMT performs significantly better in learning ASTTrans Representation over code tokens with up to 36% improvement on Meteor score. Moreover, we leverage ASTTrans Representation to conduct combined code search processes from the state-of-the-art code search processes using GraphCodeBERT and UniXcoder. Our NMT models of learning ASTTrans Representation can boost the Mean Reciprocal Rank of these state-of-the-art code search processes by up to 3.08% and improve 23.08% of queries' results over the CAT benchmark.
Learning to Parallelize with OpenMP by Augmented Heterogeneous AST Representation
May 09, 2023Abstract:Detecting parallelizable code regions is a challenging task, even for experienced developers. Numerous recent studies have explored the use of machine learning for code analysis and program synthesis, including parallelization, in light of the success of machine learning in natural language processing. However, applying machine learning techniques to parallelism detection presents several challenges, such as the lack of an adequate dataset for training, an effective code representation with rich information, and a suitable machine learning model to learn the latent features of code for diverse analyses. To address these challenges, we propose a novel graph-based learning approach called Graph2Par that utilizes a heterogeneous augmented abstract syntax tree (Augmented-AST) representation for code. The proposed approach primarily focused on loop-level parallelization with OpenMP. Moreover, we create an OMP\_Serial dataset with 18598 parallelizable and 13972 non-parallelizable loops to train the machine learning models. Our results show that our proposed approach achieves the accuracy of parallelizable code region detection with 85\% accuracy and outperforms the state-of-the-art token-based machine learning approach. These results indicate that our approach is competitive with state-of-the-art tools and capable of handling loops with complex structures that other tools may overlook.
Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks for Software Effort Estimation
Jun 30, 2022


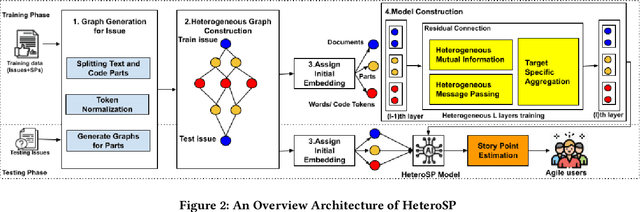
Abstract:Software effort can be measured by story point [35]. Current approaches for automatically estimating story points focus on applying pre-trained embedding models and deep learning for text regression to solve this problem which required expensive embedding models. We propose HeteroSP, a tool for estimating story points from textual input of Agile software project issues. We select GPT2SP [12] and Deep-SE [8] as the baselines for comparison. First, from the analysis of the story point dataset [8], we conclude that software issues are actually a mixture of natural language sentences with quoted code snippets and have problems related to large-size vocabulary. Second, we provide a module to normalize the input text including words and code tokens of the software issues. Third, we design an algorithm to convert an input software issue to a graph with different types of nodes and edges. Fourth, we construct a heterogeneous graph neural networks model with the support of fastText [6] for constructing initial node embedding to learn and predict the story points of new issues. We did the comparison over three scenarios of estimation, including within project, cross-project within the repository, and cross-project cross repository with our baseline approaches. We achieve the average Mean Absolute Error (MAE) as 2.38, 2.61, and 2.63 for three scenarios. We outperform GPT2SP in 2/3 of the scenarios while outperforming Deep-SE in the most challenging scenario with significantly less amount of running time. We also compare our approaches with different homogeneous graph neural network models and the results show that the heterogeneous graph neural networks model outperforms the homogeneous models in story point estimation. For time performance, we achieve about 570 seconds as the time performance in both three processes: node embedding initialization, model construction, and story point estimation.
HybridNets: End-to-End Perception Network
Mar 17, 2022



Abstract:End-to-end Network has become increasingly important in multi-tasking. One prominent example of this is the growing significance of a driving perception system in autonomous driving. This paper systematically studies an end-to-end perception network for multi-tasking and proposes several key optimizations to improve accuracy. First, the paper proposes efficient segmentation head and box/class prediction networks based on weighted bidirectional feature network. Second, the paper proposes automatically customized anchor for each level in the weighted bidirectional feature network. Third, the paper proposes an efficient training loss function and training strategy to balance and optimize network. Based on these optimizations, we have developed an end-to-end perception network to perform multi-tasking, including traffic object detection, drivable area segmentation and lane detection simultaneously, called HybridNets, which achieves better accuracy than prior art. In particular, HybridNets achieves 77.3 mean Average Precision on Berkeley DeepDrive Dataset, outperforms lane detection with 31.6 mean Intersection Over Union with 12.83 million parameters and 15.6 billion floating-point operations. In addition, it can perform visual perception tasks in real-time and thus is a practical and accurate solution to the multi-tasking problem. Code is available at https://github.com/datvuthanh/HybridNets.
Story Point Effort Estimation by Text Level Graph Neural Network
Mar 14, 2022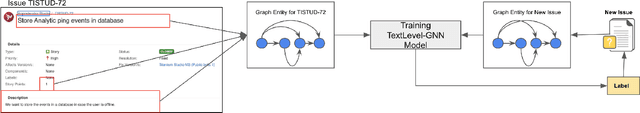
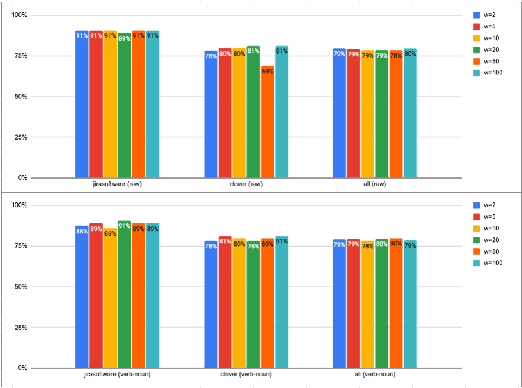
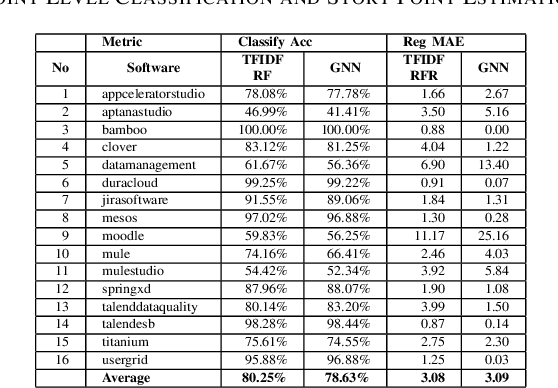
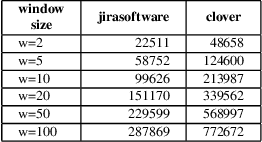
Abstract:Estimating the software projects' efforts developed by agile methods is important for project managers or technical leads. It provides a summary as a first view of how many hours and developers are required to complete the tasks. There are research works on automatic predicting the software efforts, including Term Frequency Inverse Document Frequency (TFIDF) as the traditional approach for this problem. Graph Neural Network is a new approach that has been applied in Natural Language Processing for text classification. The advantages of Graph Neural Network are based on the ability to learn information via graph data structure, which has more representations such as the relationships between words compared to approaches of vectorizing sequence of words. In this paper, we show the potential and possible challenges of Graph Neural Network text classification in story point level estimation. By the experiments, we show that the GNN Text Level Classification can achieve as high accuracy as about 80 percent for story points level classification, which is comparable to the traditional approach. We also analyze the GNN approach and point out several current disadvantages that the GNN approach can improve for this problem or other problems in software engineering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge