Kang An
Step-DeepResearch Technical Report
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:As LLMs shift toward autonomous agents, Deep Research has emerged as a pivotal metric. However, existing academic benchmarks like BrowseComp often fail to meet real-world demands for open-ended research, which requires robust skills in intent recognition, long-horizon decision-making, and cross-source verification. To address this, we introduce Step-DeepResearch, a cost-effective, end-to-end agent. We propose a Data Synthesis Strategy Based on Atomic Capabilities to reinforce planning and report writing, combined with a progressive training path from agentic mid-training to SFT and RL. Enhanced by a Checklist-style Judger, this approach significantly improves robustness. Furthermore, to bridge the evaluation gap in the Chinese domain, we establish ADR-Bench for realistic deep research scenarios. Experimental results show that Step-DeepResearch (32B) scores 61.4% on Scale AI Research Rubrics. On ADR-Bench, it significantly outperforms comparable models and rivals SOTA closed-source models like OpenAI and Gemini DeepResearch. These findings prove that refined training enables medium-sized models to achieve expert-level capabilities at industry-leading cost-efficiency.
Step-GUI Technical Report
Dec 19, 2025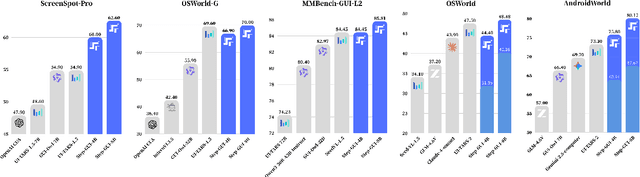
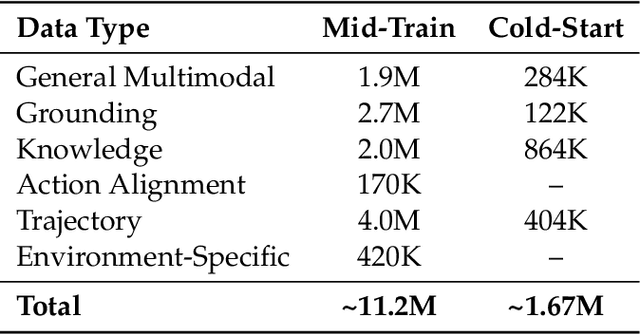
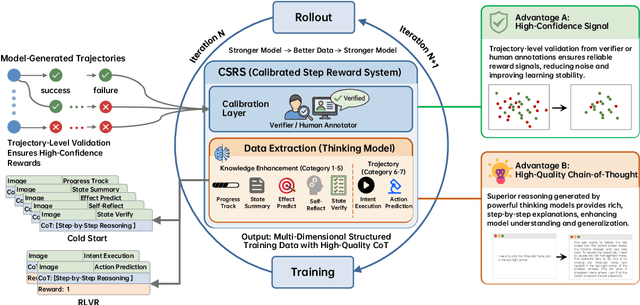

Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models unlock unprecedented opportunities for GUI automation. However, a fundamental challenge remains: how to efficiently acquire high-quality training data while maintaining annotation reliability? We introduce a self-evolving training pipeline powered by the Calibrated Step Reward System, which converts model-generated trajectories into reliable training signals through trajectory-level calibration, achieving >90% annotation accuracy with 10-100x lower cost. Leveraging this pipeline, we introduce Step-GUI, a family of models (4B/8B) that achieves state-of-the-art GUI performance (8B: 80.2% AndroidWorld, 48.5% OSWorld, 62.6% ScreenShot-Pro) while maintaining robust general capabilities. As GUI agent capabilities improve, practical deployment demands standardized interfaces across heterogeneous devices while protecting user privacy. To this end, we propose GUI-MCP, the first Model Context Protocol for GUI automation with hierarchical architecture that combines low-level atomic operations and high-level task delegation to local specialist models, enabling high-privacy execution where sensitive data stays on-device. Finally, to assess whether agents can handle authentic everyday usage, we introduce AndroidDaily, a benchmark grounded in real-world mobile usage patterns with 3146 static actions and 235 end-to-end tasks across high-frequency daily scenarios (8B: static 89.91%, end-to-end 52.50%). Our work advances the development of practical GUI agents and demonstrates strong potential for real-world deployment in everyday digital interactions.
MMRPT: MultiModal Reinforcement Pre-Training via Masked Vision-Dependent Reasoning
Dec 08, 2025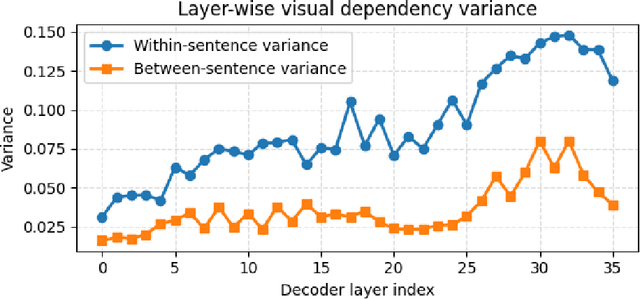
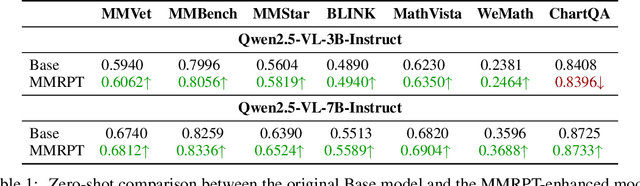

Abstract:Multimodal pre-training remains constrained by the descriptive bias of image-caption pairs, leading models to favor surface linguistic cues over grounded visual understanding. We introduce MMRPT, a masked multimodal reinforcement pre-training framework that strengthens visual reasoning in MLLMs. We are the first to incorporate reinforcement learning directly into the pre-training of large vision-language models, enabling learning signals that reward visual grounding rather than caption imitation. MMRPT constructs masked multimodal data by estimating sentence-level visual dependency via attention over visual tokens and masking highly vision-dependent segments; the model reconstructs these spans through vision-grounded reasoning guided by a semantic-visual reward. Experiments show consistent zero-shot gains across diverse benchmarks and substantially improved robustness under supervised fine-tuning, demonstrating that reinforcement-driven masked reasoning provides a more reliable and generalizable pre-training objective for multimodal models.
Erase to Improve: Erasable Reinforcement Learning for Search-Augmented LLMs
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:While search-augmented large language models (LLMs) exhibit impressive capabilities, their reliability in complex multi-hop reasoning remains limited. This limitation arises from three fundamental challenges: decomposition errors, where tasks are incorrectly broken down; retrieval missing, where key evidence fails to be retrieved; and reasoning errors, where flawed logic propagates through the reasoning chain. A single failure in any of these stages can derail the final answer. We propose Erasable Reinforcement Learning (ERL), a novel framework that transforms fragile reasoning into a robust process. ERL explicitly identifies faulty steps, erases them, and regenerates reasoning in place, preventing defective logic from propagating through the reasoning chain. This targeted correction mechanism turns brittle reasoning into a more resilient process. Models trained with ERL, termed ESearch, achieve substantial improvements on HotpotQA, MuSiQue, 2Wiki, and Bamboogle, with the 3B model achieving +8.48% EM and +11.56% F1, and the 7B model achieving +5.38% EM and +7.22% F1 over previous state-of-the-art(SOTA) results. These findings suggest that erasable reinforcement learning provides a powerful paradigm shift for robust multi-step reasoning in LLMs.
Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
Jul 24, 2025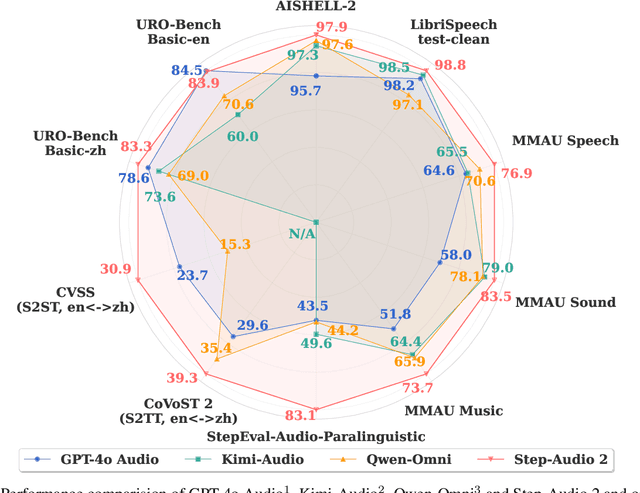

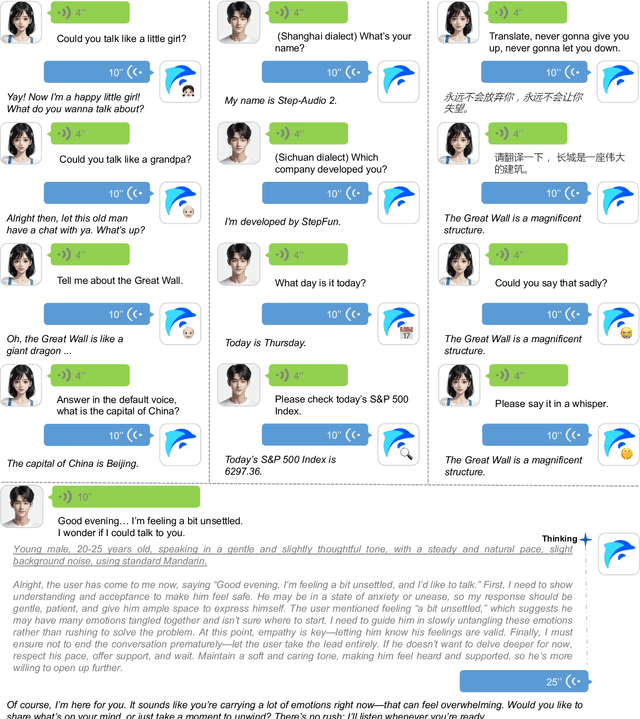

Abstract:This paper presents Step-Audio 2, an end-to-end multi-modal large language model designed for industry-strength audio understanding and speech conversation. By integrating a latent audio encoder and reasoning-centric reinforcement learning (RL), Step-Audio 2 achieves promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio understanding. To facilitate genuine end-to-end speech conversation, Step-Audio 2 incorporates the generation of discrete audio tokens into language modeling, significantly enhancing its responsiveness to paralinguistic information such as speaking styles and emotions. To effectively leverage the rich textual and acoustic knowledge in real-world data, Step-Audio 2 integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is able to call external tools such as web search to mitigate hallucination and audio search to switch timbres. Trained on millions of hours of speech and audio data, Step-Audio 2 delivers intelligence and expressiveness across diverse conversational scenarios. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various audio understanding and conversational benchmarks compared to other open-source and commercial solutions. Please visit https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio2 for more information.
StepSearch: Igniting LLMs Search Ability via Step-Wise Proximal Policy Optimization
May 21, 2025Abstract:Efficient multi-hop reasoning requires Large Language Models (LLMs) based agents to acquire high-value external knowledge iteratively. Previous work has explored reinforcement learning (RL) to train LLMs to perform search-based document retrieval, achieving notable improvements in QA performance, but underperform on complex, multi-hop QA resulting from the sparse rewards from global signal only. To address this gap in existing research, we introduce StepSearch, a framework for search LLMs that trained with step-wise proximal policy optimization method. It consists of richer and more detailed intermediate search rewards and token-level process supervision based on information gain and redundancy penalties to better guide each search step. We constructed a fine-grained question-answering dataset containing sub-question-level search trajectories based on open source datasets through a set of data pipeline method. On standard multi-hop QA benchmarks, it significantly outperforms global-reward baselines, achieving 11.2% and 4.2% absolute improvements for 3B and 7B models over various search with RL baselines using only 19k training data, demonstrating the effectiveness of fine-grained, stepwise supervision in optimizing deep search LLMs. Our implementation is publicly available at https://github.com/zxh20001117/StepSearch.
ASGO: Adaptive Structured Gradient Optimization
Mar 26, 2025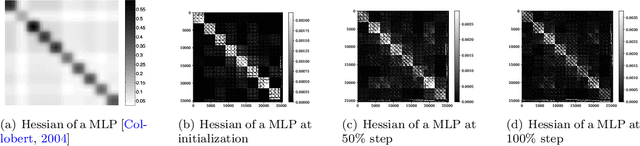
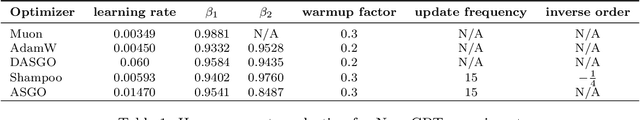
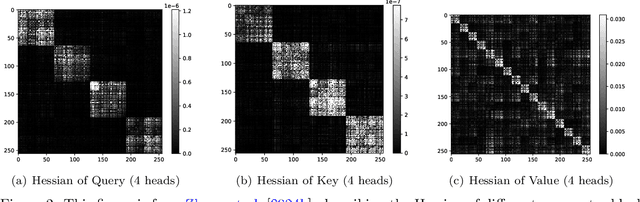
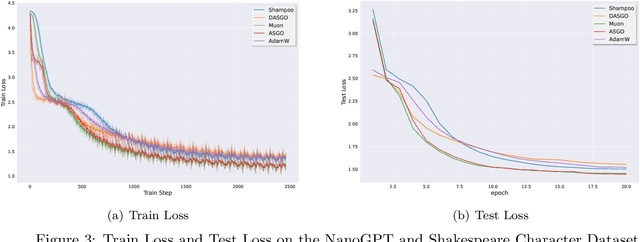
Abstract:Training deep neural networks (DNNs) is a structured optimization problem, because the parameters are naturally represented by matrices and tensors rather than simple vectors. Under this structural representation, it has been widely observed that gradients are low-rank and Hessians are approximately block-wise diagonal. These structured properties are crucial for designing efficient optimization algorithms but may not be utilized by current popular optimizers like Adam. In this paper, we present a novel optimization algorithm ASGO that capitalizes on these properties by employing a preconditioner that is adaptively updated using structured gradients. By fine-grained theoretical analysis, ASGO is proven to achieve superior convergence rates compared to existing structured gradient methods. Based on the convergence theory, we further demonstrate that ASGO can benefit from the low-rank and block-wise diagonal properties. We also discuss practical modifications of ASGO and empirically verify the effectiveness of the algorithm on language model tasks.
Step-Video-TI2V Technical Report: A State-of-the-Art Text-Driven Image-to-Video Generation Model
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:We present Step-Video-TI2V, a state-of-the-art text-driven image-to-video generation model with 30B parameters, capable of generating videos up to 102 frames based on both text and image inputs. We build Step-Video-TI2V-Eval as a new benchmark for the text-driven image-to-video task and compare Step-Video-TI2V with open-source and commercial TI2V engines using this dataset. Experimental results demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of Step-Video-TI2V in the image-to-video generation task. Both Step-Video-TI2V and Step-Video-TI2V-Eval are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Video-TI2V.
Geometry-Constrained Monocular Scale Estimation Using Semantic Segmentation for Dynamic Scenes
Mar 06, 2025



Abstract:Monocular visual localization plays a pivotal role in advanced driver assistance systems and autonomous driving by estimating a vehicle's ego-motion from a single pinhole camera. Nevertheless, conventional monocular visual odometry encoun-ters challenges in scale estimation due to the absence of depth information during projection. Previous methodologies, whether rooted in physical constraints or deep learning paradigms, con-tend with issues related to computational complexity and the management of dynamic objects. This study extends our prior research, presenting innovative strategies for ego-motion estima-tion and the selection of ground points. Striving for a nuanced equilibrium between computational efficiency and precision, we propose a hybrid method that leverages the SegNeXt model for real-time applications, encompassing both ego-motion estimation and ground point selection. Our methodology incorporates dy-namic object masks to eliminate unstable features and employs ground plane masks for meticulous triangulation. Furthermore, we exploit Geometry-constraint to delineate road regions for scale recovery. The integration of this approach with the mo-nocular version of ORB-SLAM3 culminates in the accurate esti-mation of a road model, a pivotal component in our scale recov-ery process. Rigorous experiments, conducted on the KITTI da-taset, systematically compare our method with existing monocu-lar visual odometry algorithms and contemporary scale recovery methodologies. The results undeniably confirm the superior ef-fectiveness of our approach, surpassing state-of-the-art visual odometry algorithms. Our source code is available at https://git hub.com/bFr0zNq/MVOSegScale.
Step-Audio: Unified Understanding and Generation in Intelligent Speech Interaction
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Real-time speech interaction, serving as a fundamental interface for human-machine collaboration, holds immense potential. However, current open-source models face limitations such as high costs in voice data collection, weakness in dynamic control, and limited intelligence. To address these challenges, this paper introduces Step-Audio, the first production-ready open-source solution. Key contributions include: 1) a 130B-parameter unified speech-text multi-modal model that achieves unified understanding and generation, with the Step-Audio-Chat version open-sourced; 2) a generative speech data engine that establishes an affordable voice cloning framework and produces the open-sourced lightweight Step-Audio-TTS-3B model through distillation; 3) an instruction-driven fine control system enabling dynamic adjustments across dialects, emotions, singing, and RAP; 4) an enhanced cognitive architecture augmented with tool calling and role-playing abilities to manage complex tasks effectively. Based on our new StepEval-Audio-360 evaluation benchmark, Step-Audio achieves state-of-the-art performance in human evaluations, especially in terms of instruction following. On open-source benchmarks like LLaMA Question, shows 9.3% average performance improvement, demonstrating our commitment to advancing the development of open-source multi-modal language technologies. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge