Kale-ab Tessera
$TAR^2$: Temporal-Agent Reward Redistribution for Optimal Policy Preservation in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Feb 07, 2025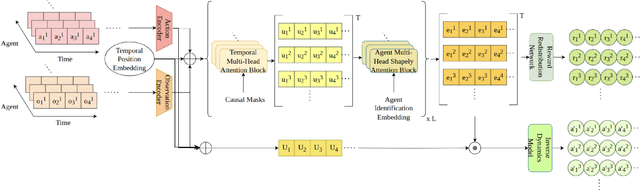


Abstract:In cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), learning effective policies is challenging when global rewards are sparse and delayed. This difficulty arises from the need to assign credit across both agents and time steps, a problem that existing methods often fail to address in episodic, long-horizon tasks. We propose Temporal-Agent Reward Redistribution $TAR^2$, a novel approach that decomposes sparse global rewards into agent-specific, time-step-specific components, thereby providing more frequent and accurate feedback for policy learning. Theoretically, we show that $TAR^2$ (i) aligns with potential-based reward shaping, preserving the same optimal policies as the original environment, and (ii) maintains policy gradient update directions identical to those under the original sparse reward, ensuring unbiased credit signals. Empirical results on two challenging benchmarks, SMACLite and Google Research Football, demonstrate that $TAR^2$ significantly stabilizes and accelerates convergence, outperforming strong baselines like AREL and STAS in both learning speed and final performance. These findings establish $TAR^2$ as a principled and practical solution for agent-temporal credit assignment in sparse-reward multi-agent systems.
Agent-Temporal Credit Assignment for Optimal Policy Preservation in Sparse Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Dec 19, 2024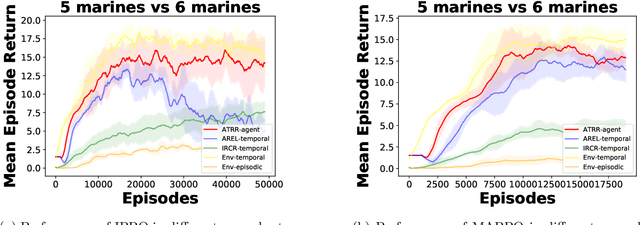
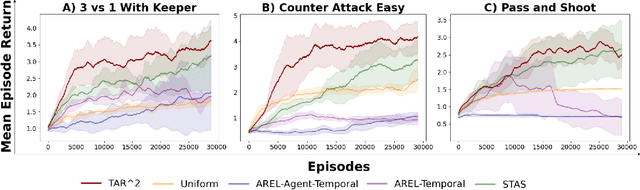
Abstract:In multi-agent environments, agents often struggle to learn optimal policies due to sparse or delayed global rewards, particularly in long-horizon tasks where it is challenging to evaluate actions at intermediate time steps. We introduce Temporal-Agent Reward Redistribution (TAR$^2$), a novel approach designed to address the agent-temporal credit assignment problem by redistributing sparse rewards both temporally and across agents. TAR$^2$ decomposes sparse global rewards into time-step-specific rewards and calculates agent-specific contributions to these rewards. We theoretically prove that TAR$^2$ is equivalent to potential-based reward shaping, ensuring that the optimal policy remains unchanged. Empirical results demonstrate that TAR$^2$ stabilizes and accelerates the learning process. Additionally, we show that when TAR$^2$ is integrated with single-agent reinforcement learning algorithms, it performs as well as or better than traditional multi-agent reinforcement learning methods.
How much can change in a year? Revisiting Evaluation in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Dec 13, 2023Abstract:Establishing sound experimental standards and rigour is important in any growing field of research. Deep Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) is one such nascent field. Although exciting progress has been made, MARL has recently come under scrutiny for replicability issues and a lack of standardised evaluation methodology, specifically in the cooperative setting. Although protocols have been proposed to help alleviate the issue, it remains important to actively monitor the health of the field. In this work, we extend the database of evaluation methodology previously published by containing meta-data on MARL publications from top-rated conferences and compare the findings extracted from this updated database to the trends identified in their work. Our analysis shows that many of the worrying trends in performance reporting remain. This includes the omission of uncertainty quantification, not reporting all relevant evaluation details and a narrowing of algorithmic development classes. Promisingly, we do observe a trend towards more difficult scenarios in SMAC-v1, which if continued into SMAC-v2 will encourage novel algorithmic development. Our data indicate that replicability needs to be approached more proactively by the MARL community to ensure trust in the field as we move towards exciting new frontiers.
Efficiently Quantifying Individual Agent Importance in Cooperative MARL
Dec 13, 2023Abstract:Measuring the contribution of individual agents is challenging in cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). In cooperative MARL, team performance is typically inferred from a single shared global reward. Arguably, among the best current approaches to effectively measure individual agent contributions is to use Shapley values. However, calculating these values is expensive as the computational complexity grows exponentially with respect to the number of agents. In this paper, we adapt difference rewards into an efficient method for quantifying the contribution of individual agents, referred to as Agent Importance, offering a linear computational complexity relative to the number of agents. We show empirically that the computed values are strongly correlated with the true Shapley values, as well as the true underlying individual agent rewards, used as the ground truth in environments where these are available. We demonstrate how Agent Importance can be used to help study MARL systems by diagnosing algorithmic failures discovered in prior MARL benchmarking work. Our analysis illustrates Agent Importance as a valuable explainability component for future MARL benchmarks.
Generalisable Agents for Neural Network Optimisation
Nov 30, 2023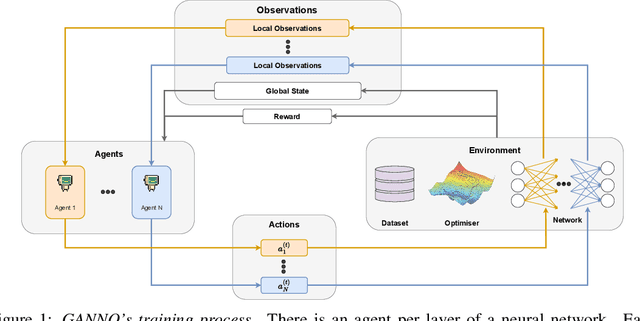
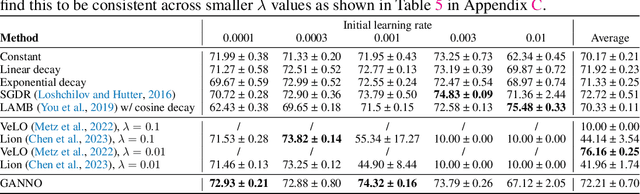
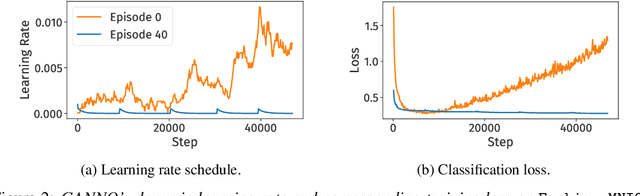
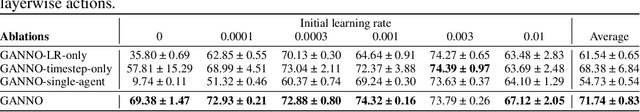
Abstract:Optimising deep neural networks is a challenging task due to complex training dynamics, high computational requirements, and long training times. To address this difficulty, we propose the framework of Generalisable Agents for Neural Network Optimisation (GANNO) -- a multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) approach that learns to improve neural network optimisation by dynamically and responsively scheduling hyperparameters during training. GANNO utilises an agent per layer that observes localised network dynamics and accordingly takes actions to adjust these dynamics at a layerwise level to collectively improve global performance. In this paper, we use GANNO to control the layerwise learning rate and show that the framework can yield useful and responsive schedules that are competitive with handcrafted heuristics. Furthermore, GANNO is shown to perform robustly across a wide variety of unseen initial conditions, and can successfully generalise to harder problems than it was trained on. Our work presents an overview of the opportunities that this paradigm offers for training neural networks, along with key challenges that remain to be overcome.
Are we going MAD? Benchmarking Multi-Agent Debate between Language Models for Medical Q&A
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) underscore their potential for responding to medical inquiries. However, ensuring that generative agents provide accurate and reliable answers remains an ongoing challenge. In this context, multi-agent debate (MAD) has emerged as a prominent strategy for enhancing the truthfulness of LLMs. In this work, we provide a comprehensive benchmark of MAD strategies for medical Q&A, along with open-source implementations. This explores the effective utilization of various strategies including the trade-offs between cost, time, and accuracy. We build upon these insights to provide a novel debate-prompting strategy based on agent agreement that outperforms previously published strategies on medical Q&A tasks.
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Selective Reincarnation in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Mar 31, 2023Abstract:'Reincarnation' in reinforcement learning has been proposed as a formalisation of reusing prior computation from past experiments when training an agent in an environment. In this paper, we present a brief foray into the paradigm of reincarnation in the multi-agent (MA) context. We consider the case where only some agents are reincarnated, whereas the others are trained from scratch -- selective reincarnation. In the fully-cooperative MA setting with heterogeneous agents, we demonstrate that selective reincarnation can lead to higher returns than training fully from scratch, and faster convergence than training with full reincarnation. However, the choice of which agents to reincarnate in a heterogeneous system is vitally important to the outcome of the training -- in fact, a poor choice can lead to considerably worse results than the alternatives. We argue that a rich field of work exists here, and we hope that our effort catalyses further energy in bringing the topic of reincarnation to the multi-agent realm.
On pseudo-absence generation and machine learning for locust breeding ground prediction in Africa
Nov 06, 2021

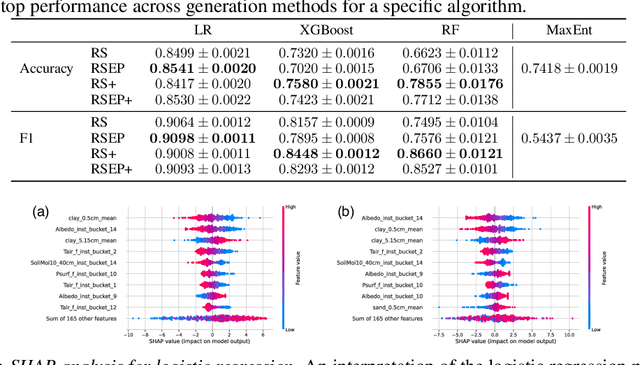
Abstract:Desert locust outbreaks threaten the food security of a large part of Africa and have affected the livelihoods of millions of people over the years. Machine learning (ML) has been demonstrated as an effective approach to locust distribution modelling which could assist in early warning. ML requires a significant amount of labelled data to train. Most publicly available labelled data on locusts are presence-only data, where only the sightings of locusts being present at a location are recorded. Therefore, prior work using ML have resorted to pseudo-absence generation methods as a way to circumvent this issue. The most commonly used approach is to randomly sample points in a region of interest while ensuring that these sampled pseudo-absence points are at least a specific distance away from true presence points. In this paper, we compare this random sampling approach to more advanced pseudo-absence generation methods, such as environmental profiling and optimal background extent limitation, specifically for predicting desert locust breeding grounds in Africa. Interestingly, we find that for the algorithms we tested, namely logistic regression, gradient boosting, random forests and maximum entropy, all popular in prior work, the logistic model performed significantly better than the more sophisticated ensemble methods, both in terms of prediction accuracy and F1 score. Although background extent limitation combined with random sampling boosted performance for ensemble methods, for LR this was not the case, and instead, a significant improvement was obtained when using environmental profiling. In light of this, we conclude that a simpler ML approach such as logistic regression combined with more advanced pseudo-absence generation, specifically environmental profiling, can be a sensible and effective approach to predicting locust breeding grounds across Africa.
Mava: a research framework for distributed multi-agent reinforcement learning
Jul 03, 2021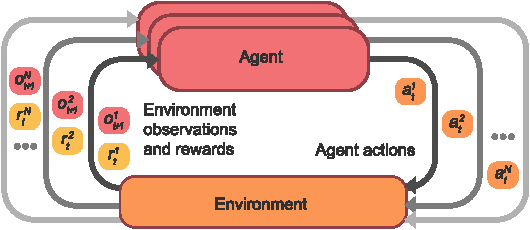
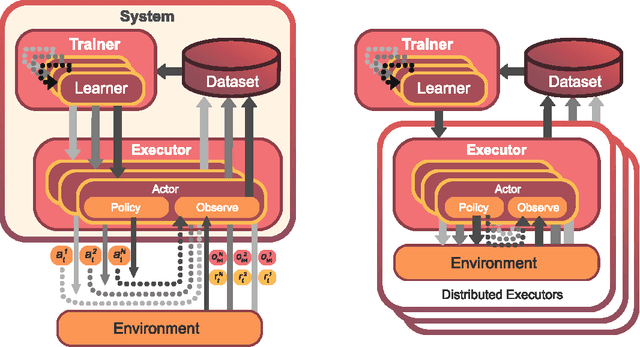
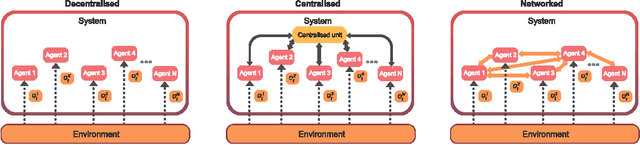

Abstract:Breakthrough advances in reinforcement learning (RL) research have led to a surge in the development and application of RL. To support the field and its rapid growth, several frameworks have emerged that aim to help the community more easily build effective and scalable agents. However, very few of these frameworks exclusively support multi-agent RL (MARL), an increasingly active field in itself, concerned with decentralised decision-making problems. In this work, we attempt to fill this gap by presenting Mava: a research framework specifically designed for building scalable MARL systems. Mava provides useful components, abstractions, utilities and tools for MARL and allows for simple scaling for multi-process system training and execution, while providing a high level of flexibility and composability. Mava is built on top of DeepMind's Acme \citep{hoffman2020acme}, and therefore integrates with, and greatly benefits from, a wide range of already existing single-agent RL components made available in Acme. Several MARL baseline systems have already been implemented in Mava. These implementations serve as examples showcasing Mava's reusable features, such as interchangeable system architectures, communication and mixing modules. Furthermore, these implementations allow existing MARL algorithms to be easily reproduced and extended. We provide experimental results for these implementations on a wide range of multi-agent environments and highlight the benefits of distributed system training.
Keep the Gradients Flowing: Using Gradient Flow to Study Sparse Network Optimization
Feb 02, 2021



Abstract:Training sparse networks to converge to the same performance as dense neural architectures has proven to be elusive. Recent work suggests that initialization is the key. However, while this direction of research has had some success, focusing on initialization alone appears to be inadequate. In this paper, we take a broader view of training sparse networks and consider the role of regularization, optimization and architecture choices on sparse models. We propose a simple experimental framework, Same Capacity Sparse vs Dense Comparison (SC-SDC), that allows for fair comparison of sparse and dense networks. Furthermore, we propose a new measure of gradient flow, Effective Gradient Flow (EGF), that better correlates to performance in sparse networks. Using top-line metrics, SC-SDC and EGF, we show that default choices of optimizers, activation functions and regularizers used for dense networks can disadvantage sparse networks. Based upon these findings, we show that gradient flow in sparse networks can be improved by reconsidering aspects of the architecture design and the training regime. Our work suggests that initialization is only one piece of the puzzle and taking a wider view of tailoring optimization to sparse networks yields promising results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge