Kevin Eloff
TransFusion: Transcribing Speech with Multinomial Diffusion
Oct 14, 2022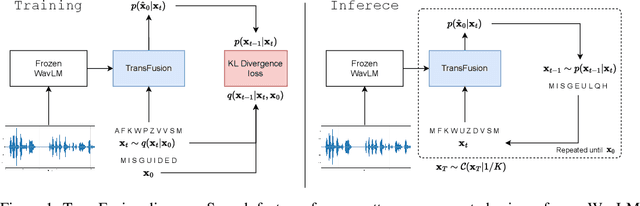
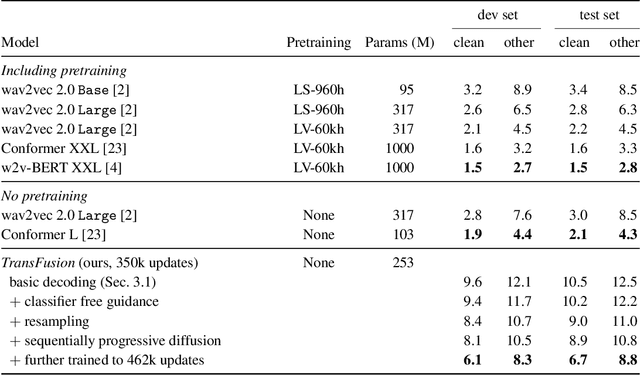
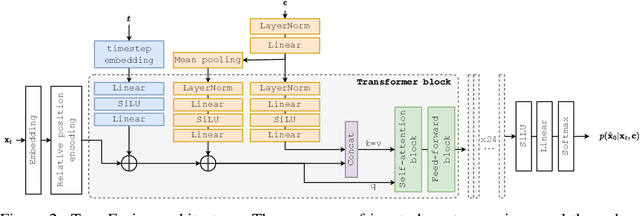
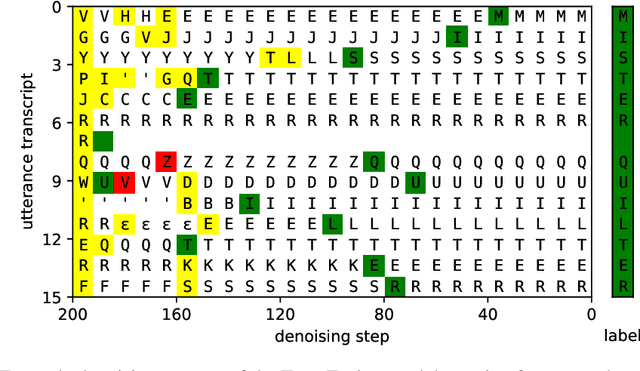
Abstract:Diffusion models have shown exceptional scaling properties in the image synthesis domain, and initial attempts have shown similar benefits for applying diffusion to unconditional text synthesis. Denoising diffusion models attempt to iteratively refine a sampled noise signal until it resembles a coherent signal (such as an image or written sentence). In this work we aim to see whether the benefits of diffusion models can also be realized for speech recognition. To this end, we propose a new way to perform speech recognition using a diffusion model conditioned on pretrained speech features. Specifically, we propose TransFusion: a transcribing diffusion model which iteratively denoises a random character sequence into coherent text corresponding to the transcript of a conditioning utterance. We demonstrate comparable performance to existing high-performing contrastive models on the LibriSpeech speech recognition benchmark. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to apply denoising diffusion to speech recognition. We also propose new techniques for effectively sampling and decoding multinomial diffusion models. These are required because traditional methods of sampling from acoustic models are not possible with our new discrete diffusion approach. Code and trained models are available: https://github.com/RF5/transfusion-asr
Towards Learning to Speak and Hear Through Multi-Agent Communication over a Continuous Acoustic Channel
Nov 04, 2021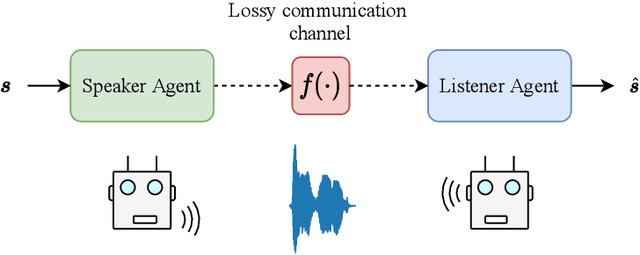

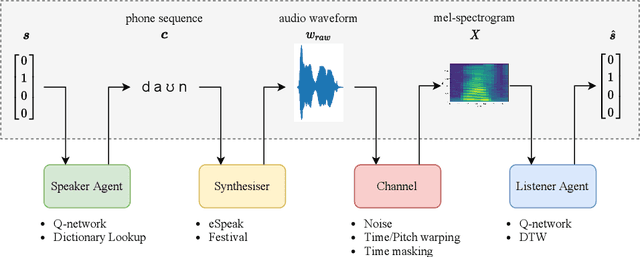
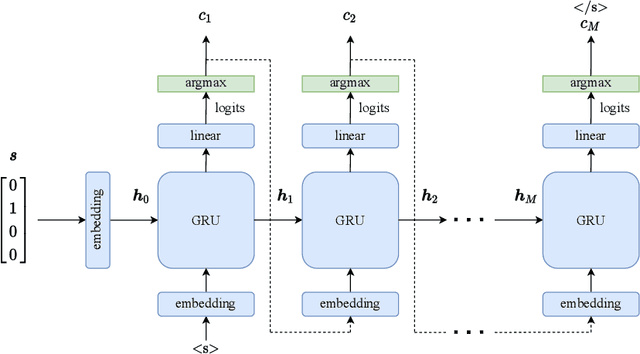
Abstract:While multi-agent reinforcement learning has been used as an effective means to study emergent communication between agents, existing work has focused almost exclusively on communication with discrete symbols. Human communication often takes place (and emerged) over a continuous acoustic channel; human infants acquire language in large part through continuous signalling with their caregivers. We therefore ask: Are we able to observe emergent language between agents with a continuous communication channel trained through reinforcement learning? And if so, what is the impact of channel characteristics on the emerging language? We propose an environment and training methodology to serve as a means to carry out an initial exploration of these questions. We use a simple messaging environment where a "speaker" agent needs to convey a concept to a "listener". The Speaker is equipped with a vocoder that maps symbols to a continuous waveform, this is passed over a lossy continuous channel, and the Listener needs to map the continuous signal to the concept. Using deep Q-learning, we show that basic compositionality emerges in the learned language representations. We find that noise is essential in the communication channel when conveying unseen concept combinations. And we show that we can ground the emergent communication by introducing a caregiver predisposed to "hearing" or "speaking" English. Finally, we describe how our platform serves as a starting point for future work that uses a combination of deep reinforcement learning and multi-agent systems to study our questions of continuous signalling in language learning and emergence.
Toward Collaborative Reinforcement Learning Agents that Communicate Through Text-Based Natural Language
Jul 21, 2021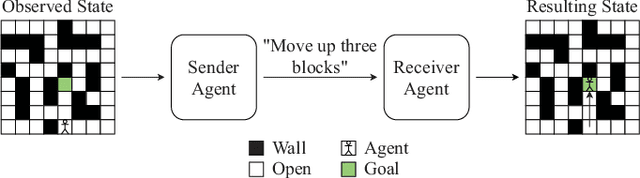
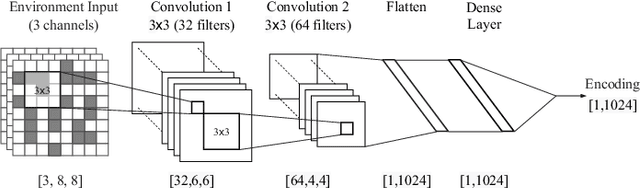
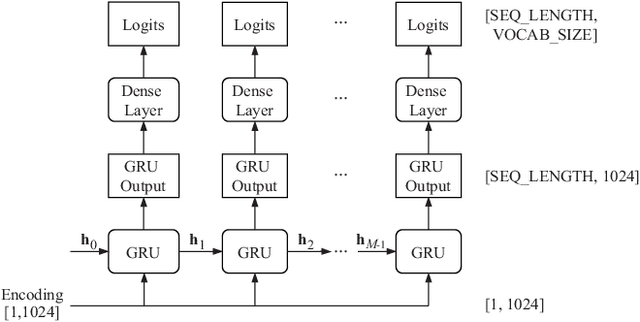
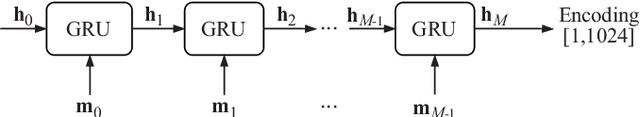
Abstract:Communication between agents in collaborative multi-agent settings is in general implicit or a direct data stream. This paper considers text-based natural language as a novel form of communication between multiple agents trained with reinforcement learning. This could be considered first steps toward a truly autonomous communication without the need to define a limited set of instructions, and natural collaboration between humans and robots. Inspired by the game of Blind Leads, we propose an environment where one agent uses natural language instructions to guide another through a maze. We test the ability of reinforcement learning agents to effectively communicate through discrete word-level symbols and show that the agents are able to sufficiently communicate through natural language with a limited vocabulary. Although the communication is not always perfect English, the agents are still able to navigate the maze. We achieve a BLEU score of 0.85, which is an improvement of 0.61 over randomly generated sequences while maintaining a 100% maze completion rate. This is a 3.5 times the performance of the random baseline using our reference set.
* 5 pages, 6 figures, 3 tables; published in 2021 Southern African Universities Power Engineering Conference/Robotics and Mechatronics/Pattern Recognition Association of South Africa (SAUPEC/RobMech/PRASA), 2021, pp. 1-6, (c) 2021 IEEE
Mava: a research framework for distributed multi-agent reinforcement learning
Jul 03, 2021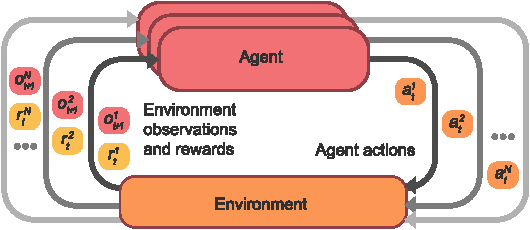
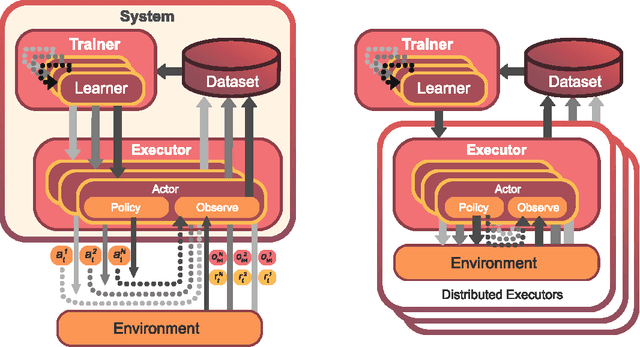
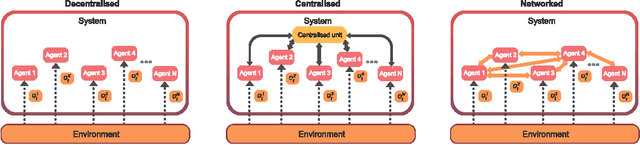

Abstract:Breakthrough advances in reinforcement learning (RL) research have led to a surge in the development and application of RL. To support the field and its rapid growth, several frameworks have emerged that aim to help the community more easily build effective and scalable agents. However, very few of these frameworks exclusively support multi-agent RL (MARL), an increasingly active field in itself, concerned with decentralised decision-making problems. In this work, we attempt to fill this gap by presenting Mava: a research framework specifically designed for building scalable MARL systems. Mava provides useful components, abstractions, utilities and tools for MARL and allows for simple scaling for multi-process system training and execution, while providing a high level of flexibility and composability. Mava is built on top of DeepMind's Acme \citep{hoffman2020acme}, and therefore integrates with, and greatly benefits from, a wide range of already existing single-agent RL components made available in Acme. Several MARL baseline systems have already been implemented in Mava. These implementations serve as examples showcasing Mava's reusable features, such as interchangeable system architectures, communication and mixing modules. Furthermore, these implementations allow existing MARL algorithms to be easily reproduced and extended. We provide experimental results for these implementations on a wide range of multi-agent environments and highlight the benefits of distributed system training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge