Joel R. Tetreault
NLP for Social Good: A Survey of Challenges, Opportunities, and Responsible Deployment
May 28, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have unlocked unprecedented possibilities across a range of applications. However, as a community, we believe that the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) has a growing need to approach deployment with greater intentionality and responsibility. In alignment with the broader vision of AI for Social Good (Toma\v{s}ev et al., 2020), this paper examines the role of NLP in addressing pressing societal challenges. Through a cross-disciplinary analysis of social goals and emerging risks, we highlight promising research directions and outline challenges that must be addressed to ensure responsible and equitable progress in NLP4SG research.
Uchaguzi-2022: A Dataset of Citizen Reports on the 2022 Kenyan Election
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Online reporting platforms have enabled citizens around the world to collectively share their opinions and report in real time on events impacting their local communities. Systematically organizing (e.g., categorizing by attributes) and geotagging large amounts of crowdsourced information is crucial to ensuring that accurate and meaningful insights can be drawn from this data and used by policy makers to bring about positive change. These tasks, however, typically require extensive manual annotation efforts. In this paper we present Uchaguzi-2022, a dataset of 14k categorized and geotagged citizen reports related to the 2022 Kenyan General Election containing mentions of election-related issues such as official misconduct, vote count irregularities, and acts of violence. We use this dataset to investigate whether language models can assist in scalably categorizing and geotagging reports, thus highlighting its potential application in the AI for Social Good space.
Defining a New NLP Playground
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:The recent explosion of performance of large language models (LLMs) has changed the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) more abruptly and seismically than any other shift in the field's 80-year history. This has resulted in concerns that the field will become homogenized and resource-intensive. The new status quo has put many academic researchers, especially PhD students, at a disadvantage. This paper aims to define a new NLP playground by proposing 20+ PhD-dissertation-worthy research directions, covering theoretical analysis, new and challenging problems, learning paradigms, and interdisciplinary applications.
Harnessing the Power of LLMs: Evaluating Human-AI Text Co-Creation through the Lens of News Headline Generation
Oct 18, 2023



Abstract:To explore how humans can best leverage LLMs for writing and how interacting with these models affects feelings of ownership and trust in the writing process, we compared common human-AI interaction types (e.g., guiding system, selecting from system outputs, post-editing outputs) in the context of LLM-assisted news headline generation. While LLMs alone can generate satisfactory news headlines, on average, human control is needed to fix undesirable model outputs. Of the interaction methods, guiding and selecting model output added the most benefit with the lowest cost (in time and effort). Further, AI assistance did not harm participants' perception of control compared to freeform editing.
XLTime: A Cross-Lingual Knowledge Transfer Framework for Temporal Expression Extraction
May 03, 2022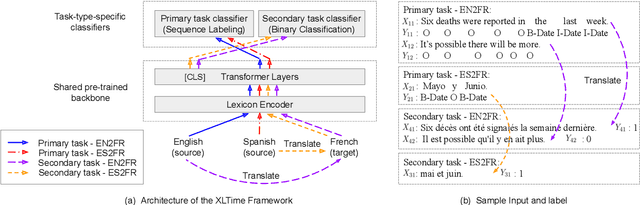
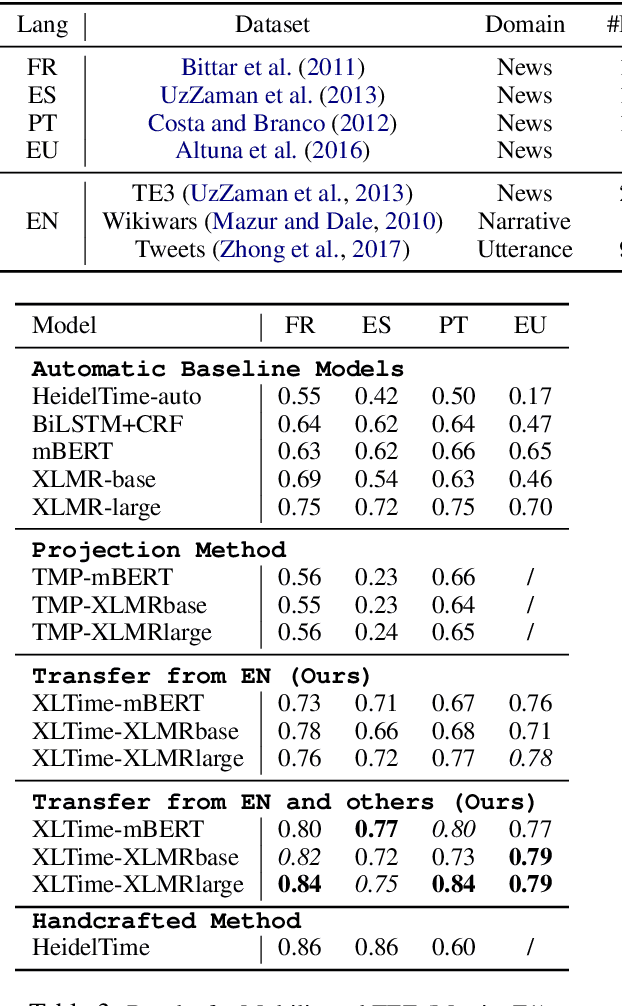
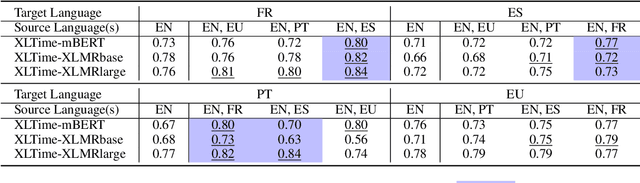
Abstract:Temporal Expression Extraction (TEE) is essential for understanding time in natural language. It has applications in Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks such as question answering, information retrieval, and causal inference. To date, work in this area has mostly focused on English as there is a scarcity of labeled data for other languages. We propose XLTime, a novel framework for multilingual TEE. XLTime works on top of pre-trained language models and leverages multi-task learning to prompt cross-language knowledge transfer both from English and within the non-English languages. XLTime alleviates problems caused by a shortage of data in the target language. We apply XLTime with different language models and show that it outperforms the previous automatic SOTA methods on French, Spanish, Portuguese, and Basque, by large margins. XLTime also closes the gap considerably on the handcrafted HeidelTime method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge