Jingwen Liu
Victor
Group-realizable multi-group learning by minimizing empirical risk
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:The sample complexity of multi-group learning is shown to improve in the group-realizable setting over the agnostic setting, even when the family of groups is infinite so long as it has finite VC dimension. The improved sample complexity is obtained by empirical risk minimization over the class of group-realizable concepts, which itself could have infinite VC dimension. Implementing this approach is also shown to be computationally intractable, and an alternative approach is suggested based on improper learning.
Fast attention mechanisms: a tale of parallelism
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Transformers have the representational capacity to simulate Massively Parallel Computation (MPC) algorithms, but they suffer from quadratic time complexity, which severely limits their scalability. We introduce an efficient attention mechanism called Approximate Nearest Neighbor Attention (ANNA) with sub-quadratic time complexity. We prove that ANNA-transformers (1) retain the expressive power previously established for standard attention in terms of matching the capabilities of MPC algorithms, and (2) can solve key reasoning tasks such as Match2 and $k$-hop with near-optimal depth. Using the MPC framework, we further prove that constant-depth ANNA-transformers can simulate constant-depth low-rank transformers, thereby providing a unified way to reason about a broad class of efficient attention approximations.
EMO-Reasoning: Benchmarking Emotional Reasoning Capabilities in Spoken Dialogue Systems
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Speech emotions play a crucial role in human-computer interaction, shaping engagement and context-aware communication. Despite recent advances in spoken dialogue systems, a holistic system for evaluating emotional reasoning is still lacking. To address this, we introduce EMO-Reasoning, a benchmark for assessing emotional coherence in dialogue systems. It leverages a curated dataset generated via text-to-speech to simulate diverse emotional states, overcoming the scarcity of emotional speech data. We further propose the Cross-turn Emotion Reasoning Score to assess the emotion transitions in multi-turn dialogues. Evaluating seven dialogue systems through continuous, categorical, and perceptual metrics, we show that our framework effectively detects emotional inconsistencies, providing insights for improving current dialogue systems. By releasing a systematic evaluation benchmark, we aim to advance emotion-aware spoken dialogue modeling toward more natural and adaptive interactions.
RenderWorld: World Model with Self-Supervised 3D Label
Sep 17, 2024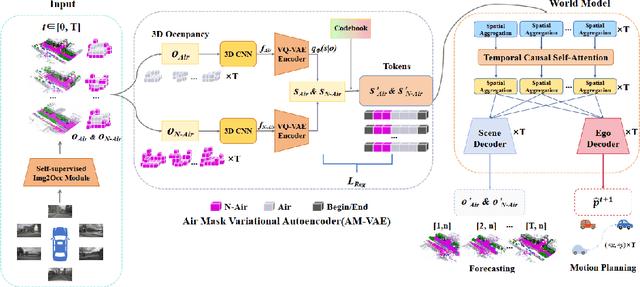
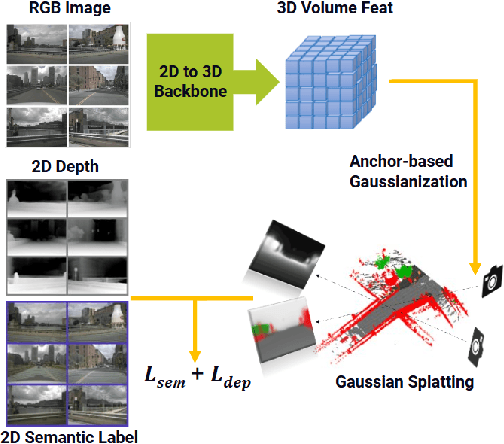
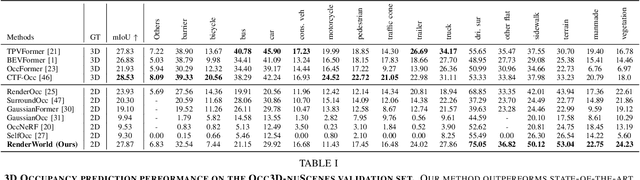
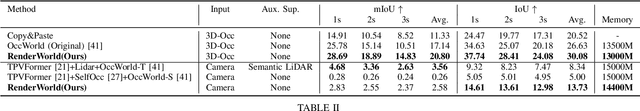
Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving with vision-only is not only more cost-effective compared to LiDAR-vision fusion but also more reliable than traditional methods. To achieve a economical and robust purely visual autonomous driving system, we propose RenderWorld, a vision-only end-to-end autonomous driving framework, which generates 3D occupancy labels using a self-supervised gaussian-based Img2Occ Module, then encodes the labels by AM-VAE, and uses world model for forecasting and planning. RenderWorld employs Gaussian Splatting to represent 3D scenes and render 2D images greatly improves segmentation accuracy and reduces GPU memory consumption compared with NeRF-based methods. By applying AM-VAE to encode air and non-air separately, RenderWorld achieves more fine-grained scene element representation, leading to state-of-the-art performance in both 4D occupancy forecasting and motion planning from autoregressive world model.
Group-wise oracle-efficient algorithms for online multi-group learning
Jun 07, 2024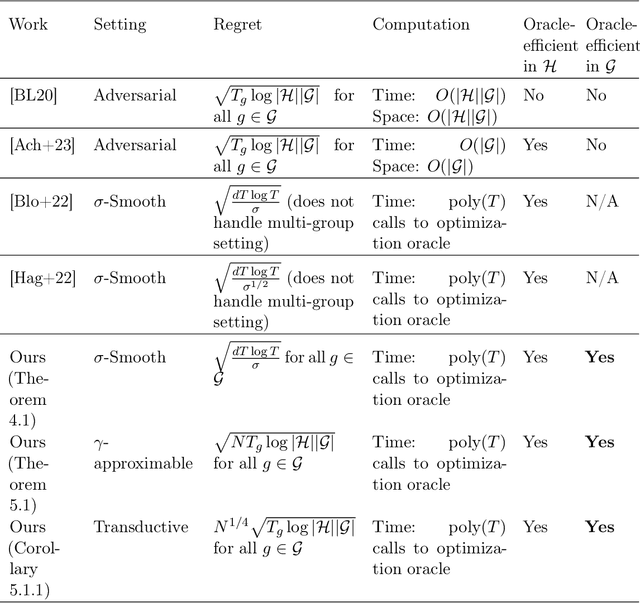
Abstract:We study the problem of online multi-group learning, a learning model in which an online learner must simultaneously achieve small prediction regret on a large collection of (possibly overlapping) subsequences corresponding to a family of groups. Groups are subsets of the context space, and in fairness applications, they may correspond to subpopulations defined by expressive functions of demographic attributes. In contrast to previous work on this learning model, we consider scenarios in which the family of groups is too large to explicitly enumerate, and hence we seek algorithms that only access groups via an optimization oracle. In this paper, we design such oracle-efficient algorithms with sublinear regret under a variety of settings, including: (i) the i.i.d. setting, (ii) the adversarial setting with smoothed context distributions, and (iii) the adversarial transductive setting.
On the Opportunities of Green Computing: A Survey
Nov 09, 2023



Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has achieved significant advancements in technology and research with the development over several decades, and is widely used in many areas including computing vision, natural language processing, time-series analysis, speech synthesis, etc. During the age of deep learning, especially with the arise of Large Language Models, a large majority of researchers' attention is paid on pursuing new state-of-the-art (SOTA) results, resulting in ever increasing of model size and computational complexity. The needs for high computing power brings higher carbon emission and undermines research fairness by preventing small or medium-sized research institutions and companies with limited funding in participating in research. To tackle the challenges of computing resources and environmental impact of AI, Green Computing has become a hot research topic. In this survey, we give a systematic overview of the technologies used in Green Computing. We propose the framework of Green Computing and devide it into four key components: (1) Measures of Greenness, (2) Energy-Efficient AI, (3) Energy-Efficient Computing Systems and (4) AI Use Cases for Sustainability. For each components, we discuss the research progress made and the commonly used techniques to optimize the AI efficiency. We conclude that this new research direction has the potential to address the conflicts between resource constraints and AI development. We encourage more researchers to put attention on this direction and make AI more environmental friendly.
VideoINR: Learning Video Implicit Neural Representation for Continuous Space-Time Super-Resolution
Jun 09, 2022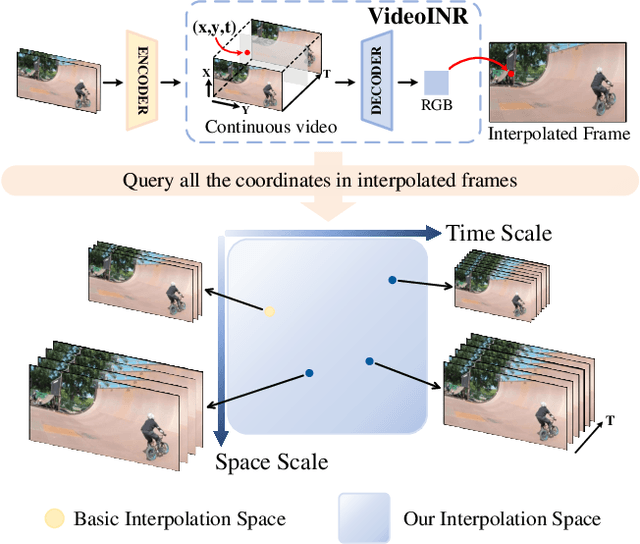
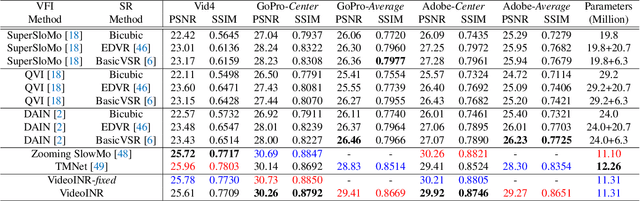
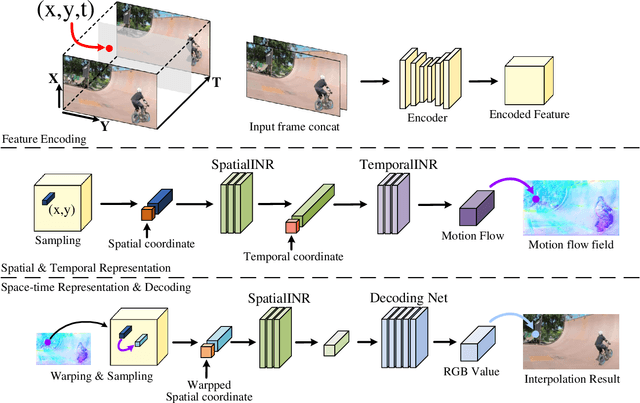
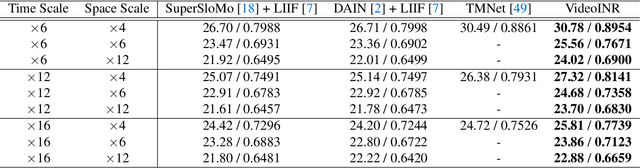
Abstract:Videos typically record the streaming and continuous visual data as discrete consecutive frames. Since the storage cost is expensive for videos of high fidelity, most of them are stored in a relatively low resolution and frame rate. Recent works of Space-Time Video Super-Resolution (STVSR) are developed to incorporate temporal interpolation and spatial super-resolution in a unified framework. However, most of them only support a fixed up-sampling scale, which limits their flexibility and applications. In this work, instead of following the discrete representations, we propose Video Implicit Neural Representation (VideoINR), and we show its applications for STVSR. The learned implicit neural representation can be decoded to videos of arbitrary spatial resolution and frame rate. We show that VideoINR achieves competitive performances with state-of-the-art STVSR methods on common up-sampling scales and significantly outperforms prior works on continuous and out-of-training-distribution scales. Our project page is at http://zeyuan-chen.com/VideoINR/ .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge