Group-wise oracle-efficient algorithms for online multi-group learning
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2024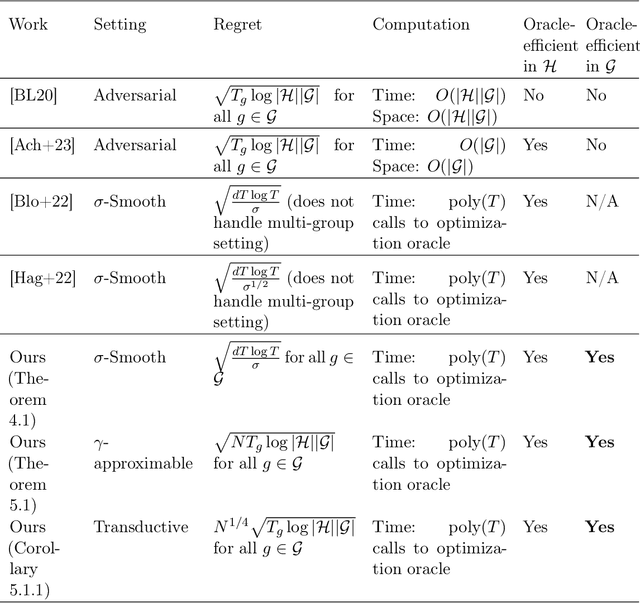
We study the problem of online multi-group learning, a learning model in which an online learner must simultaneously achieve small prediction regret on a large collection of (possibly overlapping) subsequences corresponding to a family of groups. Groups are subsets of the context space, and in fairness applications, they may correspond to subpopulations defined by expressive functions of demographic attributes. In contrast to previous work on this learning model, we consider scenarios in which the family of groups is too large to explicitly enumerate, and hence we seek algorithms that only access groups via an optimization oracle. In this paper, we design such oracle-efficient algorithms with sublinear regret under a variety of settings, including: (i) the i.i.d. setting, (ii) the adversarial setting with smoothed context distributions, and (iii) the adversarial transductive setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge