Jiaxu Leng
A2Seek: Towards Reasoning-Centric Benchmark for Aerial Anomaly Understanding
May 28, 2025Abstract:While unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) offer wide-area, high-altitude coverage for anomaly detection, they face challenges such as dynamic viewpoints, scale variations, and complex scenes. Existing datasets and methods, mainly designed for fixed ground-level views, struggle to adapt to these conditions, leading to significant performance drops in drone-view scenarios. To bridge this gap, we introduce A2Seek (Aerial Anomaly Seek), a large-scale, reasoning-centric benchmark dataset for aerial anomaly understanding. This dataset covers various scenarios and environmental conditions, providing high-resolution real-world aerial videos with detailed annotations, including anomaly categories, frame-level timestamps, region-level bounding boxes, and natural language explanations for causal reasoning. Building on this dataset, we propose A2Seek-R1, a novel reasoning framework that generalizes R1-style strategies to aerial anomaly understanding, enabling a deeper understanding of "Where" anomalies occur and "Why" they happen in aerial frames. To this end, A2Seek-R1 first employs a graph-of-thought (GoT)-guided supervised fine-tuning approach to activate the model's latent reasoning capabilities on A2Seek. Then, we introduce Aerial Group Relative Policy Optimization (A-GRPO) to design rule-based reward functions tailored to aerial scenarios. Furthermore, we propose a novel "seeking" mechanism that simulates UAV flight behavior by directing the model's attention to informative regions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that A2Seek-R1 achieves up to a 22.04% improvement in AP for prediction accuracy and a 13.9% gain in mIoU for anomaly localization, exhibiting strong generalization across complex environments and out-of-distribution scenarios. Our dataset and code will be released at https://hayneyday.github.io/A2Seek/.
PiercingEye: Dual-Space Video Violence Detection with Hyperbolic Vision-Language Guidance
Apr 26, 2025Abstract:Existing weakly supervised video violence detection (VVD) methods primarily rely on Euclidean representation learning, which often struggles to distinguish visually similar yet semantically distinct events due to limited hierarchical modeling and insufficient ambiguous training samples. To address this challenge, we propose PiercingEye, a novel dual-space learning framework that synergizes Euclidean and hyperbolic geometries to enhance discriminative feature representation. Specifically, PiercingEye introduces a layer-sensitive hyperbolic aggregation strategy with hyperbolic Dirichlet energy constraints to progressively model event hierarchies, and a cross-space attention mechanism to facilitate complementary feature interactions between Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces. Furthermore, to mitigate the scarcity of ambiguous samples, we leverage large language models to generate logic-guided ambiguous event descriptions, enabling explicit supervision through a hyperbolic vision-language contrastive loss that prioritizes high-confusion samples via dynamic similarity-aware weighting. Extensive experiments on XD-Violence and UCF-Crime benchmarks demonstrate that PiercingEye achieves state-of-the-art performance, with particularly strong results on a newly curated ambiguous event subset, validating its superior capability in fine-grained violence detection.
EHGCN: Hierarchical Euclidean-Hyperbolic Fusion via Motion-Aware GCN for Hybrid Event Stream Perception
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:Event cameras, with microsecond temporal resolution and high dynamic range (HDR) characteristics, emit high-speed event stream for perception tasks. Despite the recent advancement in GNN-based perception methods, they are prone to use straightforward pairwise connectivity mechanisms in the pure Euclidean space where they struggle to capture long-range dependencies and fail to effectively characterize the inherent hierarchical structures of non-uniformly distributed event stream. To this end, in this paper we propose a novel approach named EHGCN, which is a pioneer to perceive event stream in both Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces for event vision. In EHGCN, we introduce an adaptive sampling strategy to dynamically regulate sampling rates, retaining discriminative events while attenuating chaotic noise. Then we present a Markov Vector Field (MVF)-driven motion-aware hyperedge generation method based on motion state transition probabilities, thereby eliminating cross-target spurious associations and providing critically topological priors while capturing long-range dependencies between events. Finally, we propose a Euclidean-Hyperbolic GCN to fuse the information locally aggregated and globally hierarchically modeled in Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces, respectively, to achieve hybrid event perception. Experimental results on event perception tasks such as object detection and recognition validate the effectiveness of our approach.
Beyond Euclidean: Dual-Space Representation Learning for Weakly Supervised Video Violence Detection
Sep 28, 2024



Abstract:While numerous Video Violence Detection (VVD) methods have focused on representation learning in Euclidean space, they struggle to learn sufficiently discriminative features, leading to weaknesses in recognizing normal events that are visually similar to violent events (\emph{i.e.}, ambiguous violence). In contrast, hyperbolic representation learning, renowned for its ability to model hierarchical and complex relationships between events, has the potential to amplify the discrimination between visually similar events. Inspired by these, we develop a novel Dual-Space Representation Learning (DSRL) method for weakly supervised VVD to utilize the strength of both Euclidean and hyperbolic geometries, capturing the visual features of events while also exploring the intrinsic relations between events, thereby enhancing the discriminative capacity of the features. DSRL employs a novel information aggregation strategy to progressively learn event context in hyperbolic spaces, which selects aggregation nodes through layer-sensitive hyperbolic association degrees constrained by hyperbolic Dirichlet energy. Furthermore, DSRL attempts to break the cyber-balkanization of different spaces, utilizing cross-space attention to facilitate information interactions between Euclidean and hyperbolic space to capture better discriminative features for final violence detection. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed DSRL.
CLIP-Driven Cloth-Agnostic Feature Learning for Cloth-Changing Person Re-Identification
Jun 13, 2024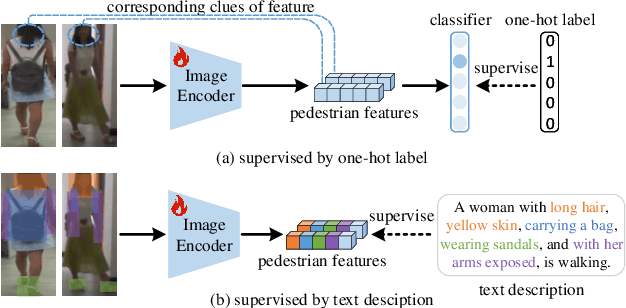

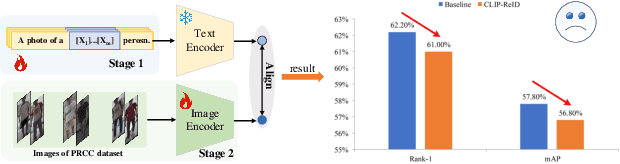
Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) has shown impressive performance in short-term Person Re-Identification (ReID) due to its ability to extract high-level semantic features of pedestrians, yet its direct application to Cloth-Changing Person Re-Identification (CC-ReID) faces challenges due to CLIP's image encoder overly focusing on clothes clues. To address this, we propose a novel framework called CLIP-Driven Cloth-Agnostic Feature Learning (CCAF) for CC-ReID. Accordingly, two modules were custom-designed: the Invariant Feature Prompting (IFP) and the Clothes Feature Minimization (CFM). These modules guide the model to extract cloth-agnostic features positively and attenuate clothes-related features negatively. Specifically, IFP is designed to extract fine-grained semantic features unrelated to clothes from the raw image, guided by the cloth-agnostic text prompts. This module first covers the clothes in the raw image at the pixel level to obtain the shielding image and then utilizes CLIP's knowledge to generate cloth-agnostic text prompts. Subsequently, it aligns the raw image-text and the raw image-shielding image in the feature space, emphasizing discriminative clues related to identity but unrelated to clothes. Furthermore, CFM is designed to examine and weaken the image encoder's ability to extract clothes features. It first generates text prompts corresponding to clothes pixels. Then, guided by these clothes text prompts, it iteratively examines and disentangles clothes features from pedestrian features, ultimately retaining inherent discriminative features. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed CCAF, achieving new state-of-the-art performance on several popular CC-ReID benchmarks without any additional inference time.
ConsistencyDet: A Robust Object Detector with a Denoising Paradigm of Consistency Model
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Object detection, a quintessential task in the realm of perceptual computing, can be tackled using a generative methodology. In the present study, we introduce a novel framework designed to articulate object detection as a denoising diffusion process, which operates on the perturbed bounding boxes of annotated entities. This framework, termed ConsistencyDet, leverages an innovative denoising concept known as the Consistency Model. The hallmark of this model is its self-consistency feature, which empowers the model to map distorted information from any temporal stage back to its pristine state, thereby realizing a "one-step denoising" mechanism. Such an attribute markedly elevates the operational efficiency of the model, setting it apart from the conventional Diffusion Model. Throughout the training phase, ConsistencyDet initiates the diffusion sequence with noise-infused boxes derived from the ground-truth annotations and conditions the model to perform the denoising task. Subsequently, in the inference stage, the model employs a denoising sampling strategy that commences with bounding boxes randomly sampled from a normal distribution. Through iterative refinement, the model transforms an assortment of arbitrarily generated boxes into definitive detections. Comprehensive evaluations employing standard benchmarks, such as MS-COCO and LVIS, corroborate that ConsistencyDet surpasses other leading-edge detectors in performance metrics. Our code is available at https://github.com/Tankowa/ConsistencyDet.
ConsistencyDet: Robust Object Detector with Denoising Paradigm of Consistency Model
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:Object detection, a quintessential task in the realm of perceptual computing, can be tackled using a generative methodology. In the present study, we introduce a novel framework designed to articulate object detection as a denoising diffusion process, which operates on perturbed bounding boxes of annotated entities. This framework, termed ConsistencyDet, leverages an innovative denoising concept known as the Consistency Model. The hallmark of this model is its self-consistency feature, which empowers the model to map distorted information from any temporal stage back to its pristine state, thereby realizing a ``one-step denoising'' mechanism. Such an attribute markedly elevates the operational efficiency of the model, setting it apart from the conventional Diffusion Model. Throughout the training phase, ConsistencyDet initiates the diffusion sequence with noise-infused boxes derived from the ground-truth annotations and conditions the model to perform the denoising task. Subsequently, in the inference stage, the model employs a denoising sampling strategy that commences with bounding boxes randomly sampled from a normal distribution. Through iterative refinement, the model transforms an assortment of arbitrarily generated boxes into the definitive detections. Comprehensive evaluations employing standard benchmarks, such as MS-COCO and LVIS, corroborate that ConsistencyDet surpasses other leading-edge detectors in performance metrics.
Peer is Your Pillar: A Data-unbalanced Conditional GANs for Few-shot Image Generation
Nov 14, 2023



Abstract:Few-shot image generation aims to train generative models using a small number of training images. When there are few images available for training (e.g. 10 images), Learning From Scratch (LFS) methods often generate images that closely resemble the training data while Transfer Learning (TL) methods try to improve performance by leveraging prior knowledge from GANs pre-trained on large-scale datasets. However, current TL methods may not allow for sufficient control over the degree of knowledge preservation from the source model, making them unsuitable for setups where the source and target domains are not closely related. To address this, we propose a novel pipeline called Peer is your Pillar (PIP), which combines a target few-shot dataset with a peer dataset to create a data-unbalanced conditional generation. Our approach includes a class embedding method that separates the class space from the latent space, and we use a direction loss based on pre-trained CLIP to improve image diversity. Experiments on various few-shot datasets demonstrate the advancement of the proposed PIP, especially reduces the training requirements of few-shot image generation.
Shape-centered Representation Learning for Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification
Oct 30, 2023



Abstract:Current Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification (VI-ReID) methods prioritize extracting distinguishing appearance features, ignoring the natural resistance of body shape against modality changes. Initially, we gauged the discriminative potential of shapes by a straightforward concatenation of shape and appearance features. However, two unresolved issues persist in the utilization of shape features. One pertains to the dependence on auxiliary models for shape feature extraction in the inference phase, along with the errors in generated infrared shapes due to the intrinsic modality disparity. The other issue involves the inadequately explored correlation between shape and appearance features. To tackle the aforementioned challenges, we propose the Shape-centered Representation Learning framework (ScRL), which focuses on learning shape features and appearance features associated with shapes. Specifically, we devise the Shape Feature Propagation (SFP), facilitating direct extraction of shape features from original images with minimal complexity costs during inference. To restitute inaccuracies in infrared body shapes at the feature level, we present the Infrared Shape Restitution (ISR). Furthermore, to acquire appearance features related to shape, we design the Appearance Feature Enhancement (AFE), which accentuates identity-related features while suppressing identity-unrelated features guided by shape features. Extensive experiments are conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed ScRL. Achieving remarkable results, the Rank-1 (mAP) accuracy attains 76.1%, 71.2%, 92.4% (72.6%, 52.9%, 86.7%) on the SYSU-MM01, HITSZ-VCM, RegDB datasets respectively, outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods.
Query-adaptive DETR for Crowded Pedestrian Detection
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:DEtection TRansformer (DETR) and its variants (DETRs) have been successfully applied to crowded pedestrian detection, which achieved promising performance. However, we find that, in different degrees of crowded scenes, the number of DETRs' queries must be adjusted manually, otherwise, the performance would degrade to varying degrees. In this paper, we first analyze the two current query generation methods and summarize four guidelines for designing the adaptive query generation method. Then, we propose Rank-based Adaptive Query Generation (RAQG) to alleviate the problem. Specifically, we design a rank prediction head that can predict the rank of the lowest confidence positive training sample produced by the encoder. Based on the predicted rank, we design an adaptive selection method that can adaptively select coarse detection results produced by the encoder to generate queries. Moreover, to train the rank prediction head better, we propose Soft Gradient L1 Loss. The gradient of Soft Gradient L1 Loss is continuous, which can describe the relationship between the loss value and the updated value of model parameters granularly. Our method is simple and effective, which can be plugged into any DETRs to make it query-adaptive in theory. The experimental results on Crowdhuman dataset and Citypersons dataset show that our method can adaptively generate queries for DETRs and achieve competitive results. Especially, our method achieves state-of-the-art 39.4% MR on Crowdhuman dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge