Jiangming Liu
MACT: Model-Agnostic Cross-Lingual Training for Discourse Representation Structure Parsing
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:Discourse Representation Structure (DRS) is an innovative semantic representation designed to capture the meaning of texts with arbitrary lengths across languages. The semantic representation parsing is essential for achieving natural language understanding through logical forms. Nevertheless, the performance of DRS parsing models remains constrained when trained exclusively on monolingual data. To tackle this issue, we introduce a cross-lingual training strategy. The proposed method is model-agnostic yet highly effective. It leverages cross-lingual training data and fully exploits the alignments between languages encoded in pre-trained language models. The experiments conducted on the standard benchmarks demonstrate that models trained using the cross-lingual training method exhibit significant improvements in DRS clause and graph parsing in English, German, Italian and Dutch. Comparing our final models to previous works, we achieve state-of-the-art results in the standard benchmarks. Furthermore, the detailed analysis provides deep insights into the performance of the parsers, offering inspiration for future research in DRS parsing. We keep updating new results on benchmarks to the appendix.
Uncovering What, Why and How: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Causation Understanding of Video Anomaly
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:Video anomaly understanding (VAU) aims to automatically comprehend unusual occurrences in videos, thereby enabling various applications such as traffic surveillance and industrial manufacturing. While existing VAU benchmarks primarily concentrate on anomaly detection and localization, our focus is on more practicality, prompting us to raise the following crucial questions: "what anomaly occurred?", "why did it happen?", and "how severe is this abnormal event?". In pursuit of these answers, we present a comprehensive benchmark for Causation Understanding of Video Anomaly (CUVA). Specifically, each instance of the proposed benchmark involves three sets of human annotations to indicate the "what", "why" and "how" of an anomaly, including 1) anomaly type, start and end times, and event descriptions, 2) natural language explanations for the cause of an anomaly, and 3) free text reflecting the effect of the abnormality. In addition, we also introduce MMEval, a novel evaluation metric designed to better align with human preferences for CUVA, facilitating the measurement of existing LLMs in comprehending the underlying cause and corresponding effect of video anomalies. Finally, we propose a novel prompt-based method that can serve as a baseline approach for the challenging CUVA. We conduct extensive experiments to show the superiority of our evaluation metric and the prompt-based approach. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/fesvhtr/CUVA.
Semi-Supervised Cross-Silo Advertising with Partial Knowledge Transfer
May 31, 2022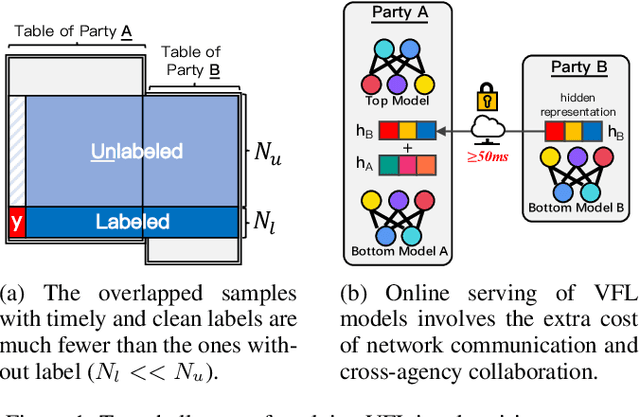
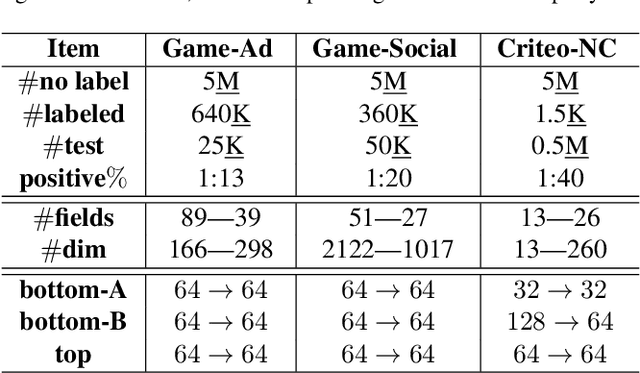
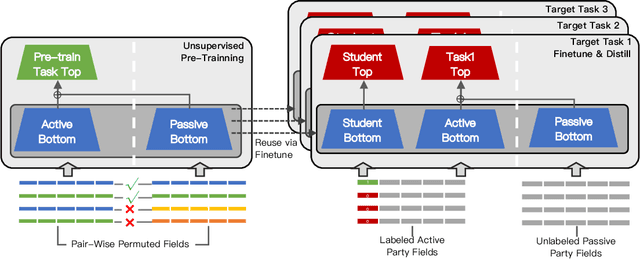
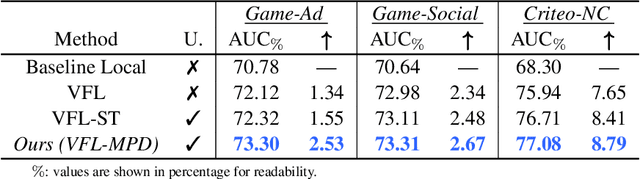
Abstract:As an emerging secure learning paradigm in leveraging cross-agency private data, vertical federated learning (VFL) is expected to improve advertising models by enabling the joint learning of complementary user attributes privately owned by the advertiser and the publisher. However, there are two key challenges in applying it to advertising systems: a) the limited scale of labeled overlapping samples, and b) the high cost of real-time cross-agency serving. In this paper, we propose a semi-supervised split distillation framework VFed-SSD to alleviate the two limitations. We identify that: i) there are massive unlabeled overlapped data available in advertising systems, and ii) we can keep a balance between model performance and inference cost by decomposing the federated model. Specifically, we develop a self-supervised task Matched Pair Detection (MPD) to exploit the vertically partitioned unlabeled data and propose the Split Knowledge Distillation (SplitKD) schema to avoid cross-agency serving. Empirical studies on three industrial datasets exhibit the effectiveness of our methods, with the median AUC over all datasets improved by 0.86% and 2.6% in the local deployment mode and the federated deployment mode respectively. Overall, our framework provides an efficient federation-enhanced solution for real-time display advertising with minimal deploying cost and significant performance lift.
DRTS Parsing with Structure-Aware Encoding and Decoding
May 14, 2020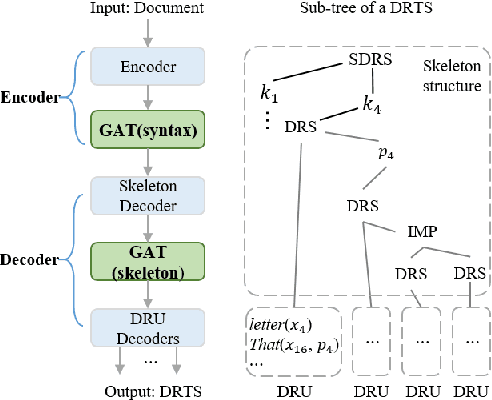
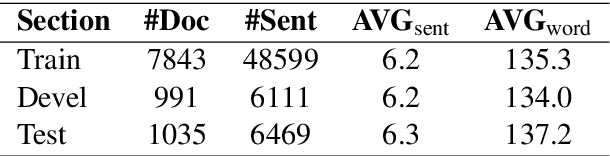
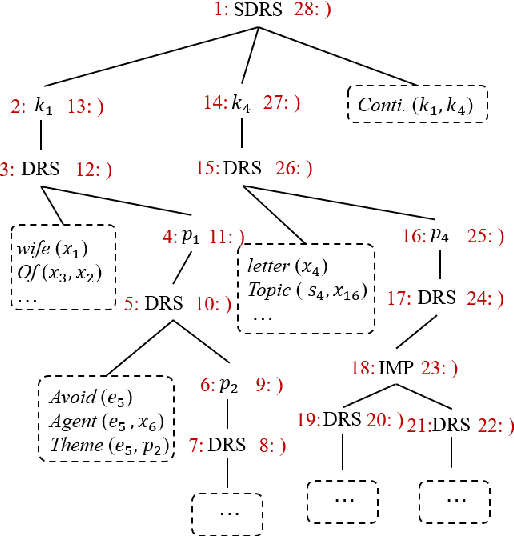
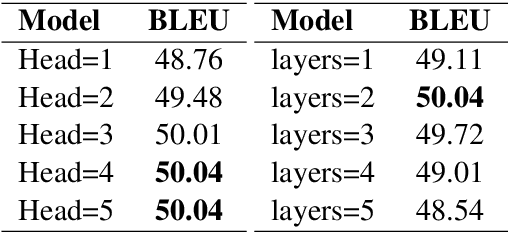
Abstract:Discourse representation tree structure (DRTS) parsing is a novel semantic parsing task which has been concerned most recently. State-of-the-art performance can be achieved by a neural sequence-to-sequence model, treating the tree construction as an incremental sequence generation problem. Structural information such as input syntax and the intermediate skeleton of the partial output has been ignored in the model, which could be potentially useful for the DRTS parsing. In this work, we propose a structural-aware model at both the encoder and decoder phase to integrate the structural information, where graph attention network (GAT) is exploited for effectively modeling. Experimental results on a benchmark dataset show that our proposed model is effective and can obtain the best performance in the literature.
Multi-Step Inference for Reasoning Over Paragraphs
Apr 06, 2020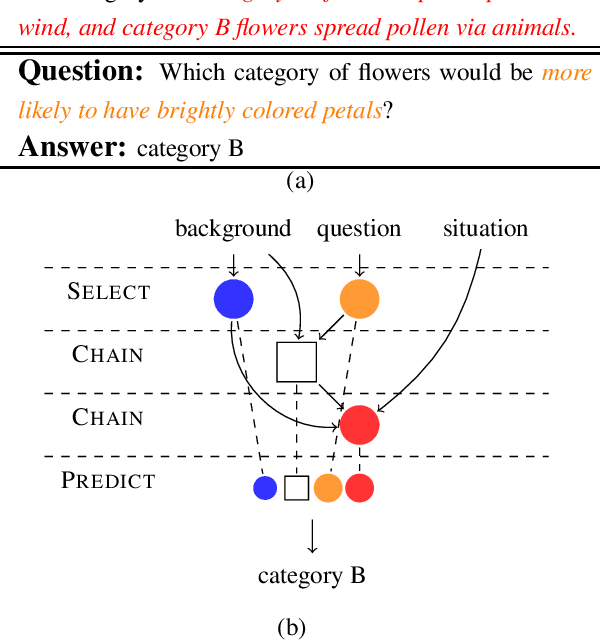
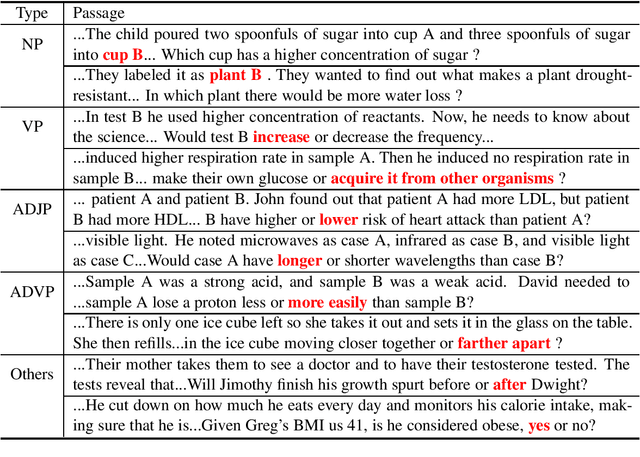
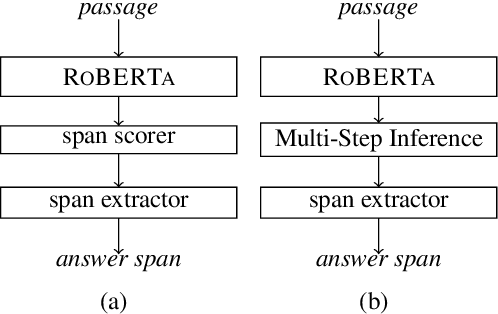
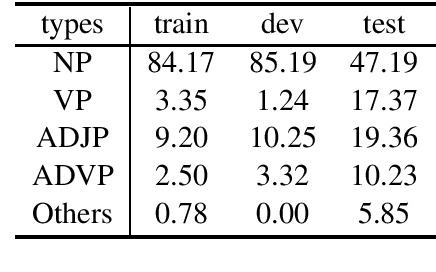
Abstract:Complex reasoning over text requires understanding and chaining together free-form predicates and logical connectives. Prior work has largely tried to do this either symbolically or with black-box transformers. We present a middle ground between these two extremes: a compositional model reminiscent of neural module networks that can perform chained logical reasoning. This model first finds relevant sentences in the context and then chains them together using neural modules. Our model gives significant performance improvements (up to 29\% relative error reduction when combined with a reranker) on ROPES, a recently-introduced complex reasoning dataset
Evaluating NLP Models via Contrast Sets
Apr 06, 2020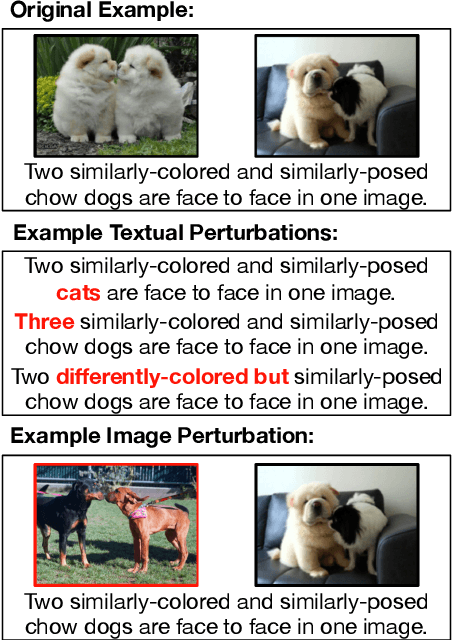
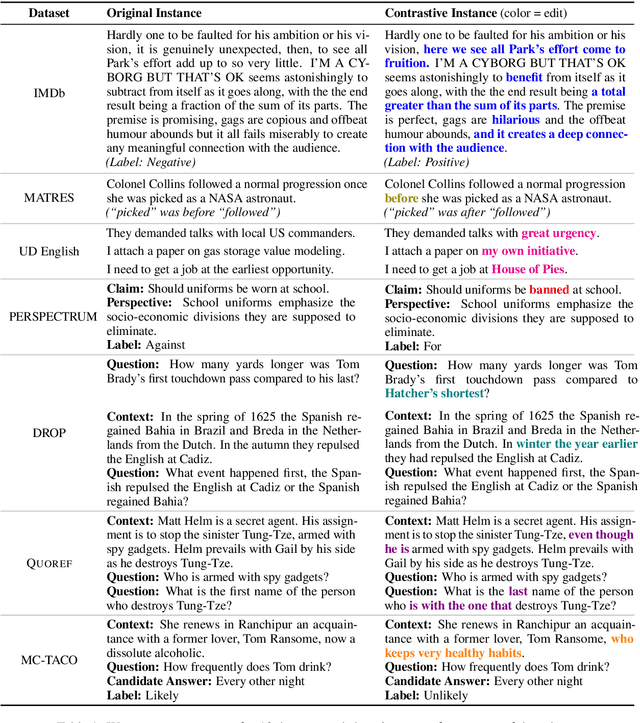
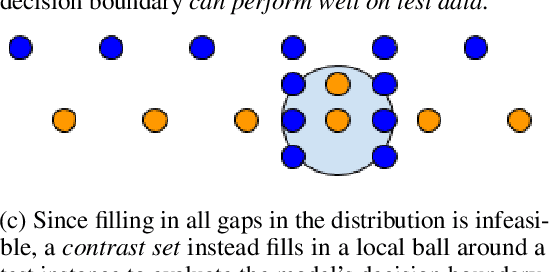
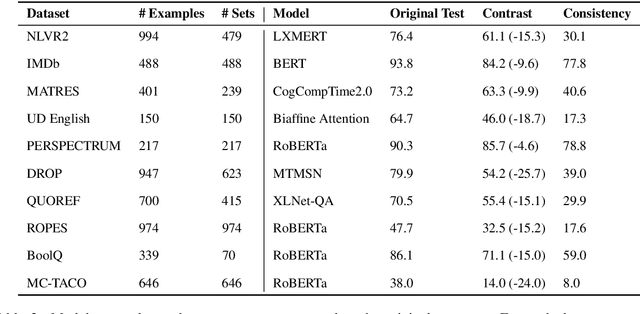
Abstract:Standard test sets for supervised learning evaluate in-distribution generalization. Unfortunately, when a dataset has systematic gaps (e.g., annotation artifacts), these evaluations are misleading: a model can learn simple decision rules that perform well on the test set but do not capture a dataset's intended capabilities. We propose a new annotation paradigm for NLP that helps to close systematic gaps in the test data. In particular, after a dataset is constructed, we recommend that the dataset authors manually perturb the test instances in small but meaningful ways that (typically) change the gold label, creating contrast sets. Contrast sets provide a local view of a model's decision boundary, which can be used to more accurately evaluate a model's true linguistic capabilities. We demonstrate the efficacy of contrast sets by creating them for 10 diverse NLP datasets (e.g., DROP reading comprehension, UD parsing, IMDb sentiment analysis). Although our contrast sets are not explicitly adversarial, model performance is significantly lower on them than on the original test sets---up to 25\% in some cases. We release our contrast sets as new evaluation benchmarks and encourage future dataset construction efforts to follow similar annotation processes.
In-Order Transition-based Constituent Parsing
Jul 17, 2017Abstract:Both bottom-up and top-down strategies have been used for neural transition-based constituent parsing. The parsing strategies differ in terms of the order in which they recognize productions in the derivation tree, where bottom-up strategies and top-down strategies take post-order and pre-order traversal over trees, respectively. Bottom-up parsers benefit from rich features from readily built partial parses, but lack lookahead guidance in the parsing process; top-down parsers benefit from non-local guidance for local decisions, but rely on a strong encoder over the input to predict a constituent hierarchy before its construction.To mitigate both issues, we propose a novel parsing system based on in-order traversal over syntactic trees, designing a set of transition actions to find a compromise between bottom-up constituent information and top-down lookahead information. Based on stack-LSTM, our psycholinguistically motivated constituent parsing system achieves 91.8 F1 on WSJ benchmark. Furthermore, the system achieves 93.6 F1 with supervised reranking and 94.2 F1 with semi-supervised reranking, which are the best results on the WSJ benchmark.
Encoder-Decoder Shift-Reduce Syntactic Parsing
Jun 24, 2017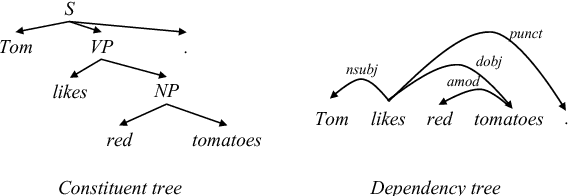
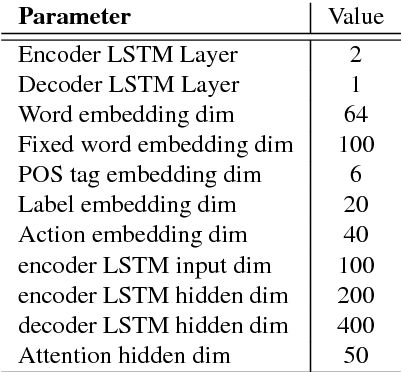
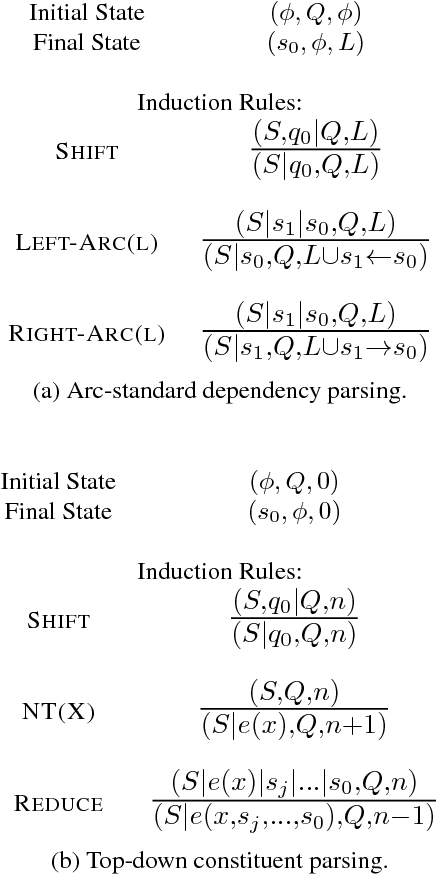
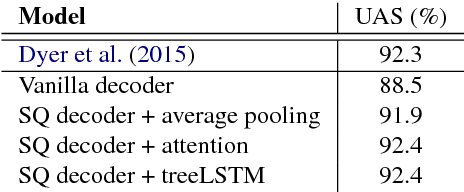
Abstract:Starting from NMT, encoder-decoder neu- ral networks have been used for many NLP problems. Graph-based models and transition-based models borrowing the en- coder components achieve state-of-the-art performance on dependency parsing and constituent parsing, respectively. How- ever, there has not been work empirically studying the encoder-decoder neural net- works for transition-based parsing. We apply a simple encoder-decoder to this end, achieving comparable results to the parser of Dyer et al. (2015) on standard de- pendency parsing, and outperforming the parser of Vinyals et al. (2015) on con- stituent parsing.
Shift-Reduce Constituent Parsing with Neural Lookahead Features
Dec 02, 2016Abstract:Transition-based models can be fast and accurate for constituent parsing. Compared with chart-based models, they leverage richer features by extracting history information from a parser stack, which spans over non-local constituents. On the other hand, during incremental parsing, constituent information on the right hand side of the current word is not utilized, which is a relative weakness of shift-reduce parsing. To address this limitation, we leverage a fast neural model to extract lookahead features. In particular, we build a bidirectional LSTM model, which leverages the full sentence information to predict the hierarchy of constituents that each word starts and ends. The results are then passed to a strong transition-based constituent parser as lookahead features. The resulting parser gives 1.3% absolute improvement in WSJ and 2.3% in CTB compared to the baseline, given the highest reported accuracies for fully-supervised parsing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge