Haoming Xu
Illusions of Confidence? Diagnosing LLM Truthfulness via Neighborhood Consistency
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world settings, correctness alone is insufficient. Reliable deployment requires maintaining truthful beliefs under contextual perturbations. Existing evaluations largely rely on point-wise confidence like Self-Consistency, which can mask brittle belief. We show that even facts answered with perfect self-consistency can rapidly collapse under mild contextual interference. To address this gap, we propose Neighbor-Consistency Belief (NCB), a structural measure of belief robustness that evaluates response coherence across a conceptual neighborhood. To validate the efficiency of NCB, we introduce a new cognitive stress-testing protocol that probes outputs stability under contextual interference. Experiments across multiple LLMs show that the performance of high-NCB data is relatively more resistant to interference. Finally, we present Structure-Aware Training (SAT), which optimizes context-invariant belief structure and reduces long-tail knowledge brittleness by approximately 30%. Code will be available at https://github.com/zjunlp/belief.
LightMem: Lightweight and Efficient Memory-Augmented Generation
Oct 21, 2025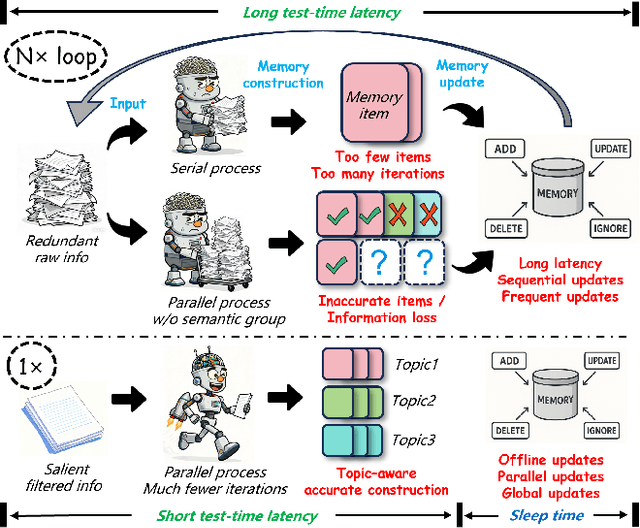
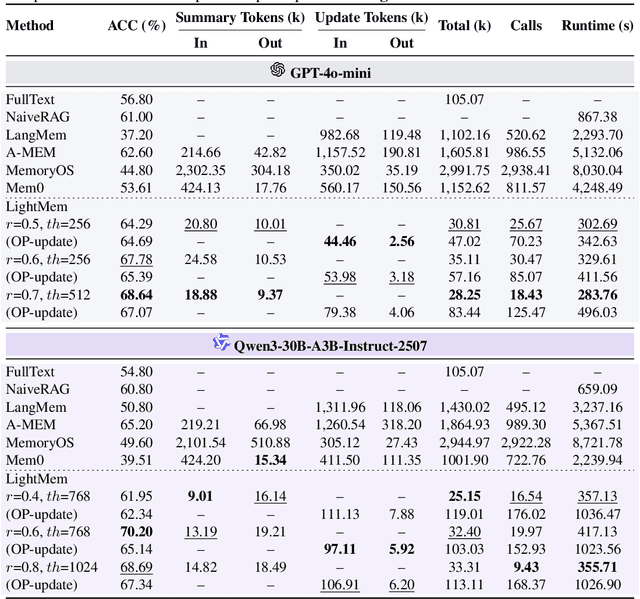
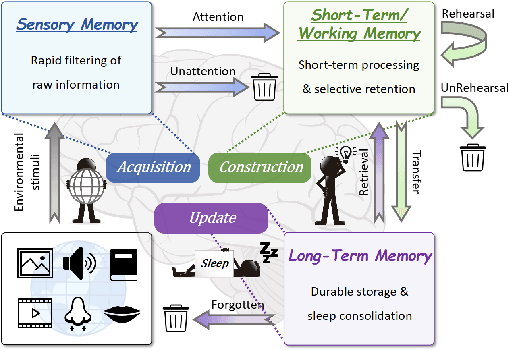
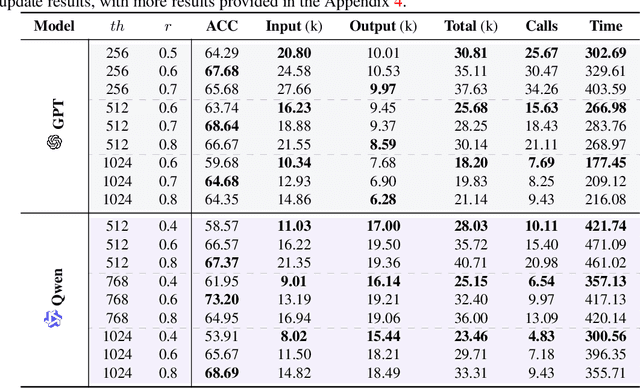
Abstract:Despite their remarkable capabilities, Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle to effectively leverage historical interaction information in dynamic and complex environments. Memory systems enable LLMs to move beyond stateless interactions by introducing persistent information storage, retrieval, and utilization mechanisms. However, existing memory systems often introduce substantial time and computational overhead. To this end, we introduce a new memory system called LightMem, which strikes a balance between the performance and efficiency of memory systems. Inspired by the Atkinson-Shiffrin model of human memory, LightMem organizes memory into three complementary stages. First, cognition-inspired sensory memory rapidly filters irrelevant information through lightweight compression and groups information according to their topics. Next, topic-aware short-term memory consolidates these topic-based groups, organizing and summarizing content for more structured access. Finally, long-term memory with sleep-time update employs an offline procedure that decouples consolidation from online inference. Experiments on LongMemEval with GPT and Qwen backbones show that LightMem outperforms strong baselines in accuracy (up to 10.9% gains) while reducing token usage by up to 117x, API calls by up to 159x, and runtime by over 12x. The code is available at https://github.com/zjunlp/LightMem.
EasyEdit2: An Easy-to-use Steering Framework for Editing Large Language Models
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce EasyEdit2, a framework designed to enable plug-and-play adjustability for controlling Large Language Model (LLM) behaviors. EasyEdit2 supports a wide range of test-time interventions, including safety, sentiment, personality, reasoning patterns, factuality, and language features. Unlike its predecessor, EasyEdit2 features a new architecture specifically designed for seamless model steering. It comprises key modules such as the steering vector generator and the steering vector applier, which enable automatic generation and application of steering vectors to influence the model's behavior without modifying its parameters. One of the main advantages of EasyEdit2 is its ease of use-users do not need extensive technical knowledge. With just a single example, they can effectively guide and adjust the model's responses, making precise control both accessible and efficient. Empirically, we report model steering performance across different LLMs, demonstrating the effectiveness of these techniques. We have released the source code on GitHub at https://github.com/zjunlp/EasyEdit along with a demonstration notebook. In addition, we provide a demo video at https://zjunlp.github.io/project/EasyEdit2/video for a quick introduction.
ZJUKLAB at SemEval-2025 Task 4: Unlearning via Model Merging
Mar 27, 2025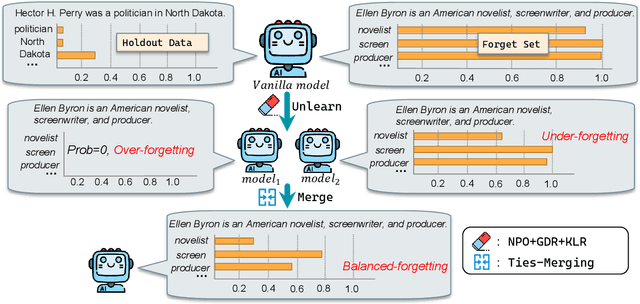
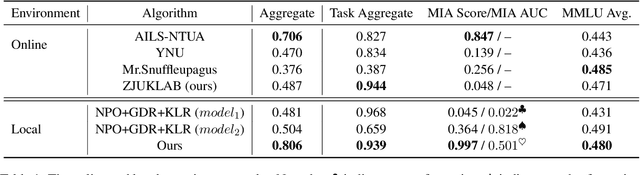
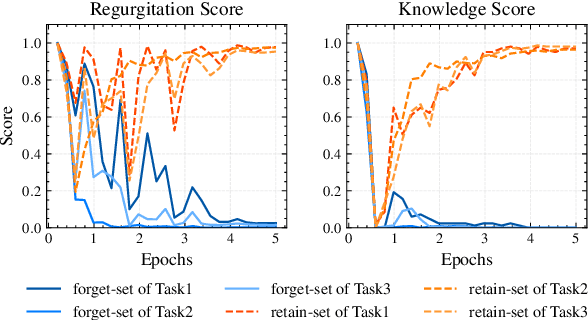
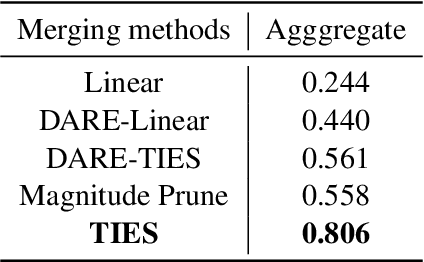
Abstract:This paper presents the ZJUKLAB team's submission for SemEval-2025 Task 4: Unlearning Sensitive Content from Large Language Models. This task aims to selectively erase sensitive knowledge from large language models, avoiding both over-forgetting and under-forgetting issues. We propose an unlearning system that leverages Model Merging (specifically TIES-Merging), combining two specialized models into a more balanced unlearned model. Our system achieves competitive results, ranking second among 26 teams, with an online score of 0.944 for Task Aggregate and 0.487 for overall Aggregate. In this paper, we also conduct local experiments and perform a comprehensive analysis of the unlearning process, examining performance trajectories, loss dynamics, and weight perspectives, along with several supplementary experiments, to understand the effectiveness of our method. Furthermore, we analyze the shortcomings of our method and evaluation metrics, emphasizing that MIA scores and ROUGE-based metrics alone are insufficient to fully evaluate successful unlearning. Finally, we emphasize the need for more comprehensive evaluation methodologies and rethinking of unlearning objectives in future research. Code is available at https://github.com/zjunlp/unlearn/tree/main/semeval25.
MLLM can see? Dynamic Correction Decoding for Hallucination Mitigation
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) frequently exhibit hallucination phenomena, but the underlying reasons remain poorly understood. In this paper, we present an empirical analysis and find that, although MLLMs incorrectly generate the objects in the final output, they are actually able to recognize visual objects in the preceding layers. We speculate that this may be due to the strong knowledge priors of the language model suppressing the visual information, leading to hallucinations. Motivated by this, we propose a novel dynamic correction decoding method for MLLMs (DeCo), which adaptively selects the appropriate preceding layers and proportionally integrates knowledge into the final layer to adjust the output logits. Note that DeCo is model agnostic and can be seamlessly incorporated with various classic decoding strategies and applied to different MLLMs. We evaluate DeCo on widely-used benchmarks, demonstrating that it can reduce hallucination rates by a large margin compared to baselines, highlighting its potential to mitigate hallucinations. Code is available at https://github.com/zjunlp/DeCo.
Knowledge-tuning Large Language Models with Structured Medical Knowledge Bases for Reliable Response Generation in Chinese
Sep 08, 2023Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable success in diverse natural language processing (NLP) tasks in general domains. However, LLMs sometimes generate responses with the hallucination about medical facts due to limited domain knowledge. Such shortcomings pose potential risks in the utilization of LLMs within medical contexts. To address this challenge, we propose knowledge-tuning, which leverages structured medical knowledge bases for the LLMs to grasp domain knowledge efficiently and facilitate reliable response generation. We also release cMedKnowQA, a Chinese medical knowledge question-answering dataset constructed from medical knowledge bases to assess the medical knowledge proficiency of LLMs. Experimental results show that the LLMs which are knowledge-tuned with cMedKnowQA, can exhibit higher levels of accuracy in response generation compared with vanilla instruction-tuning and offer a new reliable way for the domain adaptation of LLMs.
Dense Regression Network for Video Grounding
Apr 07, 2020



Abstract:We address the problem of video grounding from natural language queries. The key challenge in this task is that one training video might only contain a few annotated starting/ending frames that can be used as positive examples for model training. Most conventional approaches directly train a binary classifier using such imbalance data, thus achieving inferior results. The key idea of this paper is to use the distances between the frame within the ground truth and the starting (ending) frame as dense supervisions to improve the video grounding accuracy. Specifically, we design a novel dense regression network (DRN) to regress the distances from each frame to the starting (ending) frame of the video segment described by the query. We also propose a simple but effective IoU regression head module to explicitly consider the localization quality of the grounding results (i.e., the IoU between the predicted location and the ground truth). Experimental results show that our approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-arts on three datasets (i.e., Charades-STA, ActivityNet-Captions, and TACoS).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge