Giovanni Pezzulo
Sensory robustness through top-down feedback and neural stochasticity in recurrent vision models
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Biological systems leverage top-down feedback for visual processing, yet most artificial vision models succeed in image classification using purely feedforward or recurrent architectures, calling into question the functional significance of descending cortical pathways. Here, we trained convolutional recurrent neural networks (ConvRNN) on image classification in the presence or absence of top-down feedback projections to elucidate the specific computational contributions of those feedback pathways. We found that ConvRNNs with top-down feedback exhibited remarkable speed-accuracy trade-off and robustness to noise perturbations and adversarial attacks, but only when they were trained with stochastic neural variability, simulated by randomly silencing single units via dropout. By performing detailed analyses to identify the reasons for such benefits, we observed that feedback information substantially shaped the representational geometry of the post-integration layer, combining the bottom-up and top-down streams, and this effect was amplified by dropout. Moreover, feedback signals coupled with dropout optimally constrained network activity onto a low-dimensional manifold and encoded object information more efficiently in out-of-distribution regimes, with top-down information stabilizing the representational dynamics at the population level. Together, these findings uncover a dual mechanism for resilient sensory coding. On the one hand, neural stochasticity prevents unit-level co-adaptation albeit at the cost of more chaotic dynamics. On the other hand, top-down feedback harnesses high-level information to stabilize network activity on compact low-dimensional manifolds.
Integrating cognitive map learning and active inference for planning in ambiguous environments
Aug 16, 2023



Abstract:Living organisms need to acquire both cognitive maps for learning the structure of the world and planning mechanisms able to deal with the challenges of navigating ambiguous environments. Although significant progress has been made in each of these areas independently, the best way to integrate them is an open research question. In this paper, we propose the integration of a statistical model of cognitive map formation within an active inference agent that supports planning under uncertainty. Specifically, we examine the clone-structured cognitive graph (CSCG) model of cognitive map formation and compare a naive clone graph agent with an active inference-driven clone graph agent, in three spatial navigation scenarios. Our findings demonstrate that while both agents are effective in simple scenarios, the active inference agent is more effective when planning in challenging scenarios, in which sensory observations provide ambiguous information about location.
Integrating large language models and active inference to understand eye movements in reading and dyslexia
Aug 09, 2023Abstract:We present a novel computational model employing hierarchical active inference to simulate reading and eye movements. The model characterizes linguistic processing as inference over a hierarchical generative model, facilitating predictions and inferences at various levels of granularity, from syllables to sentences. Our approach combines the strengths of large language models for realistic textual predictions and active inference for guiding eye movements to informative textual information, enabling the testing of predictions. The model exhibits proficiency in reading both known and unknown words and sentences, adhering to the distinction between lexical and nonlexical routes in dual-route theories of reading. Notably, our model permits the exploration of maladaptive inference effects on eye movements during reading, such as in dyslexia. To simulate this condition, we attenuate the contribution of priors during the reading process, leading to incorrect inferences and a more fragmented reading style, characterized by a greater number of shorter saccades. This alignment with empirical findings regarding eye movements in dyslexic individuals highlights the model's potential to aid in understanding the cognitive processes underlying reading and eye movements, as well as how reading deficits associated with dyslexia may emerge from maladaptive predictive processing. In summary, our model represents a significant advancement in comprehending the intricate cognitive processes involved in reading and eye movements, with potential implications for understanding and addressing dyslexia through the simulation of maladaptive inference. It may offer valuable insights into this condition and contribute to the development of more effective interventions for treatment.
World Models and Predictive Coding for Cognitive and Developmental Robotics: Frontiers and Challenges
Jan 14, 2023Abstract:Creating autonomous robots that can actively explore the environment, acquire knowledge and learn skills continuously is the ultimate achievement envisioned in cognitive and developmental robotics. Their learning processes should be based on interactions with their physical and social world in the manner of human learning and cognitive development. Based on this context, in this paper, we focus on the two concepts of world models and predictive coding. Recently, world models have attracted renewed attention as a topic of considerable interest in artificial intelligence. Cognitive systems learn world models to better predict future sensory observations and optimize their policies, i.e., controllers. Alternatively, in neuroscience, predictive coding proposes that the brain continuously predicts its inputs and adapts to model its own dynamics and control behavior in its environment. Both ideas may be considered as underpinning the cognitive development of robots and humans capable of continual or lifelong learning. Although many studies have been conducted on predictive coding in cognitive robotics and neurorobotics, the relationship between world model-based approaches in AI and predictive coding in robotics has rarely been discussed. Therefore, in this paper, we clarify the definitions, relationships, and status of current research on these topics, as well as missing pieces of world models and predictive coding in conjunction with crucially related concepts such as the free-energy principle and active inference in the context of cognitive and developmental robotics. Furthermore, we outline the frontiers and challenges involved in world models and predictive coding toward the further integration of AI and robotics, as well as the creation of robots with real cognitive and developmental capabilities in the future.
Interactive inference: a multi-agent model of cooperative joint actions
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:We advance a novel computational model of multi-agent, cooperative joint actions that is grounded in the cognitive framework of active inference. The model assumes that to solve a joint task, such as pressing together a red or blue button, two (or more) agents engage in a process of interactive inference. Each agent maintains probabilistic beliefs about the goal of the joint task (e.g., should we press the red or blue button?) and updates them by observing the other agent's movements, while in turn selecting movements that make his own intentions legible and easy to infer by the other agent (i.e., sensorimotor communication). Over time, the interactive inference aligns both the beliefs and the behavioral strategies of the agents, hence ensuring the success of the joint action. We exemplify the functioning of the model in two simulations. The first simulation illustrates a ''leaderless'' joint action. It shows that when two agents lack a strong preference about their joint task goal, they jointly infer it by observing each other's movements. In turn, this helps the interactive alignment of their beliefs and behavioral strategies. The second simulation illustrates a "leader-follower" joint action. It shows that when one agent ("leader") knows the true joint goal, it uses sensorimotor communication to help the other agent ("follower") infer it, even if doing this requires selecting a more costly individual plan. These simulations illustrate that interactive inference supports successful multi-agent joint actions and reproduces key cognitive and behavioral dynamics of "leaderless" and "leader-follower" joint actions observed in human-human experiments. In sum, interactive inference provides a cognitively inspired, formal framework to realize cooperative joint actions and consensus in multi-agent systems.
Active Tree Search in Large POMDPs
Mar 25, 2021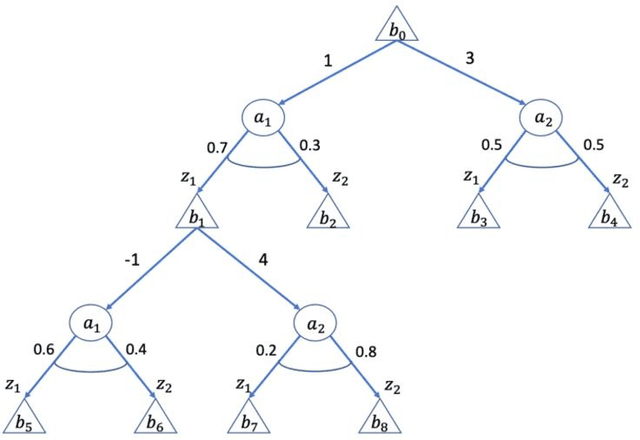
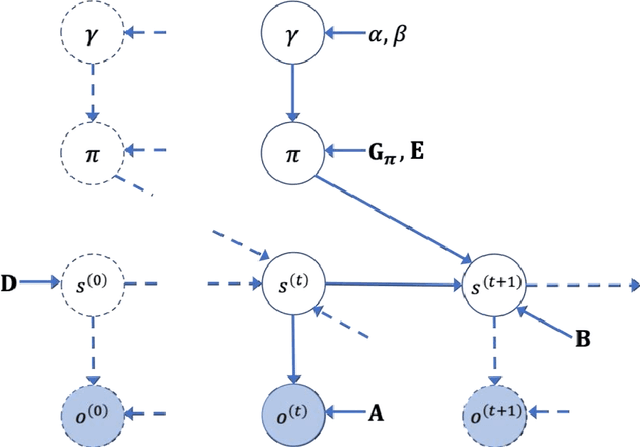
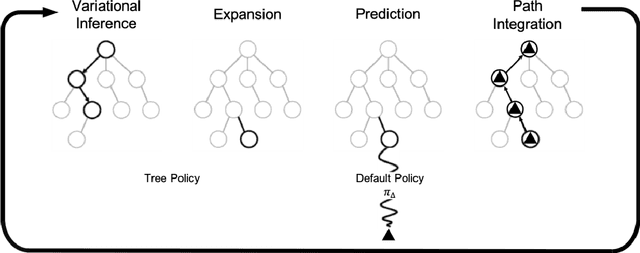
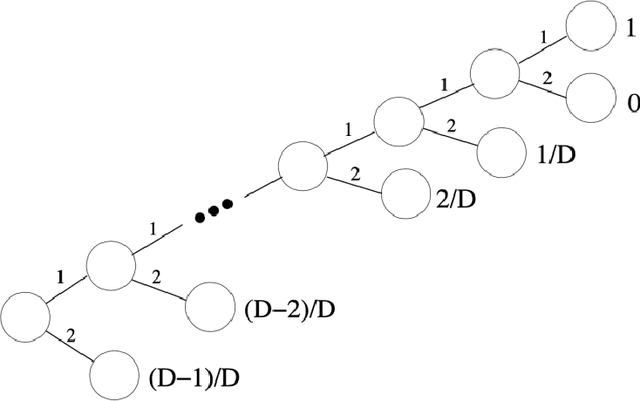
Abstract:Model-based planning and prospection are widely studied in both cognitive neuroscience and artificial intelligence (AI), but from different perspectives - and with different desiderata in mind (biological realism versus scalability) that are difficult to reconcile. Here, we introduce a novel method to plan in large POMDPs - Active Tree Search - that combines the normative character and biological realism of a leading planning theory in neuroscience (Active Inference) and the scalability of Monte-Carlo methods in AI. This unification is beneficial for both approaches. On the one hand, using Monte-Carlo planning permits scaling up the biologically grounded approach of Active Inference to large-scale problems. On the other hand, the theory of Active Inference provides a principled solution to the balance of exploration and exploitation, which is often addressed heuristically in Monte-Carlo methods. Our simulations show that Active Tree Search successfully navigates binary trees that are challenging for sampling-based methods, problems that require adaptive exploration, and the large POMDP problem Rocksample. Furthermore, we illustrate how Active Tree Search can be used to simulate neurophysiological responses (e.g., in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex) of humans and other animals that contain large planning problems. These simulations show that Active Tree Search is a principled realisation of neuroscientific and AI theories of planning, which offers both biological realism and scalability.
Predictive Processing in Cognitive Robotics: a Review
Jan 22, 2021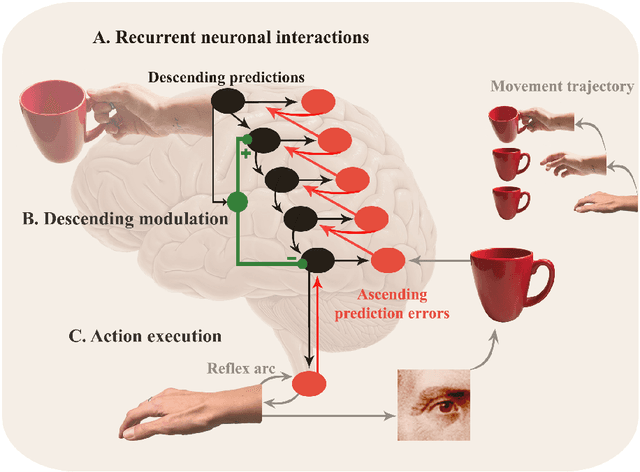
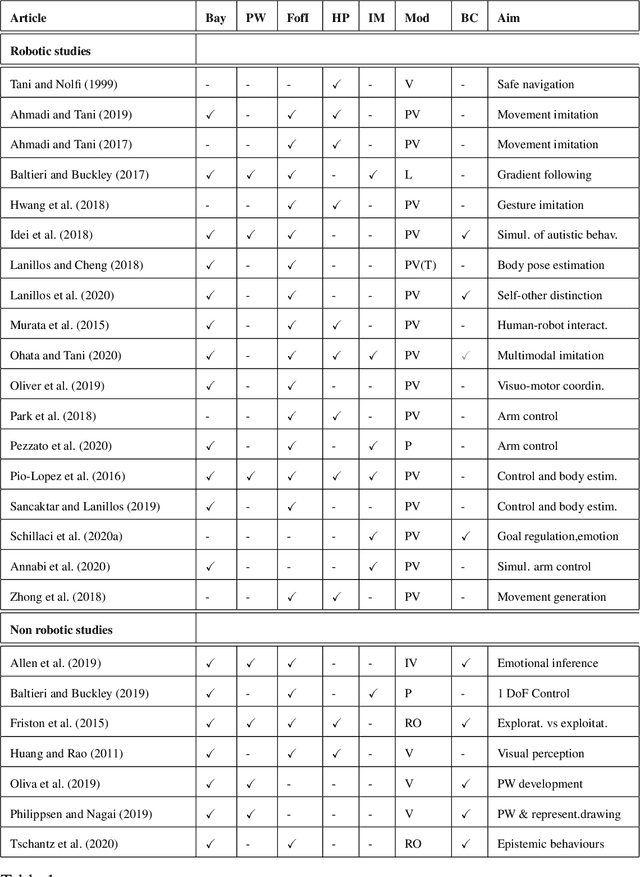
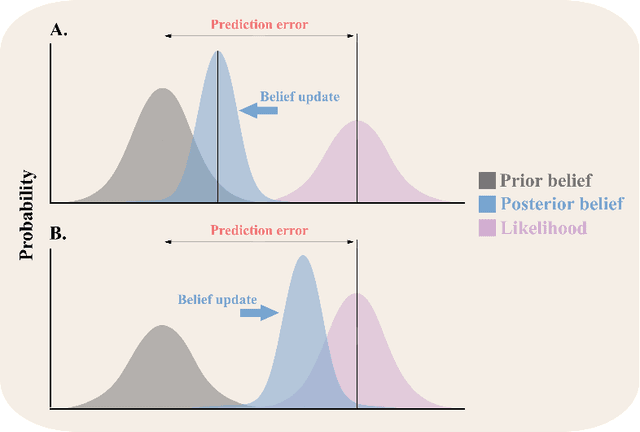
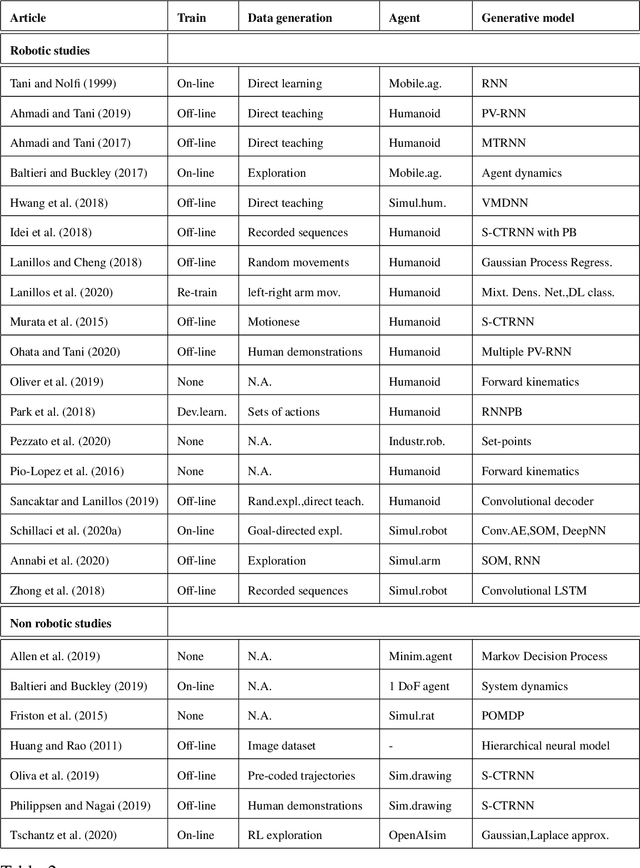
Abstract:Predictive processing has become an influential framework in cognitive sciences. This framework turns the traditional view of perception upside down, claiming that the main flow of information processing is realized in a top-down hierarchical manner. Furthermore, it aims at unifying perception, cognition, and action as a single inferential process. However, in the related literature, the predictive processing framework and its associated schemes such as predictive coding, active inference, perceptual inference, free-energy principle, tend to be used interchangeably. In the field of cognitive robotics there is no clear-cut distinction on which schemes have been implemented and under which assumptions. In this paper, working definitions are set with the main aim of analyzing the state of the art in cognitive robotics research working under the predictive processing framework as well as some related non-robotic models. The analysis suggests that, first, both research in cognitive robotics implementations and non-robotic models needs to be extended to the study of how multiple exteroceptive modalities can be integrated into prediction error minimization schemes. Second, a relevant distinction found here is that cognitive robotics implementations tend to emphasize the learning of a generative model, while in non-robotics models it is almost absent. Third, despite the relevance for active inference, few cognitive robotics implementations examine the issues around control and whether it should result from the substitution of inverse models with proprioceptive predictions. Finally, limited attention has been placed on precision weighting and the tracking of prediction error dynamics. These mechanisms should help to explore more complex behaviors and tasks in cognitive robotics research under the predictive processing framework.
Haptic communication optimises joint decisions and affords implicit confidence sharing
Dec 29, 2019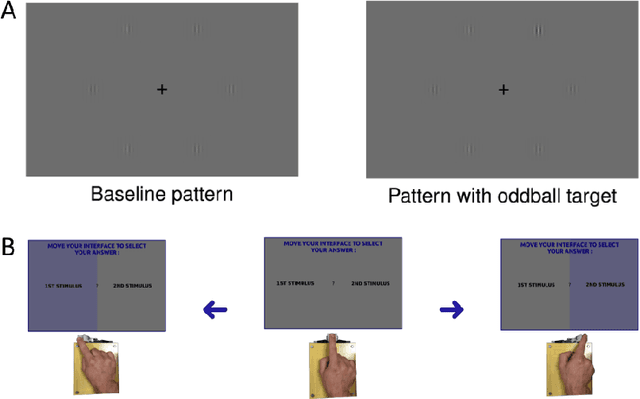
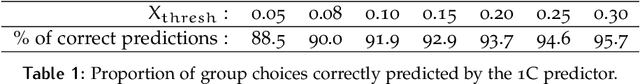
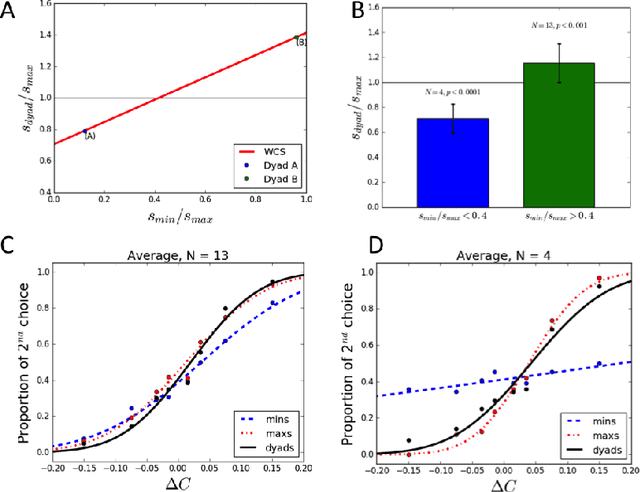
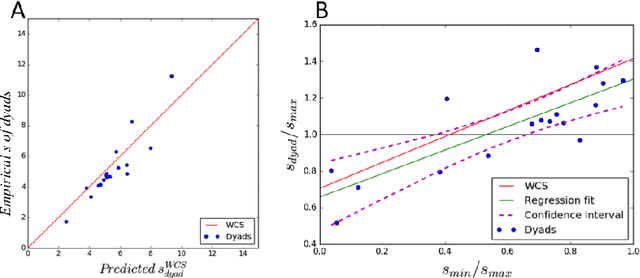
Abstract:Group decisions can outperform the choices of the best individual group members. Previous research suggested that optimal group decisions require individuals to communicate explicitly (e.g., verbally) their confidence levels. Our study addresses the untested hypothesis that implicit communication using a sensorimotor channel -- haptic coupling -- may afford optimal group decisions, too. We report that haptically coupled dyads solve a perceptual discrimination task more accurately than their best individual members; and five times faster than dyads using explicit communication. Furthermore, our computational analyses indicate that the haptic channel affords implicit confidence sharing. We found that dyads take leadership over the choice and communicate their confidence in it by modulating both the timing and the force of their movements. Our findings may pave the way to negotiation technologies using fast sensorimotor communication to solve problems in groups.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge