Haptic communication optimises joint decisions and affords implicit confidence sharing
Paper and Code
Dec 29, 2019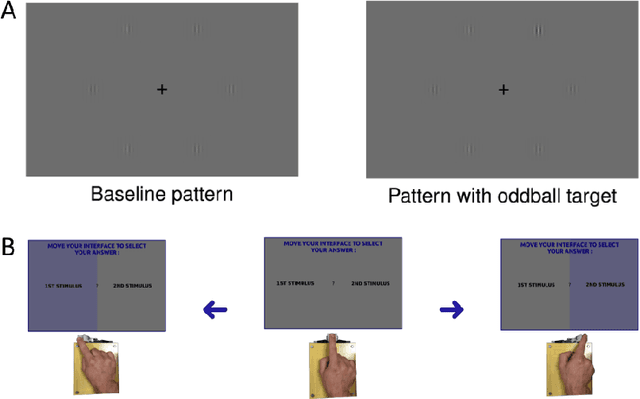
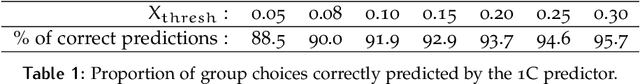
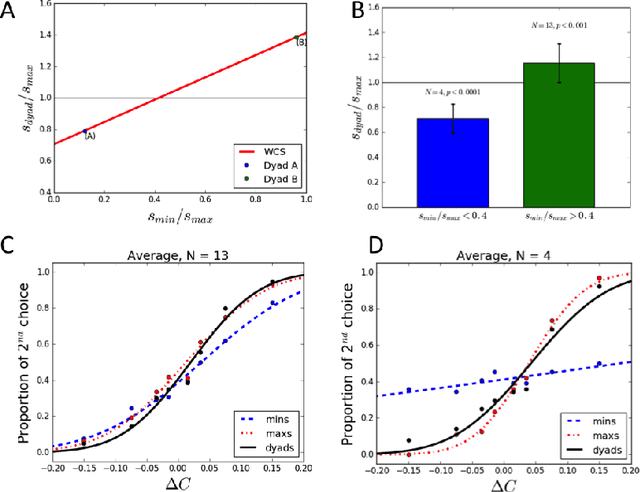
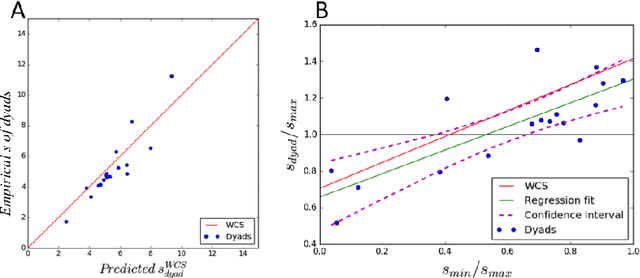
Group decisions can outperform the choices of the best individual group members. Previous research suggested that optimal group decisions require individuals to communicate explicitly (e.g., verbally) their confidence levels. Our study addresses the untested hypothesis that implicit communication using a sensorimotor channel -- haptic coupling -- may afford optimal group decisions, too. We report that haptically coupled dyads solve a perceptual discrimination task more accurately than their best individual members; and five times faster than dyads using explicit communication. Furthermore, our computational analyses indicate that the haptic channel affords implicit confidence sharing. We found that dyads take leadership over the choice and communicate their confidence in it by modulating both the timing and the force of their movements. Our findings may pave the way to negotiation technologies using fast sensorimotor communication to solve problems in groups.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge