Feixiang Zhou
Leveraging Persistence Image to Enhance Robustness and Performance in Curvilinear Structure Segmentation
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Segmenting curvilinear structures in medical images is essential for analyzing morphological patterns in clinical applications. Integrating topological properties, such as connectivity, improves segmentation accuracy and consistency. However, extracting and embedding such properties - especially from Persistence Diagrams (PD) - is challenging due to their non-differentiability and computational cost. Existing approaches mostly encode topology through handcrafted loss functions, which generalize poorly across tasks. In this paper, we propose PIs-Regressor, a simple yet effective module that learns persistence image (PI) - finite, differentiable representations of topological features - directly from data. Together with Topology SegNet, which fuses these features in both downsampling and upsampling stages, our framework integrates topology into the network architecture itself rather than auxiliary losses. Unlike existing methods that depend heavily on handcrafted loss functions, our approach directly incorporates topological information into the network structure, leading to more robust segmentation. Our design is flexible and can be seamlessly combined with other topology-based methods to further enhance segmentation performance. Experimental results show that integrating topological features enhances model robustness, effectively handling challenges like overexposure and blurring in medical imaging. Our approach on three curvilinear benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in both pixel-level accuracy and topological fidelity.
GROK: From Quantitative Biomarkers to Qualitative Diagnosis via a Grounded MLLM with Knowledge-Guided Instruction
Oct 05, 2025
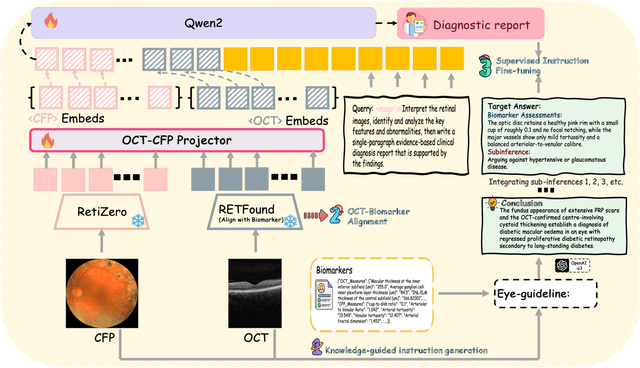

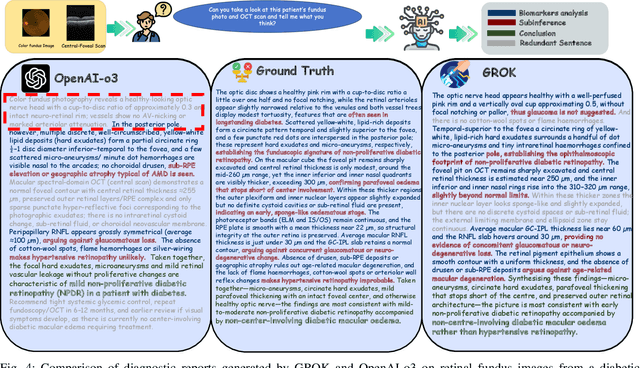
Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) hold promise for integrating diverse data modalities, but current medical adaptations such as LLaVA-Med often fail to fully exploit the synergy between color fundus photography (CFP) and optical coherence tomography (OCT), and offer limited interpretability of quantitative biomarkers. We introduce GROK, a grounded multimodal large language model that jointly processes CFP, OCT, and text to deliver clinician-grade diagnoses of ocular and systemic disease. GROK comprises three core modules: Knowledge-Guided Instruction Generation, CLIP-Style OCT-Biomarker Alignment, and Supervised Instruction Fine-Tuning, which together establish a quantitative-to-qualitative diagnostic chain of thought, mirroring real clinical reasoning when producing detailed lesion annotations. To evaluate our approach, we introduce the Grounded Ophthalmic Understanding benchmark, which covers six disease categories and three tasks: macro-level diagnostic classification, report generation quality, and fine-grained clinical assessment of the generated chain of thought. Experiments show that, with only LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) fine-tuning of a 7B-parameter Qwen2 backbone, GROK outperforms comparable 7B and 32B baselines on both report quality and fine-grained clinical metrics, and even exceeds OpenAI o3. Code and data are publicly available in the GROK repository.
Aligning Neuronal Coding of Dynamic Visual Scenes with Foundation Vision Models
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:Our brains represent the ever-changing environment with neurons in a highly dynamic fashion. The temporal features of visual pixels in dynamic natural scenes are entrapped in the neuronal responses of the retina. It is crucial to establish the intrinsic temporal relationship between visual pixels and neuronal responses. Recent foundation vision models have paved an advanced way of understanding image pixels. Yet, neuronal coding in the brain largely lacks a deep understanding of its alignment with pixels. Most previous studies employ static images or artificial videos derived from static images for emulating more real and complicated stimuli. Despite these simple scenarios effectively help to separate key factors influencing visual coding, complex temporal relationships receive no consideration. To decompose the temporal features of visual coding in natural scenes, here we propose Vi-ST, a spatiotemporal convolutional neural network fed with a self-supervised Vision Transformer (ViT) prior, aimed at unraveling the temporal-based encoding patterns of retinal neuronal populations. The model demonstrates robust predictive performance in generalization tests. Furthermore, through detailed ablation experiments, we demonstrate the significance of each temporal module. Furthermore, we introduce a visual coding evaluation metric designed to integrate temporal considerations and compare the impact of different numbers of neuronal populations on complementary coding. In conclusion, our proposed Vi-ST demonstrates a novel modeling framework for neuronal coding of dynamic visual scenes in the brain, effectively aligning our brain representation of video with neuronal activity. The code is available at https://github.com/wurining/Vi-ST.
Towards Adaptive Pseudo-label Learning for Semi-Supervised Temporal Action Localization
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:Alleviating noisy pseudo labels remains a key challenge in Semi-Supervised Temporal Action Localization (SS-TAL). Existing methods often filter pseudo labels based on strict conditions, but they typically assess classification and localization quality separately, leading to suboptimal pseudo-label ranking and selection. In particular, there might be inaccurate pseudo labels within selected positives, alongside reliable counterparts erroneously assigned to negatives. To tackle these problems, we propose a novel Adaptive Pseudo-label Learning (APL) framework to facilitate better pseudo-label selection. Specifically, to improve the ranking quality, Adaptive Label Quality Assessment (ALQA) is proposed to jointly learn classification confidence and localization reliability, followed by dynamically selecting pseudo labels based on the joint score. Additionally, we propose an Instance-level Consistency Discriminator (ICD) for eliminating ambiguous positives and mining potential positives simultaneously based on inter-instance intrinsic consistency, thereby leading to a more precise selection. We further introduce a general unsupervised Action-aware Contrastive Pre-training (ACP) to enhance the discrimination both within actions and between actions and backgrounds, which benefits SS-TAL. Extensive experiments on THUMOS14 and ActivityNet v1.3 demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance under various semi-supervised settings.
SMC-NCA: Semantic-guided Multi-level Contrast for Semi-supervised Action Segmentation
Dec 19, 2023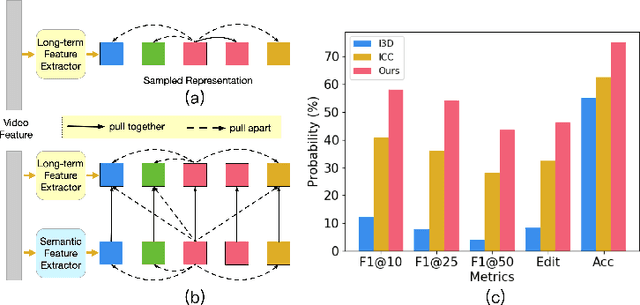

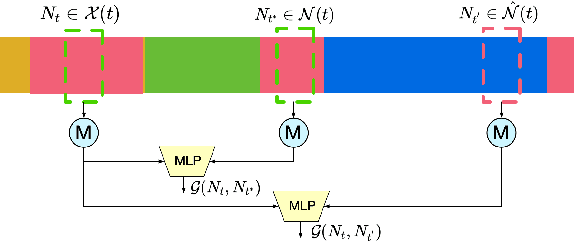
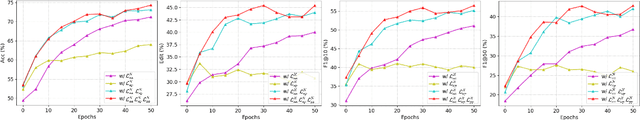
Abstract:Semi-supervised action segmentation aims to perform frame-wise classification in long untrimmed videos, where only a fraction of videos in the training set have labels. Recent studies have shown the potential of contrastive learning in unsupervised representation learning using unlabelled data. However, learning the representation of each frame by unsupervised contrastive learning for action segmentation remains an open and challenging problem. In this paper, we propose a novel Semantic-guided Multi-level Contrast scheme with a Neighbourhood-Consistency-Aware unit (SMC-NCA) to extract strong frame-wise representations for semi-supervised action segmentation. Specifically, for representation learning, SMC is firstly used to explore intra- and inter-information variations in a unified and contrastive way, based on dynamic clustering process of the original input, encoded semantic and temporal features. Then, the NCA module, which is responsible for enforcing spatial consistency between neighbourhoods centered at different frames to alleviate over-segmentation issues, works alongside SMC for semi-supervised learning. Our SMC outperforms the other state-of-the-art methods on three benchmarks, offering improvements of up to 17.8% and 12.6% in terms of edit distance and accuracy, respectively. Additionally, the NCA unit results in significant better segmentation performance against the others in the presence of only 5% labelled videos. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method on our Parkinson's Disease Mouse Behaviour (PDMB) dataset. The code and datasets will be made publicly available.
DGNet: Distribution Guided Efficient Learning for Oil Spill Image Segmentation
Dec 19, 2022

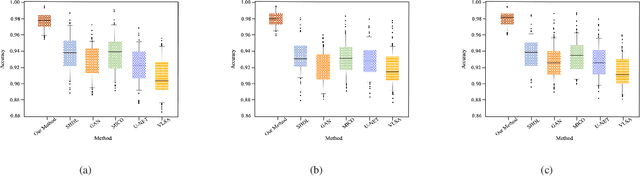

Abstract:Successful implementation of oil spill segmentation in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images is vital for marine environmental protection. In this paper, we develop an effective segmentation framework named DGNet, which performs oil spill segmentation by incorporating the intrinsic distribution of backscatter values in SAR images. Specifically, our proposed segmentation network is constructed with two deep neural modules running in an interactive manner, where one is the inference module to achieve latent feature variable inference from SAR images, and the other is the generative module to produce oil spill segmentation maps by drawing the latent feature variables as inputs. Thus, to yield accurate segmentation, we take into account the intrinsic distribution of backscatter values in SAR images and embed it in our segmentation model. The intrinsic distribution originates from SAR imagery, describing the physical characteristics of oil spills. In the training process, the formulated intrinsic distribution guides efficient learning of optimal latent feature variable inference for oil spill segmentation. The efficient learning enables the training of our proposed DGNet with a small amount of image data. This is economically beneficial to oil spill segmentation where the availability of oil spill SAR image data is limited in practice. Additionally, benefiting from optimal latent feature variable inference, our proposed DGNet performs accurate oil spill segmentation. We evaluate the segmentation performance of our proposed DGNet with different metrics, and experimental evaluations demonstrate its effective segmentations.
Cross-Skeleton Interaction Graph Aggregation Network for Representation Learning of Mouse Social Behaviour
Aug 07, 2022



Abstract:Automated social behaviour analysis of mice has become an increasingly popular research area in behavioural neuroscience. Recently, pose information (i.e., locations of keypoints or skeleton) has been used to interpret social behaviours of mice. Nevertheless, effective encoding and decoding of social interaction information underlying the keypoints of mice has been rarely investigated in the existing methods. In particular, it is challenging to model complex social interactions between mice due to highly deformable body shapes and ambiguous movement patterns. To deal with the interaction modelling problem, we here propose a Cross-Skeleton Interaction Graph Aggregation Network (CS-IGANet) to learn abundant dynamics of freely interacting mice, where a Cross-Skeleton Node-level Interaction module (CS-NLI) is used to model multi-level interactions (i.e., intra-, inter- and cross-skeleton interactions). Furthermore, we design a novel Interaction-Aware Transformer (IAT) to dynamically learn the graph-level representation of social behaviours and update the node-level representation, guided by our proposed interaction-aware self-attention mechanism. Finally, to enhance the representation ability of our model, an auxiliary self-supervised learning task is proposed for measuring the similarity between cross-skeleton nodes. Experimental results on the standard CRMI13-Skeleton and our PDMB-Skeleton datasets show that our proposed model outperforms several other state-of-the-art approaches.
Structured Context Enhancement Network for Mouse Pose Estimation
Dec 01, 2020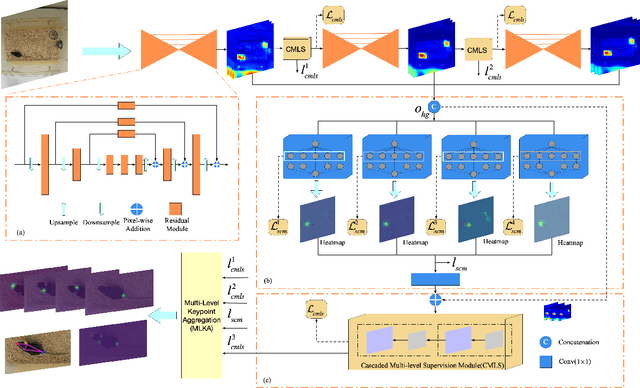
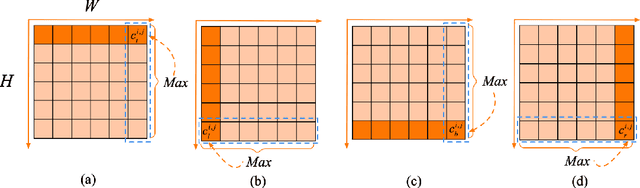
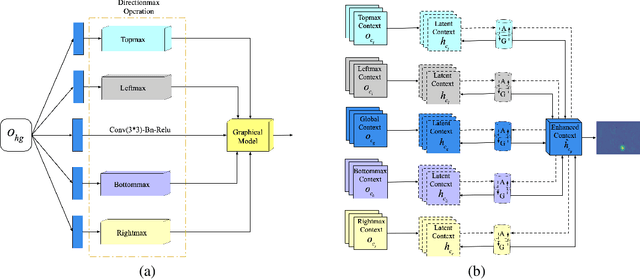
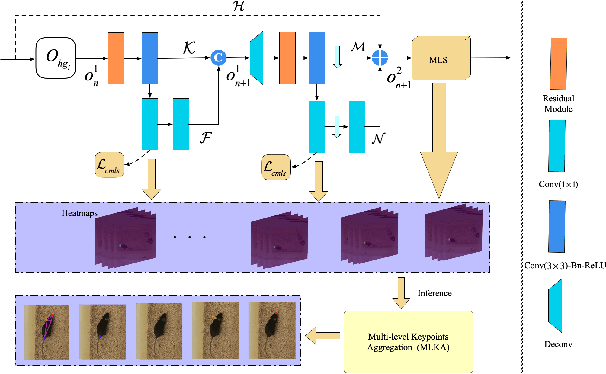
Abstract:Automated analysis of mouse behaviours is crucial for many applications in neuroscience. However, quantifying mouse behaviours from videos or images remains a challenging problem, where pose estimation plays an important role in describing mouse behaviours. Although deep learning based methods have made promising advances in mouse or other animal pose estimation, they cannot properly handle complicated scenarios (e.g., occlusions, invisible keypoints, and abnormal poses). Particularly, since mouse body is highly deformable, it is a big challenge to accurately locate different keypoints on the mouse body. In this paper, we propose a novel hourglass network based model, namely Graphical Model based Structured Context Enhancement Network (GM-SCENet) where two effective modules, i.e., Structured Context Mixer (SCM) and Cascaded Multi-Level Supervision module (CMLS) are designed. The SCM can adaptively learn and enhance the proposed structured context information of each mouse part by a novel graphical model with close consideration on the difference between body parts. Then, the CMLS module is designed to jointly train the proposed SCM and the hourglass network by generating multi-level information, which increases the robustness of the whole network. Based on the multi-level predictions from the SCM and the CMLS module, we also propose an inference method to enhance the localization results. Finally, we evaluate our proposed approach against several baselines...
Muti-view Mouse Social Behaviour Recognition with Deep Graphical Model
Nov 04, 2020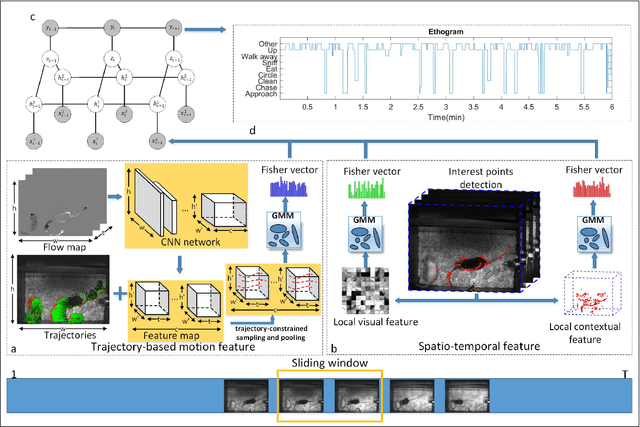

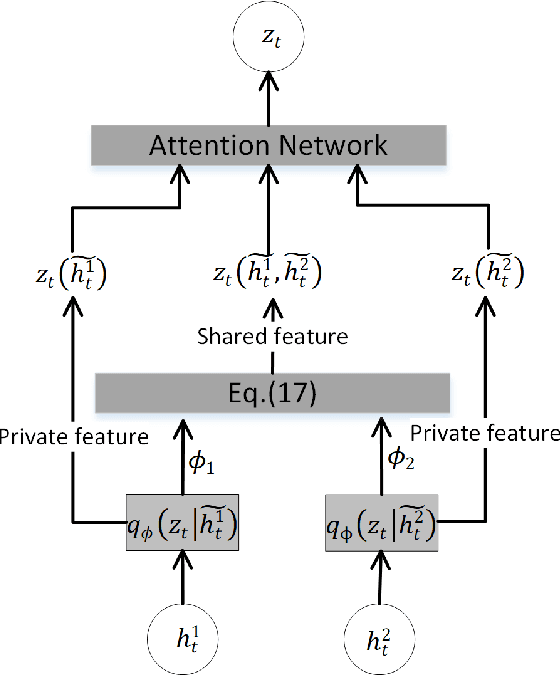

Abstract:Home-cage social behaviour analysis of mice is an invaluable tool to assess therapeutic efficacy of neurodegenerative diseases. Despite tremendous efforts made within the research community, single-camera video recordings are mainly used for such analysis. Because of the potential to create rich descriptions of mouse social behaviors, the use of multi-view video recordings for rodent observations is increasingly receiving much attention. However, identifying social behaviours from various views is still challenging due to the lack of correspondence across data sources. To address this problem, we here propose a novel multiview latent-attention and dynamic discriminative model that jointly learns view-specific and view-shared sub-structures, where the former captures unique dynamics of each view whilst the latter encodes the interaction between the views. Furthermore, a novel multi-view latent-attention variational autoencoder model is introduced in learning the acquired features, enabling us to learn discriminative features in each view. Experimental results on the standard CRMI13 and our multi-view Parkinson's Disease Mouse Behaviour (PDMB) datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms the other state of the arts technologies and effectively deals with the imbalanced data problem.
SWIPENET: Object detection in noisy underwater images
Oct 19, 2020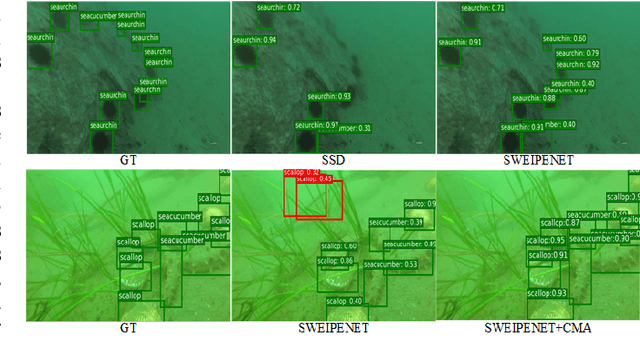
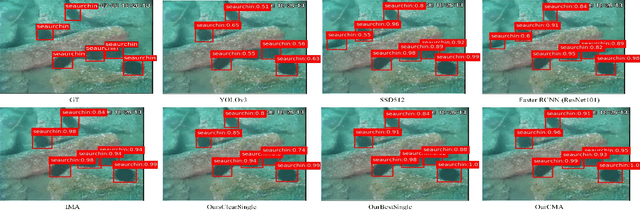


Abstract:In recent years, deep learning based object detection methods have achieved promising performance in controlled environments. However, these methods lack sufficient capabilities to handle underwater object detection due to these challenges: (1) images in the underwater datasets and real applications are blurry whilst accompanying severe noise that confuses the detectors and (2) objects in real applications are usually small. In this paper, we propose a novel Sample-WeIghted hyPEr Network (SWIPENET), and a robust training paradigm named Curriculum Multi-Class Adaboost (CMA), to address these two problems at the same time. Firstly, the backbone of SWIPENET produces multiple high resolution and semantic-rich Hyper Feature Maps, which significantly improve small object detection. Secondly, a novel sample-weighted detection loss function is designed for SWIPENET, which focuses on learning high weight samples and ignore learning low weight samples. Moreover, inspired by the human education process that drives the learning from easy to hard concepts, we here propose the CMA training paradigm that first trains a clean detector which is free from the influence of noisy data. Then, based on the clean detector, multiple detectors focusing on learning diverse noisy data are trained and incorporated into a unified deep ensemble of strong noise immunity. Experiments on two underwater robot picking contest datasets (URPC2017 and URPC2018) show that the proposed SWIPENET+CMA framework achieves better accuracy in object detection against several state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge